Yakedake Nakao tephra; An Attempt to use the local tephra as a Late Holocene age marker for the southern part of the Northern Japan Alps
Nishio, Gaku*; Kagami, Saya 

 ; Yokoyama, Tatsunori
; Yokoyama, Tatsunori 

 ; Kariya, Yoshihiko*; Kojima, Satoru*
; Kariya, Yoshihiko*; Kojima, Satoru*
We attempt to use local tephra derived from nearby volcanoes as an age marker. The Kamikochi area in the southern part of the Northern Alps is strongly affected by the Yakedake volcano. We prepared distinctive tephras, (1) one sample of glassy volcanic ash in hand auger boring cores drilled at the near-shore Kinugasanoike Pond, about 4.7 km northeast of Mt. Yakedake and (2) two samples of glassy volcanic ash in the Nakao pyroclastic flow deposites, which is considered to be a product of the last magmatic eruption about 2,300 years ago, distributed about 1.5 km north-northwest of Mt. Yakedake. We investigated the clast composition of these tephras and the chemical composition and refractive index of volcanic glass. Approximately 70% of the clasts were volcanic glasses, and most of them were vesicular and blocky types. These glasses were characterized by high SiO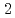 , K
, K O, Na
O, Na O and low Al
O and low Al O
O , FeO, which were clearly distinguishable from the volcanic glasses in Quaternary widespread tephras. The refractive indices of 30 volcanic glasses for each tephra were 1.4958-1.5011 with a peak in the range of 1.497 to 1.499. The results of this study indicate the tephra from Kinugasanoike Pond were erupted from Mt. Yakedake about 2,300 years ago. Therefore, the tephra with the above characteristics can be used as a useful age marker for the southern part of the Northern Alps about 2,300 years ago.
, FeO, which were clearly distinguishable from the volcanic glasses in Quaternary widespread tephras. The refractive indices of 30 volcanic glasses for each tephra were 1.4958-1.5011 with a peak in the range of 1.497 to 1.499. The results of this study indicate the tephra from Kinugasanoike Pond were erupted from Mt. Yakedake about 2,300 years ago. Therefore, the tephra with the above characteristics can be used as a useful age marker for the southern part of the Northern Alps about 2,300 years ago.