Structural phase transition in cobalt oxyfluoride Co Sb
Sb O
O F
F observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffraction
observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffraction
Shimono, Seiya*; Ishibashi, Hiroki*; Nagayoshi, Yusuke*; Ikeno, Hidekazu*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Hagihara, Masato 

 ; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Ichihashi, Katsuya*; Nishihara, Sadafumi*; Inoue, Katsuya*; Ishii, Yui*; Kubota, Yoshiki*
; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Ichihashi, Katsuya*; Nishihara, Sadafumi*; Inoue, Katsuya*; Ishii, Yui*; Kubota, Yoshiki*
The structural phase transition from cubic (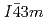 ) to a
) to a 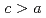 tetragonal (
tetragonal (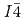 ) at
) at 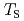
 180 K was found in non-centrosymmetric oxyfluoride Co
180 K was found in non-centrosymmetric oxyfluoride Co Sb
Sb O
O F
F by high-resolution neutron and synchrotron powder diffraction. To investigate this phase transition, specific heat, magnetization, and dielectric measurements were performed. Although the specific heat and dielectric constant showed anomalies at
by high-resolution neutron and synchrotron powder diffraction. To investigate this phase transition, specific heat, magnetization, and dielectric measurements were performed. Although the specific heat and dielectric constant showed anomalies at 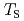 , a phase transition to ferroelectricity was not observed in the polarization hysteresis loop down to 30 K. The rotation of the CoO
, a phase transition to ferroelectricity was not observed in the polarization hysteresis loop down to 30 K. The rotation of the CoO F
F octahedron was observed at
octahedron was observed at 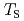 from the structural analysis using synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data. It was found that the magnetic phase transition from paramagnetic to G-type antiferromagnetic occurred at
from the structural analysis using synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data. It was found that the magnetic phase transition from paramagnetic to G-type antiferromagnetic occurred at 
 67 K, at which a peak was observed in the specific heat measurements, via magnetic structure analysis using neutron powder diffraction data. The magnetic moments of Co
67 K, at which a peak was observed in the specific heat measurements, via magnetic structure analysis using neutron powder diffraction data. The magnetic moments of Co were aligned along the tetragonal
were aligned along the tetragonal  -axis direction with a Co
-axis direction with a Co moment of 2.80(1)
moment of 2.80(1) 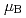 at 13 K.
at 13 K.