Identification of the crossing point at  = 21 between normal and intruder configurations
= 21 between normal and intruder configurations
Lic , R.*; Rotaru, F.*; Borge, M. J. G.*; Gr
, R.*; Rotaru, F.*; Borge, M. J. G.*; Gr vy, S.*; Negoita, F.*; Poves, A.*; Sorlin, O.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Borcea, R.*; Costache, C.*; De Witte, H.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Huyse, M.*; Ionescu, A.*; Kisyov, S.*; Konki, J.*; Lazarus, I.*; Madurga, M.*; M
vy, S.*; Negoita, F.*; Poves, A.*; Sorlin, O.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Borcea, R.*; Costache, C.*; De Witte, H.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Huyse, M.*; Ionescu, A.*; Kisyov, S.*; Konki, J.*; Lazarus, I.*; Madurga, M.*; M rginean, N.*; M
rginean, N.*; M rginean, R.*; Mihai, C.*; Mihai, R. E.*; Negret, A.*; Page, R. D.*; Pakarinen, J.*; Pascu, S.*; Pucknell, V.*; Rahkila, P.*; Rapisarda, E.*;
rginean, R.*; Mihai, C.*; Mihai, R. E.*; Negret, A.*; Page, R. D.*; Pakarinen, J.*; Pascu, S.*; Pucknell, V.*; Rahkila, P.*; Rapisarda, E.*;  erban, A.*; Sotty, C. O.*; Stan, L.*; St
erban, A.*; Sotty, C. O.*; Stan, L.*; St noiu, M.*; Tengblad, O.*; Turturic
noiu, M.*; Tengblad, O.*; Turturic , A.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Wadsworth, R.*; Warr, N.*
, A.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Wadsworth, R.*; Warr, N.*
The 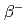 decay of
decay of 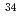 Mg was used to study the
Mg was used to study the 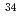 Al nucleus through
Al nucleus through  spectroscopy at the Isotope Separator On-Line facility of CERN. Previous studies identified two
spectroscopy at the Isotope Separator On-Line facility of CERN. Previous studies identified two  -decaying states in
-decaying states in 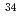 Al having spin-parity assignments
Al having spin-parity assignments 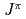 =4
=4 dominated by the normal configuration
dominated by the normal configuration  (d5/2)
(d5/2)
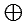
 (f7/2) and
(f7/2) and 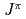 = 1
= 1 by the intruder configuration
by the intruder configuration  (d5/2)
(d5/2)
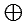
 (d3/2)
(d3/2) (f7/2)
(f7/2) . Their unknown ordering and relative energy have been the subject of debate for the placement of
. Their unknown ordering and relative energy have been the subject of debate for the placement of 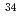 Al inside or outside the
Al inside or outside the  = 20 "island of inversion". We report here that the 1
= 20 "island of inversion". We report here that the 1 intruder lies only 46.6 keV above the 4
intruder lies only 46.6 keV above the 4 ground state. In addition, a new half-life of
ground state. In addition, a new half-life of 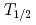 =44.9(4)ms, that is twice as long as thepreviously measured 20(10) ms, has been determined for
=44.9(4)ms, that is twice as long as thepreviously measured 20(10) ms, has been determined for 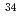 Mg. Large-scale shell-model calculations with the recently developed SDPF-U-MIX interaction are compared with the new data and used to interpret the mechanisms at play at the very border of the
Mg. Large-scale shell-model calculations with the recently developed SDPF-U-MIX interaction are compared with the new data and used to interpret the mechanisms at play at the very border of the  = 20 island of inversion.
= 20 island of inversion.