Effect of the dilation caused by helium bubbles on edge dislocation motion in  -iron; Molecular dynamics simulation
-iron; Molecular dynamics simulation
Abe, Yosuke 
 ; Tsuru, Tomohito
; Tsuru, Tomohito 

 ; Shi, S.*; Ono, Naoko*; Ukai, Shigeharu*
; Shi, S.*; Ono, Naoko*; Ukai, Shigeharu*
Various types of nanometric defects such as voids and helium (He) bubbles produced by high energy neutron irradiations are known to degrade the mechanical properties of irradiated materials. In this study, we have evaluated the obstacle strength of He bubbles to the mobility of an edge dislocation in  -iron for 2 and 4 nm bubbles with He-to-vacancy (He/V) ratios ranging from 0 to 1 at 300 and 500 K, by molecular dynamics simulation. Results showed that as the He/V ratio increases, the obstacle strength needed for the release of a dislocation from the bubble becomes stronger up to a moderate He/V ratio, and a further increase in the He/V ratio leads to weakening of the obstacle strength. For He/V = 1, the obstacle strengths are
-iron for 2 and 4 nm bubbles with He-to-vacancy (He/V) ratios ranging from 0 to 1 at 300 and 500 K, by molecular dynamics simulation. Results showed that as the He/V ratio increases, the obstacle strength needed for the release of a dislocation from the bubble becomes stronger up to a moderate He/V ratio, and a further increase in the He/V ratio leads to weakening of the obstacle strength. For He/V = 1, the obstacle strengths are 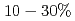 weaker than those at moderate He/V ratios depending on the bubble size and temperature. The extent of obstacle strength was found to be correlated with the dilation caused by He bubbles depending on the bubble size, He/V ratio, and temperature.
weaker than those at moderate He/V ratios depending on the bubble size and temperature. The extent of obstacle strength was found to be correlated with the dilation caused by He bubbles depending on the bubble size, He/V ratio, and temperature.