Development of a new continuous dissolution apparatus with a hydrophobic membrane for superheavy element chemistry
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato 
 ; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro 
 ; Kitayama, Yuta*; Koga, Kazuki*; Komori, Yukiko*; Koyama, Takumi*; Kratz, J. V.*; Lerum, H. V.*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oshimi, Yoshinari*; Pershina, V.*; Sato, Daisuke*; Sato, Tetsuya
; Kitayama, Yuta*; Koga, Kazuki*; Komori, Yukiko*; Koyama, Takumi*; Kratz, J. V.*; Lerum, H. V.*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oshimi, Yoshinari*; Pershina, V.*; Sato, Daisuke*; Sato, Tetsuya 

 ; Shigekawa, Yudai*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Tanaka, Akira*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki
; Shigekawa, Yudai*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Tanaka, Akira*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki 
 ; Tsuto, Shohei*; Yokokita, Takuya*; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Omtvedt, J. P.*; Nagame, Yuichiro
; Tsuto, Shohei*; Yokokita, Takuya*; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Omtvedt, J. P.*; Nagame, Yuichiro  ; Sch
; Sch del, M.*
del, M.*
A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 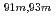 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.