Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Machida, Masahiko
Parallel Computing; On the Road to Exascale, p.361 - 369, 2016/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.01(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki
Physica C, 484, p.43 - 45, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.93(Physics, Applied)We investigate electronic structures of a typical iron-based superconductor LaFeAsO by first-principles calculations in order to clarify the most stable ground-state of the mother compound. With use of around mean field (AMF) for LDA +  formalism, we obtain an orbital ordered state showing relatively low magnetic moment widely for intermediate
formalism, we obtain an orbital ordered state showing relatively low magnetic moment widely for intermediate  values. In the low moment state, we find that electric quadrupole moment develops around iron atom, i.e., the charge profile deforms from a spherical to a collapsed one in contrast to the high moment state with almost zero quadrupole moment. Moreover, we examine as height dependence of the low moment state and find that the low moment state is also widely stable for the variation of As height compared to the high moment one.
values. In the low moment state, we find that electric quadrupole moment develops around iron atom, i.e., the charge profile deforms from a spherical to a collapsed one in contrast to the high moment state with almost zero quadrupole moment. Moreover, we examine as height dependence of the low moment state and find that the low moment state is also widely stable for the variation of As height compared to the high moment one.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 484, p.39 - 42, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.17(Physics, Applied)We investigate electronic states and phonon structure of recently discovered iron-based superconductor (CaFeAs) Pt
Pt As
As by first-principles calculations. Though Pt electrons affect the band structure and density of states around the Fermi energy, the Fermi surface produced by Fe
by first-principles calculations. Though Pt electrons affect the band structure and density of states around the Fermi energy, the Fermi surface produced by Fe  -electrons is similar to those of the usual iron-based superconductors. Phonon density of states formed by Fe-atom vibrations is also consistent with those of usual. Thus, we expect that this material has the same superconducting mechanism as other iron-based superconductors.
-electrons is similar to those of the usual iron-based superconductors. Phonon density of states formed by Fe-atom vibrations is also consistent with those of usual. Thus, we expect that this material has the same superconducting mechanism as other iron-based superconductors.
 -wave island with a single vortex
-wave island with a single vortexNagai, Yuki; Tanaka, Kaori*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko*
Physical Review B, 86(9), p.094526_1 - 094526_9, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:57.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We demonstrate an efficient numerical method for obtaining unique solutions to the Eilenberger equation for a mesoscopic or nanoscale superconductor. In particular, we calculate the local density of states of a circular  -wave island containing a single vortex. The "vortex shadow" effect is found to depend strongly on the quasiparticle energy in such small systems. We show how to construct by geometry quasiparticle trajectories confined in a finite-size system with specular reflections at the boundary, and we discuss the stability of the numerical solutions even in the case of vanishing order parameter as for nodal quasiparticles in a
-wave island containing a single vortex. The "vortex shadow" effect is found to depend strongly on the quasiparticle energy in such small systems. We show how to construct by geometry quasiparticle trajectories confined in a finite-size system with specular reflections at the boundary, and we discuss the stability of the numerical solutions even in the case of vanishing order parameter as for nodal quasiparticles in a  -wave superconductor or for quasiparticles passing through the vortex center with zero energy.
-wave superconductor or for quasiparticles passing through the vortex center with zero energy.
 -scan analysis of the neutron scattering in iron-based superconductors
-scan analysis of the neutron scattering in iron-based superconductorsNagai, Yuki; Kuroki, Kazuhiko*
Physical Review B, 85(13), p.134521_1 - 134521_7, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.10(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We propose a way to determine the pairing state of the iron pnictide superconductors exploiting the momentum ( ) scan of the neutron scattering data. We investigate the spin susceptibility in the
) scan of the neutron scattering data. We investigate the spin susceptibility in the 
 and
and 
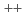 superconducting states for various doping levels using the effective five-orbital model and considering the quasiparticle damping. The peak position of the intensity shifts from the position on the line
superconducting states for various doping levels using the effective five-orbital model and considering the quasiparticle damping. The peak position of the intensity shifts from the position on the line 
 =
=  to that on the line
to that on the line 
 = 0 as the doping level is decreased from electron doping to hole doping. We find that the
= 0 as the doping level is decreased from electron doping to hole doping. We find that the  dependence of the ratio of the intensity in the superconducting state to that in the normal state is qualitatively different between the
dependence of the ratio of the intensity in the superconducting state to that in the normal state is qualitatively different between the 
 -wave and
-wave and 
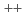 -wave pairings. We propose to investigate experimentally this ratio in
-wave pairings. We propose to investigate experimentally this ratio in  space to distinguish the two pairing states.
space to distinguish the two pairing states.
Nagai, Yuki; Nakai, Noriyuki*; Machida, Masahiko
Physical Review B, 85(9), p.092505_1 - 092505_4, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:43.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We perform large-scale self-consistent numerical calculations, solving the Bogoliubov-de Gennes (BdG) equations in the magnetic field together with random impurities to directly demonstrate the typical quasiparticle interference (QPI) in the presence of vortices as observed by scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy experiments in unconventional superconductors. The calculations reveal that the vortex itself never works as a scatter, causing the QPI pattern, but the vortex core containing impurity brings about the enhancement of the sign-preserving QPI peaks. Its origin is Andreev-bound states distorted by impurity, and all the measurement findings are consistently explained by the scenario based on the numerical results.
