Multiscale thermodynamic analysis on hydrogen-induced intergranular cracking in an alloy steel with segregated solutes
不純物偏析を伴う合金鋼の水素誘起粒界破壊におけるマルチスケール解析
山口 正剛 

 ; 海老原 健一
; 海老原 健一 

 ; 板倉 充洋
; 板倉 充洋 

Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
原子炉材料劣化メカニズム研究の一環として、不純物元素(Sb, Sn, P)の粒界偏析を伴うNi-Cr鋼(降伏強度840MPa)の粒界水素脆性メカニズムを調べるため、粒界凝集エネルギーの第一原理計算を行い、破壊靭性試験データと組み合わせた解析を行った。粒界凝集エネルギーの計算には、亀裂の進展中に動きまわり破面形成を助長するように破面吸着するモバイル水素の影響を考慮した。さらに不純物元素の偏析による効果を加えた上で、非常に低い固溶水素濃度(10 原子分率)においても20-30%程度の十分な凝集エネルギー低下が生じうることを示した。解析により、水素ガス環境下で生じる低速な粒界破壊に対して測定された限界応力拡大係数
原子分率)においても20-30%程度の十分な凝集エネルギー低下が生じうることを示した。解析により、水素ガス環境下で生じる低速な粒界破壊に対して測定された限界応力拡大係数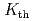 と粒界凝集エネルギーとのマルチスケールな関係を求め、
と粒界凝集エネルギーとのマルチスケールな関係を求め、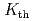 の変化が粒界凝集エネルギー変化によってよくコントロールされていることを示した。
の変化が粒界凝集エネルギー変化によってよくコントロールされていることを示した。
A multiscale analysis has been conducted on hydrogen-induced intergranular cracking at ambient temperature in medium strength (840 MPa) Ni-Cr steel with antimony, tin, and phosphorous segregation. Combining first-principles calculations and fracture mechanics experiments, a multiscale relationship between threshold stress intensity factor (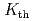 ) and cohesive energy of grain boundary (the ideal work of interfacial separation, 2
) and cohesive energy of grain boundary (the ideal work of interfacial separation, 2
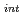 ) was revealed. The
) was revealed. The 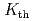 was found to decrease rapidly under a certain threshold of 2
was found to decrease rapidly under a certain threshold of 2
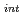 , where the 2
, where the 2
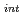 decreases mainly by mobile hydrogen segregation on fracture surfaces. This segregation is considered to arise during formation of the fracture surfaces under thermodynamic equilibrium in slow crack growth. The resulting strong decohesion probably makes it difficult to emit dislocations at microcrack tip region, leading to a large reduction of stress intensity factor. Our analysis based on this mobile hydrogen decohesion demonstrates that the
decreases mainly by mobile hydrogen segregation on fracture surfaces. This segregation is considered to arise during formation of the fracture surfaces under thermodynamic equilibrium in slow crack growth. The resulting strong decohesion probably makes it difficult to emit dislocations at microcrack tip region, leading to a large reduction of stress intensity factor. Our analysis based on this mobile hydrogen decohesion demonstrates that the 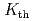 decreases dramatically within a low and narrow range of hydrogen content in iron lattice in high-strength steels.
decreases dramatically within a low and narrow range of hydrogen content in iron lattice in high-strength steels.