LaBr
 -ray spectrometer for detecting
-ray spectrometer for detecting  B in debris of melted nuclear fuel
B in debris of melted nuclear fuel
LaBr
 線スペクトロメータを用いた溶融燃料デブリ中
線スペクトロメータを用いた溶融燃料デブリ中 Bの検出
Bの検出
小泉 光生  ; 土屋 晴文
; 土屋 晴文  ; 北谷 文人
; 北谷 文人 
 ; 原田 秀郎
; 原田 秀郎 

 ; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) has been proposed as a non-destructive analytical method for quantifying Special Nuclear Material (SNM) in the rock- and particle-like debris that is to be removed from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The method is based on Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis combined with Prompt Gamma Ray Analysis (NRCA/PGA). Although quantification of SNM will predominantly rely on NRTA, this will be hampered by the presence of strong neutron-absorbing matrix materials, in particular  B. Results obtained with NRCA/PGA are used to improve the interpretation of NRTA data. Prompt
B. Results obtained with NRCA/PGA are used to improve the interpretation of NRTA data. Prompt  -rays originating from the
-rays originating from the  B(n,
B(n, 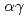 ) reaction are used to assess the amount of
) reaction are used to assess the amount of  B. The 478 keV
B. The 478 keV  -rays from
-rays from  B, however, need to be measured under a high-radiation environment, especially from
B, however, need to be measured under a high-radiation environment, especially from  Cs. In order to meet this requirement, we have developed a well-shaped
Cs. In order to meet this requirement, we have developed a well-shaped  -ray spectrometer consisting of a cylindrical and four rectangular cuboid LaBr
-ray spectrometer consisting of a cylindrical and four rectangular cuboid LaBr scintillators, and a fast data acquisition system.
scintillators, and a fast data acquisition system.