Incommensurate helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
Tanaka, Seiya*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji 
 ; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Maruyama, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Shigenori*
; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Maruyama, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Shigenori*
Sc-substituted hexagonal ferrite Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O has an incommensurate helimagnetic structure. However, the incommensurate helimagnetic structure has not been sufficiently determined, and the mechanism via which the helimagnetism develops has not been studied. Time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffraction measurements were performed on single-crystal samples of Ba(Fe
has an incommensurate helimagnetic structure. However, the incommensurate helimagnetic structure has not been sufficiently determined, and the mechanism via which the helimagnetism develops has not been studied. Time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffraction measurements were performed on single-crystal samples of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O with Sc concentrations of x = 0, 0.128, 0.153, and 0.193. The magnetic structure analyses revealed that the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe
with Sc concentrations of x = 0, 0.128, 0.153, and 0.193. The magnetic structure analyses revealed that the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O is a cone type whose base is in the ab plane and height is in the c-axis direction. The magnetic moments of Fe2(4
is a cone type whose base is in the ab plane and height is in the c-axis direction. The magnetic moments of Fe2(4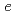 ), Fe4(4
), Fe4(4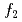 ), and Fe5(12
), and Fe5(12 ) are aligned with distinct angles, leading to the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe
) are aligned with distinct angles, leading to the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O , and can be explained by assuming that there is an antiferromagnetic superexchange interaction
, and can be explained by assuming that there is an antiferromagnetic superexchange interaction 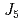 between Fe2(4
between Fe2(4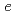 ) and Fe5(12
) and Fe5(12 ) that is negligible in the x = 0 crystal. The shorter bond distance of Fe2-O1 in Sc-rich crystals revealed by the crystal structure analyses enhances the superexchange interaction
) that is negligible in the x = 0 crystal. The shorter bond distance of Fe2-O1 in Sc-rich crystals revealed by the crystal structure analyses enhances the superexchange interaction 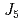 . The relatively strong
. The relatively strong 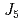 leads to competition among the three superexchange interactions,
leads to competition among the three superexchange interactions, 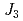 ,
, 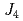 , and
, and 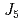 , resulting in the development of the helimagnetic structure. These findings facilitate the understanding of the essentials of the basic magnetic material BaFe
, resulting in the development of the helimagnetic structure. These findings facilitate the understanding of the essentials of the basic magnetic material BaFe O
O .
.