Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagai, Haruyasu; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki; Tanimori, Toru*
Dai-52-Kai Kashika Joho Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/07
A novel monitoring method for the quantitative visualization of 3D distribution of a radioactive plume accidentally released from a nuclear facility is proposed, and the feasibility of its analysis method is demonstrated by preliminary test using hypothetical data. The proposed method is the combination of gamma-ray imaging spectroscopy with the electron tracking Compton camera (ETCC) and real-time high-resolution atmospheric dispersion simulation based on 3D wind observation with Doppler lidar. ETCC can acquire the angle distribution images of direct gamma-ray from a specific radionuclide in a target radioactive plume. The 3D distribution of radioactive plume is inversely reconstructed from direct gamma-ray images by several ETCCs located around the target by harmonizing with the air concentration distribution pattern of the plume predicted by real-time atmospheric dispersion simulation. Analysis methods were developed and tested by using hypothetical data generated by numerical simulations of atmospheric dispersion and radiation transport.
Parker, J. D.*; Harada, Masahide; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.102 - 107, 2020/05
Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 13(12), p.e0208909_1 - e0208909_12, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Imaging of  Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).
Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).  Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV
Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV  rays, and was produced in the
rays, and was produced in the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction with a
Tc reaction with a  Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the
Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the  Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of
Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of  Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three
Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three  rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing
rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing  -ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy
-ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy  -ray emitters such as
-ray emitters such as  Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
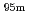 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1283 - 1285, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.23(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is used in radioactive medical diagonostic tests, for example as a radioactive tracer that medical equipment can detect in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 141 keV
Tc) is used in radioactive medical diagonostic tests, for example as a radioactive tracer that medical equipment can detect in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 141 keV  rays, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). There are at least 31 commonly used radiopharmaceuticals based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. Recent years, with the develop-ment of the Compton camera which can realize high position resolution, technetium isotopes emitting high energy
rays, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). There are at least 31 commonly used radiopharmaceuticals based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. Recent years, with the develop-ment of the Compton camera which can realize high position resolution, technetium isotopes emitting high energy  -rays are required. In this study, technetium-95m which emits some
-rays are required. In this study, technetium-95m which emits some  rays around 800 keV was produced by the
rays around 800 keV was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n)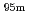 Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.
Harada, Masahide; Parker, J. D.*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Kubo, Hidetoshi*; Tanimori, Toru*; Shinohara, Takenao; Maekawa, Fujio; Sakai, Kenji
Physics Procedia, 43, p.314 - 322, 2013/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.82(Physics, Applied)The purposes of this study are to perform Neutron Resonance Absorption NRA test experiments using the Micro Pixel Chamber, and to confirm its quantitativity. The detector was located at 14.5 m from the moderator in the experimental room of NOBORU. The samples, consisting of thin Tantalum (Ta) foils, with thicknesses of 5, 10, 20 and 100  m, were placed individually at 15 cm upstream from the detector. In the experiment, the transmission spectra with the Ta samples and no sample were obtained. Background components were not so small in these measurements. From the neutron transport simulation, it was surmised that the origin of this background was due to scattering of neutrons in the experimental room. Therefore, the assumed background components were subtracted from the measurement data. Finally, it was found that the difference between the measurement data and the nuclear data was within about 7%.
m, were placed individually at 15 cm upstream from the detector. In the experiment, the transmission spectra with the Ta samples and no sample were obtained. Background components were not so small in these measurements. From the neutron transport simulation, it was surmised that the origin of this background was due to scattering of neutrons in the experimental room. Therefore, the assumed background components were subtracted from the measurement data. Finally, it was found that the difference between the measurement data and the nuclear data was within about 7%.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Tanaka, Hiroki; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; Ochi, Atsuhiko*; Tanimori, Toru*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 573(1-2), p.187 - 190, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have been developing a neutron imaging gas detector with a high spatial resolution and with a high temporal response for the neutron scattering instruments at the pulsed neutron source in the Japan proton accelerator research complex. The gas detector system with individual read-outs was developed to meet the requirements for the instruments for neutron reflectometry or for small angle neutron scattering. The performances of the prototype detector using a multi-wire (MW) or micro-strip (MS) detector head were evaluated using a collimated neutron beam, and we confirmed the MS detector exhibiting a spatial resolution of 1.5 mm and a pulse-pair resolution of about 100 ns with a gas pressure of 6 atm helium with a mixture of 30% CF . The performances for the MS detector were also evaluated up to the total gas pressure of 8 atm.
. The performances for the MS detector were also evaluated up to the total gas pressure of 8 atm.
