Radiation-induced effects on the extraction properties of hexa- -octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) complexes of americium and europium
-octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) complexes of americium and europium
Toigawa, Tomohiro 

 ; Peterman, D. R.*; Meeker, D. S.*; Grimes, T. S.*; Zalupski, P. R.*; Mezyk, S. P.*; Cook, A. R.*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kumagai, Yuta
; Peterman, D. R.*; Meeker, D. S.*; Grimes, T. S.*; Zalupski, P. R.*; Mezyk, S. P.*; Cook, A. R.*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kumagai, Yuta 

 ; Matsumura, Tatsuro
; Matsumura, Tatsuro 
 ; Horne, G. P.*
; Horne, G. P.*
The candidate An(III)/Ln(III) separation ligand hexa- -octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) was irradiated under envisioned SELECT (Solvent Extraction from Liquid waste using Extractants of CHON-type for Transmutation) process conditions using a solvent test loop in conjunction with cobalt-60 gamma irradiation. We demonstrate that HONTA undergoes exponential decay with increasing gamma dose to produce a range of degradation products which have been identified and quantified by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS techniques. The combination of HONTA destruction and degradation product ingrowth, particularly dioctylamine, negatively impacts the extraction and back-extraction of both americium and europium ions. The loss of HONTA was attributed to its reaction with the solvent (
-octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) was irradiated under envisioned SELECT (Solvent Extraction from Liquid waste using Extractants of CHON-type for Transmutation) process conditions using a solvent test loop in conjunction with cobalt-60 gamma irradiation. We demonstrate that HONTA undergoes exponential decay with increasing gamma dose to produce a range of degradation products which have been identified and quantified by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS techniques. The combination of HONTA destruction and degradation product ingrowth, particularly dioctylamine, negatively impacts the extraction and back-extraction of both americium and europium ions. The loss of HONTA was attributed to its reaction with the solvent ( -dodecane) radical cation of
-dodecane) radical cation of  (HONTA + R
(HONTA + R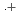 ) = (7.61
) = (7.61  0.82)
0.82)  10
10 M
M s
s obtained by pulse radiolysis techniques. However, when this ligand is bound to either americium or europium ions, the observed
obtained by pulse radiolysis techniques. However, when this ligand is bound to either americium or europium ions, the observed  -dodecane radical cation kinetics increase by over an order of magnitude. This large reactivity increase to additional reaction pathways occurring upon metal-ion binding. Lastly nanosecond time-resolved measurements showed that both direct and indirect HONTA radiolysis yielded the short-lived (
-dodecane radical cation kinetics increase by over an order of magnitude. This large reactivity increase to additional reaction pathways occurring upon metal-ion binding. Lastly nanosecond time-resolved measurements showed that both direct and indirect HONTA radiolysis yielded the short-lived ( 100 ns) HONTA radical cation as well as a longer-lived (
100 ns) HONTA radical cation as well as a longer-lived ( s) HONTA triplet excited state. These HONTA species are important precursors to the suite of HONTA degradation products observed.
s) HONTA triplet excited state. These HONTA species are important precursors to the suite of HONTA degradation products observed.