Angular distribution of  rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
La
Okudaira, Takuya*; Takada, Shusuke*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi 

 ; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nagamoto, Kosuke*; Nakao, Taro*; Okada, Anju*; Sakai, Kenji
; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nagamoto, Kosuke*; Nakao, Taro*; Okada, Anju*; Sakai, Kenji  ; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshioka, Tamaki*
; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshioka, Tamaki*
The angular distribution of individual  rays, emitted from a neutron-induced compound-nuclear state via radiative capture reaction of
rays, emitted from a neutron-induced compound-nuclear state via radiative capture reaction of  La
La has been studied as a function of incident neutron energy in the epithermal region by using germanium detectors. An asymmetry
has been studied as a function of incident neutron energy in the epithermal region by using germanium detectors. An asymmetry 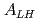 was defined as
was defined as 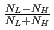 , where
, where 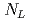 and
and 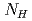 are integrals of low- and high-energy region of a neutron resonance respectively, and we found that
are integrals of low- and high-energy region of a neutron resonance respectively, and we found that 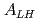 has the angular dependence of
has the angular dependence of 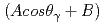 , where
, where 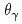 is the emitted angle of
is the emitted angle of  rays, with
rays, with 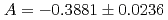 and
and 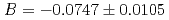 in 0.74-eV p-wave resonance. This angular distribution was analyzed within the framework of interference between s- and p-wave amplitudes in the entrance channel to the compound-nuclear state, and it is interpreted as the value of the partial p-wave neutron width corresponding to the total angular momentum of the incident neutron combined with the weak matrix element, in the context of the mechanism of enhanced parity-violating effects. Additionally, we use the result to quantify the possible enhancement of the breaking of time-reversal invariance in the vicinity of the p-wave resonance.
in 0.74-eV p-wave resonance. This angular distribution was analyzed within the framework of interference between s- and p-wave amplitudes in the entrance channel to the compound-nuclear state, and it is interpreted as the value of the partial p-wave neutron width corresponding to the total angular momentum of the incident neutron combined with the weak matrix element, in the context of the mechanism of enhanced parity-violating effects. Additionally, we use the result to quantify the possible enhancement of the breaking of time-reversal invariance in the vicinity of the p-wave resonance.