Measurement of high-energy prompt fission  -ray emission in
-ray emission in  U (
U ( )
)
Makii, Hiroyuki 

 ; Nishio, Katsuhisa
; Nishio, Katsuhisa 

 ; Hirose, Kentaro
; Hirose, Kentaro 
 ; Orlandi, R.
; Orlandi, R. 

 ; L
; L guillon, R.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko
guillon, R.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko 

 ; Soldner, T.*; K
; Soldner, T.*; K ster, U.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; Kawano, Toshihiko*; A
ster, U.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; Kawano, Toshihiko*; A che, M.*; Astier, A.*; Czajkowski, S.*; Frost, R. J. W.*; Guo, S.*; Mathieu, L.*; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Petrache, C. M.*; Pollitt, A.*; Sekimoto, Shun*; Takamiya, Koichi*; Tsekhanovich, I.*
che, M.*; Astier, A.*; Czajkowski, S.*; Frost, R. J. W.*; Guo, S.*; Mathieu, L.*; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Petrache, C. M.*; Pollitt, A.*; Sekimoto, Shun*; Takamiya, Koichi*; Tsekhanovich, I.*
Prompt fission  -ray spectra (PFGS) are important as they allow us to study the structure and de-excitation process of neutron-rich fission fragments. They are also required for the design of the Gen-IV fast reactors and advanced light-water reactors. For spontaneous fission of
-ray spectra (PFGS) are important as they allow us to study the structure and de-excitation process of neutron-rich fission fragments. They are also required for the design of the Gen-IV fast reactors and advanced light-water reactors. For spontaneous fission of  Cf,
Cf,  Cf(sf), prompt fission
Cf(sf), prompt fission  rays were observed up to energies of about
rays were observed up to energies of about 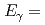 20 MeV. For neutron-induced fissions, however, the measured PFGS are limited below
20 MeV. For neutron-induced fissions, however, the measured PFGS are limited below 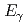 = 9
= 9 10 MeV. In this work we extended the measurement of the PFGS for cold neutron-induced fission of
10 MeV. In this work we extended the measurement of the PFGS for cold neutron-induced fission of  U up to
U up to 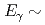 20 MeV by gaining a factor of about 10
20 MeV by gaining a factor of about 10 in statistics compared to the measurements performed so far. The measurement was carried out at the PF1B cold-neutron facility of the ILL, Grenoble, France. The spectrum exhibits local bump structures at
in statistics compared to the measurements performed so far. The measurement was carried out at the PF1B cold-neutron facility of the ILL, Grenoble, France. The spectrum exhibits local bump structures at 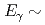 4 MeV and
4 MeV and  6 MeV and also a broad one at
6 MeV and also a broad one at  15 MeV. In this contribution, we will discuss the origins of the bump structures in comparison with the statistical Hauser-Feshbach model calculation.
15 MeV. In this contribution, we will discuss the origins of the bump structures in comparison with the statistical Hauser-Feshbach model calculation.