Analysis of solvent extraction equilibria with consideration of cluster formation of zirconium complexes
Okamura, Hiroyuki 

 ; Ueda, Yuki
; Ueda, Yuki 

 ; Motokawa, Ryuhei
; Motokawa, Ryuhei 

 ; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
Recently, cluster formation of metal-extractant complexes in organic solvents has been shown to play important roles in liquid-liquid extraction. Although a number of reaction mechanisms have been proposed for liquid-liquid extraction, application of slope analysis method for evaluating metal-extractant stoichiometry fails when the solute concentrations are high. In this study, we performed the analysis of solvent extraction equilibria for practical liquid-liquid systems with consideration of the formation of cluster aggregates in the organic phase during the extraction process. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation indicates the formation of aggregated clusters of 1 to 9 Zr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) complexes in
complexes in  -octane, leading to the determination of composition and molar fraction of each cluster. Furthermore, the extraction equilibrium reactions were studied, and the extraction equilibrium constant K
-octane, leading to the determination of composition and molar fraction of each cluster. Furthermore, the extraction equilibrium reactions were studied, and the extraction equilibrium constant K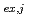 (
( = 1-9) for each cluster could be determined from the parameters obtained by the MD analysis. The distribution curve calculated from K
= 1-9) for each cluster could be determined from the parameters obtained by the MD analysis. The distribution curve calculated from K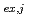 agrees well with the experimental values. Therefore, one MD simulation can accurately reproduce the distribution curve in the clustering/aggregation liquid-liquid extraction system, which enabled us to overcome the limitations of slope analysis method.
agrees well with the experimental values. Therefore, one MD simulation can accurately reproduce the distribution curve in the clustering/aggregation liquid-liquid extraction system, which enabled us to overcome the limitations of slope analysis method.