Effect of HIx solution concentration on ion-exchange membrane performance in electro-electrodialysis
Tanaka, Nobuyuki  ; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Asano, Masaharu*; Terai, Takayuki*
; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Asano, Masaharu*; Terai, Takayuki*
Electro-electrodialysis (EED) has been applied to thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production in order to enhance the HI component in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity (
O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity ( ) and transport number (
) and transport number ( ) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H
) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H and I
and I content and the diffusion coefficients of H
content and the diffusion coefficients of H and I
and I in the evaluated membranes on
in the evaluated membranes on  and
and  were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of
were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of  and t
and t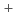 , which indicates that the dominant factors for
, which indicates that the dominant factors for  and
and  would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For
would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For  of Nafion 212, H
of Nafion 212, H diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I
diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I
was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I diffusion should be considered. I
diffusion should be considered. I diffusion could more strongly affect
diffusion could more strongly affect  for the evaluated membranes rather than H
for the evaluated membranes rather than H diffusion, which indicates that H
diffusion, which indicates that H selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I
selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I behavior in the membranes.
behavior in the membranes.