New insights into nuclear quantum effects of liquid water from first principles calculations
Thomsen, B. 
 ; Shiga, Motoyuki
; Shiga, Motoyuki 


In a recently published paper we explore the NQEs on the autoionization constant (pK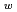 ) of water. We do this by using coordination number restrained path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD), which allows for molecular dynamics (MD) including NQEs in an ab-initio fashion. We employ two different methods for calculating the pK
) of water. We do this by using coordination number restrained path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD), which allows for molecular dynamics (MD) including NQEs in an ab-initio fashion. We employ two different methods for calculating the pK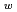 of water using the calculated free energy curve of proton dissociation from a water molecule. The first is a two- state model which enables the calculation of the quantitative pK
of water using the calculated free energy curve of proton dissociation from a water molecule. The first is a two- state model which enables the calculation of the quantitative pK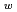 of water. The second, based on the work of M. Sprik, presents a method for calculate the pK
of water. The second, based on the work of M. Sprik, presents a method for calculate the pK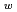 of the water isotopologs relative to that of water. The electronic potential is in our calculations described by an empirical force field (OSS2), the semi-empirical Density Functional based Tight Binding (DFTB), and ab-initio density functional theory (DFT). Our ongoing research focuses on the NQEs in water at standard, sub critical, and super critical conditions. This builds on a previous study, which found that at room temperature the NQEs in the hydrogen bonds enabled a population of hydrogen in the predissociation region of the O-H radial distribution function (RDF). The current calculations of the O-H RDF using PIMD shown in Figure 1 display an excellent agreement with experimental data as well as highlighting the density only present in the simulations including the NQEs. Our initial results indicate that the NQEs remain the sole source of predissociative density in the O-H RDF even at sub and super critical conditions, underlining the necessity of modelling NQEs in a calculation targeting the quantitative value of waters pK
of the water isotopologs relative to that of water. The electronic potential is in our calculations described by an empirical force field (OSS2), the semi-empirical Density Functional based Tight Binding (DFTB), and ab-initio density functional theory (DFT). Our ongoing research focuses on the NQEs in water at standard, sub critical, and super critical conditions. This builds on a previous study, which found that at room temperature the NQEs in the hydrogen bonds enabled a population of hydrogen in the predissociation region of the O-H radial distribution function (RDF). The current calculations of the O-H RDF using PIMD shown in Figure 1 display an excellent agreement with experimental data as well as highlighting the density only present in the simulations including the NQEs. Our initial results indicate that the NQEs remain the sole source of predissociative density in the O-H RDF even at sub and super critical conditions, underlining the necessity of modelling NQEs in a calculation targeting the quantitative value of waters pK . The size of the NQEs does also vary according to temperature, which may explain the part of the strong temperature/pressure dependence of the pK
. The size of the NQEs does also vary according to temperature, which may explain the part of the strong temperature/pressure dependence of the pK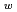 of water.
of water.