Measurement and Pu-content dependence of (U,Pu)O
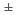
 oxygen potential
oxygen potential
Horii, Yuta  ; Hirooka, Shun
; Hirooka, Shun  ; Vauchy, R.
; Vauchy, R. 
 ; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Saito, Kosuke
; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Saito, Kosuke
Oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratio is one of the fundamental parameters that determine various properties of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel. The O/M ratio of MOX can be adjusted by an equilibrating reaction of oxygen between a solid phase of MOX fuel and a gas phase. In the equilibrium system, the partial molar Gibbs free energy of oxygen atmosphere is used to describe the oxygen potential of MOX fuel. In previous studies, the oxygen potential data of UO , PuO
, PuO , and MOX with Pu contents from 12% to 68% was obtained as part of the studies on MOX fuel properties for fast reactors. However, a Pu-content gap in the oxygen potential data exists between UO
, and MOX with Pu contents from 12% to 68% was obtained as part of the studies on MOX fuel properties for fast reactors. However, a Pu-content gap in the oxygen potential data exists between UO and 12%Pu-MOX, which is critical to analyze the effect of Pu content in MOX. In this study, sintered pellets of (U
and 12%Pu-MOX, which is critical to analyze the effect of Pu content in MOX. In this study, sintered pellets of (U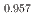 Pu
Pu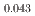 )O
)O
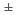
 and (U
and (U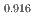 Pu
Pu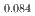 )O
)O
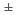
 were prepared by diluting MOX raw powder with UO
were prepared by diluting MOX raw powder with UO powder and the oxygen potential measurement of them was carried out at the temperatures of 1673 K, 1773 K and 1873 K in an Ar-H
powder and the oxygen potential measurement of them was carried out at the temperatures of 1673 K, 1773 K and 1873 K in an Ar-H gas mixture with various moisture contents by oxidation-reduction gravimetric method using a thermo gravimeter (TG-DTA). The experimental data was evaluated based on defect chemistry and the relationship between O/M ratio and oxygen potential was derived as a function of surrounding oxygen partial pressure. The dependence of Pu content on the oxygen potential of MOX was analyzed with the previous studies.
gas mixture with various moisture contents by oxidation-reduction gravimetric method using a thermo gravimeter (TG-DTA). The experimental data was evaluated based on defect chemistry and the relationship between O/M ratio and oxygen potential was derived as a function of surrounding oxygen partial pressure. The dependence of Pu content on the oxygen potential of MOX was analyzed with the previous studies.