Thermophysical properties of sodium-concrete reaction products
Kawaguchi, Munemichi 

 ; Miyahara, Shinya
; Miyahara, Shinya 
 ; Uno, Masayoshi*
; Uno, Masayoshi*
Liquid sodium (Na) has been used as the coolant of fast reactors for the various merits, such as the high thermal conductivity. On the other hand, it is postulated that a steel liner may fail and lead to a sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) during the Na-leak accident. Because of concrete ablation and release of hydrogen gas due to the chemical reactions between Na and concrete components, the SCR is one of the important phenomena in the Na-leak accident. In the study, fundamental experiments related to the SCR were performed using Na and concrete powder. Here, the used concrete powder is milled siliceous concrete which is usually used as the structural concrete in Japanese nuclear power plants. The obvious temperature changes at 3 temperature regions were observed for the reaction process such as Na-melt, NaOH-SiO and Na-H
and Na-H O-SiO
O-SiO reaction, which occurred around 100, 300 and 500
reaction, which occurred around 100, 300 and 500 C, respectively. Especially, the violent reaction around 500
C, respectively. Especially, the violent reaction around 500 C caused the temperature peak to
C caused the temperature peak to 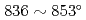 C, and the reaction heat of
C, and the reaction heat of 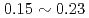 kW/g was estimated under the Na-concrete mixing ratio such as
kW/g was estimated under the Na-concrete mixing ratio such as 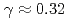 . The main components of the reaction products was identified as Na
. The main components of the reaction products was identified as Na SiO
SiO with X-ray diffraction technique. Moreover, the measured thermophysical properties such as melting point, density, specific heat, thermal conductivity and viscosity were similar to those of
with X-ray diffraction technique. Moreover, the measured thermophysical properties such as melting point, density, specific heat, thermal conductivity and viscosity were similar to those of  Na
Na O-
O-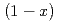 SiO
SiO (
(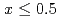 ).
).