Nagai, Yuki; Ota, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(2), p.024710_1 - 024710_6, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:79.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose an efficient numerical algorithm to solve Bogoliubov-de Gennes equations self-consistently for inhomogeneous superconducting systems with a reformulated polynomial expansion scheme. This proposed method is applied to typical issues such as a vortex under randomly distributed impurities and a normal conducting junction sandwiched between superconductors. With various technical remarks, we show that its efficiency becomes remarkable in large-scale parallel performance.
Nagai, Yuki; Ota, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Physics Procedia, 27, p.72 - 75, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:79.93(Physics, Applied)We develop an efficient numerical method on the basis of the spectral-density polynomial expansion to calculate two-particle Green's function in Bogoliubov-de Gennes (BdG) framework for inhomogeneous superconducting systems. With use of this method, one can systematically and effectively evaluate various physical quantities such as spin or charge susceptibility, nuclear magnetic relaxation rate, optical or thermal conductivity even in magnetic fields. We demonstrate its remarkable feature, i.e. high efficiency with large-scale parallel computing techniques.
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC '11) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2011/11
One of the most fascinating issues in modern condensed matter physics is to understand highly-correlated electronic structures and propose their novel device designs toward the reduced carbon-dioxide future. Among various developed numerical approaches for highly-correlated electrons, the density matrix renormalization group (DMRG) has been widely accepted as the most promising numerical scheme compared to Monte Carlo and exact diagonalization in terms of accuracy and accessible system size. In fact, DMRG almost perfectly resolves one-dimensional chain like long quantum systems. In this paper, we suggest its extended approach toward higher-dimensional systems by high-performance computing techniques. The computing target in DMRG is a huge non-uniform sparse matrix diagonalization. In order to efficiently parallelize the part, we implement communication step doubling together with reuse of the mid-point data between the doubled two steps to avoid severe bottleneck of all-to-all communications essential for the diagonalization. The technique is successful even for clusters composed of more than 1000 cores and offers a trustworthy exploration way for two-dimensional highly-correlated systems.
Sasa, Narimasa; Machida, Masahiko
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.609 - 612, 2011/10
Large scale numerical simulation of quantum turbulence is performed by using 3-D time-dependent Gross-Pitaevskii equation. The energy spectrum obeying Kolmogorov law and large scale self-similar structure of quantum vortex tangle are found in a fully developed dumped turbulent state. Width of the inertial range becomes large depending on the system size of the simulation that is consistent with the result of the normal fluid turbulence. On the other hand, bottleneck effect near coherent length prevents the inertial range from extending to smaller scale.
Sasa, Narimasa; Kano, Takuma*; Machida, Masahiko; L'vov, V. S.*; Rudenko, O.*; Tsubota, Makoto*
Physical Review B, 84(5), p.054525_1 - 054525_6, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:84.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In a 2048 simulation of quantum turbulence within the Gross-Pitaevskii equation, it is demonstrated that the large-scale motions have a classical Kolmogorov-1941 energy spectrum
simulation of quantum turbulence within the Gross-Pitaevskii equation, it is demonstrated that the large-scale motions have a classical Kolmogorov-1941 energy spectrum 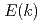

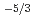 , followed by an energy accumulation with
, followed by an energy accumulation with 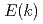
 const at
const at  about the reciprocal mean intervortex distance. This behavior was predicted by the L'vov-Nazarenko-Rudenko bottleneck model of gradual eddy-wave crossover, further developed in the paper.
about the reciprocal mean intervortex distance. This behavior was predicted by the L'vov-Nazarenko-Rudenko bottleneck model of gradual eddy-wave crossover, further developed in the paper.
Imai, Yoshinori*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Kitagawa, Kentaro*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Nakai, Noriyuki*; Nagai, Yuki; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Machida, Masahiko; Maeda, Atsutaka*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(1), p.013704_1 - 013704_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:81.68(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hiroki; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Nakai, Noriyuki; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 469(15-20), p.908 - 911, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:68.42(Physics, Applied)In order to resolve a discrepancy of the magnetic moment on Fe between the experimental and calculation results, we perform first-principle electronic structure calculations for iron-based superconductors LaFeAsO F
F in which
in which 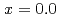 and
and 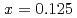 by using the LSDA+
by using the LSDA+ framework. Consequently, we confirm in both the mother and doped compounds that negative
framework. Consequently, we confirm in both the mother and doped compounds that negative  correction is crucial in matching the calculated magnetic moment with the observed one. A reason of the negative correction is that the Coulomb interaction on Fe orbitals is unexpectedly screened than LSDA's expectation. We discuss which type of situation emerges when the negative
correction is crucial in matching the calculated magnetic moment with the observed one. A reason of the negative correction is that the Coulomb interaction on Fe orbitals is unexpectedly screened than LSDA's expectation. We discuss which type of situation emerges when the negative  is a good correction in these compounds.
is a good correction in these compounds.
