Spectroscopy of 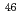 Ar by the (
Ar by the (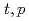 ) two-neutron transfer reaction
) two-neutron transfer reaction
Nowak, K.*; Wimmer, K.*; Hellgartner, S.*; M cher, D.*; Bildstein, V.*; Diriken, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; Gaffney, L. P.*; Gernh
cher, D.*; Bildstein, V.*; Diriken, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; Gaffney, L. P.*; Gernh user, R.*; Iwanicki, J.*; Johansen, J. G.*; Huyse, M.*; Konki, J.*; Kr
user, R.*; Iwanicki, J.*; Johansen, J. G.*; Huyse, M.*; Konki, J.*; Kr ll, T.*; Kr
ll, T.*; Kr cken, R.*; Lutter, R.*; Orlandi, R.
cken, R.*; Lutter, R.*; Orlandi, R. 

 ; Pakarinen, J.*; Raabe, R.*; Reiter, P.*; Roger, T.*; Schrieder, G.*; Seidlitz, M.*; Sorlin, O.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Warr, N.*; De Witte, H.*; Zieli
; Pakarinen, J.*; Raabe, R.*; Reiter, P.*; Roger, T.*; Schrieder, G.*; Seidlitz, M.*; Sorlin, O.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Warr, N.*; De Witte, H.*; Zieli ska, M.*
ska, M.*
The 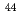 Ar(
Ar(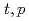 )
) Ar two-neutron transfer reaction at 2.16 MeV/u was studied at CERN using a
Ar two-neutron transfer reaction at 2.16 MeV/u was studied at CERN using a  Ar radioactive beam and a tritium loaded radioactive target. Angular distributions for three final states were measured and based on the shape of the differential cross section an excited state at 3695 keV was identified as the first excited 0
Ar radioactive beam and a tritium loaded radioactive target. Angular distributions for three final states were measured and based on the shape of the differential cross section an excited state at 3695 keV was identified as the first excited 0 state. The differential cross-sections for the 0
state. The differential cross-sections for the 0 -ground state, and first excited 2
-ground state, and first excited 2 and 0
and 0 states are compared to DWBA calculations including two-step reactions through the intermediate nucleus
states are compared to DWBA calculations including two-step reactions through the intermediate nucleus  Ar. By comparison large scale shell model calculations using state-of-the-art effective interactions, with and without the tensor components of the interactions, it was observed that the cross-shell proton-neutron tensor interaction has measurable effects on the observables at low excitation energy in
Ar. By comparison large scale shell model calculations using state-of-the-art effective interactions, with and without the tensor components of the interactions, it was observed that the cross-shell proton-neutron tensor interaction has measurable effects on the observables at low excitation energy in 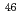 Ar.
Ar.