Development of miniature fracture toughness test technique for fast reactor long-life fuel subassembly
Tanno, Takashi 
 ; Oka, Hiroshi
; Oka, Hiroshi 

 ; Yano, Yasuhide
; Yano, Yasuhide 
 ; Kurishita, Hiroaki*
; Kurishita, Hiroaki*
Fracture toughness is an important property when ferritic martensitic steel (FMS) is irradiated and thermally aged. The goal of this study is to develop reasonably miniaturized fracture toughness test technique which can be applied for irradiated or sampled from welded small specimen. In this phase, the capability of miniature 3-point bend (3PB) test technique for evaluating toughness, and the side groove effect on miniatured specimen were confirmed. A miniature 3PB type J test conforming to ASTM 1820 was applied to the PNC-FMS developed for the fast reactor. The effect of the root radius of the side groove that controls the crack propagation was verified for the specimen miniaturized to 5 mm thickness, 3 mm width and 22.5 mm length according to the thickness of the wrapper tube. The crack winded and/or branched with root radius of 0.5 mm, the standard size of ASTM1820. But by making it 0.05 mm, it was possible to control the crack propagation along the side groove. As a result, J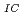 = 300 kJ/m
= 300 kJ/m was obtained, and a prospect of this technique was obtained for the fracture toughness evaluation of the wrapper tube by improving the side groove.
was obtained, and a prospect of this technique was obtained for the fracture toughness evaluation of the wrapper tube by improving the side groove.