Okumura, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Sakai, Toru
Physical Review A, 79(6), p.061602_1 - 061602_4, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.68(Optics)We study polarization effects of two-component atomic Fermi gases loaded on three-leg triangular optical lattice by using the density-matrix renormalization-group method. Concentrating on a case in which a Mott phase coexists with metallic ones, we observe plate like structures in the Mott phase polarization as a function of the input population imbalance. The structures are clearly analogous to the magnetization plateau states studied in the triangular Heisenberg lattice model under the magnetic field. In fact, we find that spin patterns peculiar to the plateau states emerge inside the Mott phase. This result suggests that the Mott phase is an excellent stage in systematically investigating frustrated spin systems.
Nogiwa, Kimihiro; Nishimura, Akihiko; Oba, Hironori; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Okubo, Tadakatsu*; Hono, Kazuhiro*
Materia, 47(12), P. 626, 2008/12
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Atsushi; Kamata, Tetsuji*; Takagi, Junichi*; Iwasaki, Kenji*; Yura, Kei
Biophysical Journal, 95(6), p.2895 - 2908, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:44.52(Biophysics)Protein is activated, but the activation mechanism and generality of the conformational change remain to be elucidated. We performed normal mode analysis of the elastic network model on integrin 
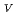

 ectodomain in the bent form and identified key residues which were influential on molecular motions. Iterative normal mode calculations demonstrated that the specific non-bonded interactions involving the key residues work as a snap to keep integrin in the bent form. The importance of the key residues for the conformational change was further verified by mutation experiments. Conservation pattern of amino acid residues among integrin family showed that the characteristic pattern of residues seen around these key residues is found in the limited groups of integrin
ectodomain in the bent form and identified key residues which were influential on molecular motions. Iterative normal mode calculations demonstrated that the specific non-bonded interactions involving the key residues work as a snap to keep integrin in the bent form. The importance of the key residues for the conformational change was further verified by mutation experiments. Conservation pattern of amino acid residues among integrin family showed that the characteristic pattern of residues seen around these key residues is found in the limited groups of integrin  chains.
chains.
 transition edge sensor
transition edge sensorOkayasu, Satoru; Katagiri, Masaki; Hojo, Kiichi; Morii, Yukio; Miki, Shigenobu*; Shimakage, Hisashi*; Wang, Z.*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Physica C, 468(15-20), p.1998 - 2000, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)We have been investigating for neutron detection with the MgB  transition edge sensor (TES). For the purpose, we have been developing a low noise measurement system for neutron detection. To confirm the usefulness of our detecting system, alpha-ray detection from an
transition edge sensor (TES). For the purpose, we have been developing a low noise measurement system for neutron detection. To confirm the usefulness of our detecting system, alpha-ray detection from an  Am source was achieved. To improve the sensitivity, short meander samples with 35
Am source was achieved. To improve the sensitivity, short meander samples with 35  m length and 1
m length and 1  m width is used. Samples are fabricated by the Kansai group. Superconducting transition temperature Tc is 23.3 K. The transition width is sharp enough less than 1 K. The detection was achieved under a constant current condition, and the resistivity changes at the sample due to the alpha-ray irradiation were detected. The bias current is 6
m width is used. Samples are fabricated by the Kansai group. Superconducting transition temperature Tc is 23.3 K. The transition width is sharp enough less than 1 K. The detection was achieved under a constant current condition, and the resistivity changes at the sample due to the alpha-ray irradiation were detected. The bias current is 6  A.
A.
Okumura, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Taniguchi, Nobuhiko*; Machida, Masahiko
Physical Review Letters, 101(1), p.016407_1 - 016407_4, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We study an interplay of disorder and correlation in the one- dimensional hole-doped Hubbard-model with disorder (Anderson-Hubbard model) by using the density-matrix renormalization group method. Concentrating on the doped-hole density profile, we find in a large 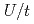 regime that the clean system exhibits a simple fluidlike behavior whereas finite disorders create locally Mott regions which expand their area with increasing the disorder strength contrary to the conventional sense. We propose that such an anomalous Mott phase formation assisted by disorder is easily observable in atomic Fermi gases by setup of the box-shape trap.
regime that the clean system exhibits a simple fluidlike behavior whereas finite disorders create locally Mott regions which expand their area with increasing the disorder strength contrary to the conventional sense. We propose that such an anomalous Mott phase formation assisted by disorder is easily observable in atomic Fermi gases by setup of the box-shape trap.
Nakamura, Yusuke*; Mine, Makoto*; Okumura, Masahiko; Yamanaka, Yoshiya*
Physical Review A, 77(4), p.043601_1 - 043601_6, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:65.63(Optics)The condition for the appearance of dynamical instability of the Bose- condensed system, characterized by the emergence of complex eigenvalues in the Bogoliubov-de Gennes equations, is studied analytically. It is concluded that the degeneracy between a positive- norm eigenmode and a negative-norm one is essential for the emergence of complex modes. Based on the conclusion, we justify the two-mode approximation applied in our previous work, in which we analytically studied the condition for the existence of complex modes when the condensate has a highly quantized vortex.
Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Igarashi, Ryo; Yamamoto, Atsushi*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English