Yamagishi, Hideshi; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; Tanaka, Hiroki*; Tanimori, Toru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Oku, Takayuki; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamazaki, Dai; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
Sonoda, Shinya*; Nabeya, Akira*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; Takada, Atsushi*; Kubo, Hidetoshi*; Komura, Shotaro*; Tanimori, Toru*; Matsuoka, Yoshihiro*; Mizumura, Yoshitaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
SPECT and PET are widely used for medical imaging. However, radio isotopes available for SPECT and PET are limited. Under these circumstances, it is expected the appearance of the new  imaging detector which can measure more various kinds of
imaging detector which can measure more various kinds of  -ray sources in order to develop new biomarkers using new radio isotopes. We set out to contribute to medical imaging technology by developing Electron-Tracking Compton Camera (ETCC) which can measure the various radioactive medicine.
-ray sources in order to develop new biomarkers using new radio isotopes. We set out to contribute to medical imaging technology by developing Electron-Tracking Compton Camera (ETCC) which can measure the various radioactive medicine.
Sonoda, Shinya*; Takada, Atsushi*; Tanimori, Toru*; Tsuda, Masaya*; Tahara, Keisuke*; Kobayashi, Koichiro*; Tanigaki, Minoru*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Nakayama, Hiromasa; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed an Electron Tracking Compton Camera (ETCC), which provides a well-defined Point Spread Function (PSF) by reconstructing a direction of each gamma as a point and realizes simultaneous measurement of brightness and spectrum of MeV gamma-rays. Here, we present the results of the gamma-imaging-spectroscopy with ETCC tested at the research reactor at the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University.
Nagai, Haruyasu; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki; Tanimori, Toru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 NID) with boron converter for energy-resolved neutron imaging at J-PARC
NID) with boron converter for energy-resolved neutron imaging at J-PARCParker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Harada, Masahide; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Su, Y. H.; et al.
no journal, ,
Nagai, Haruyasu; Tanimori, Toru*; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki; Furuta, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sonoda, Shinya*; Takada, Atsushi*; Tanimori, Toru*; Tsuda, Masaya*; Tahara, Keisuke*; Kobayashi, Koichiro*; Tanigaki, Minoru*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki
no journal, ,
We have developed an Electron Tracking Compton Camera (ETCC), which provides a well-defined Point Spread Function (PSF) by reconstructing a direction of each gamma as a point and realizes simultaneous measurement of brightness and spectrum of MeV gamma-rays. Here, we present the results of the gamma-imaging-spectroscopy with ETCC tested at the research reactor at the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University.
 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, the Compton camera which is originally developed for the astrophysical studies was applied for medical diagnostic usage. For the Compton camera imaging require technetium isotopes emitting higher energy  -rays. Two Tc isotopes,
-rays. Two Tc isotopes,  Tc (T
Tc (T = 60 d; E
= 60 d; E = 204, 582 and 835 keV) and
= 204, 582 and 835 keV) and 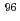 Tc(T
Tc(T = 4.28 d, E
= 4.28 d, E = 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher
= 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher  -ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with
-ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with  Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the
Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.
Sonoda, Shinya*; Nabetani, Akira*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; Takada, Atsushi*; Kubo, Hidetoshi*; Komura, Shotaro*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Tanimori, Toru*; Matsuoka, Yoshihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
We present the performance results using this new ETCC such as the imaging test using F-18 in point-like and rod-like phantoms with varying the intense of radiation. In addition, the measurementof Tc-95m which is produced by Japan Atomic Energy Agency was performed. Tc-95m emitsthe  -rays with the energy, 204, 583, and 835 keV, and then an image with multi-energies is examined. The position resolution achieves less than about 8 degrees from 10 degrees at 511 keV by this improvement. Further improvement of the angular resolution (position resolution) will be presented until 2015 spring. Also, we are developing the next ETCC by increasing the thickness of the scintillator from 1 rad. to 2 rad. and the gas pressure from 1 atm to 3 atm which improvethe detection efficiency by a factor of
-rays with the energy, 204, 583, and 835 keV, and then an image with multi-energies is examined. The position resolution achieves less than about 8 degrees from 10 degrees at 511 keV by this improvement. Further improvement of the angular resolution (position resolution) will be presented until 2015 spring. Also, we are developing the next ETCC by increasing the thickness of the scintillator from 1 rad. to 2 rad. and the gas pressure from 1 atm to 3 atm which improvethe detection efficiency by a factor of  5 at 511 keV. By these improvements, the imaging time of mouse is expected to be reduced from several hours with to
5 at 511 keV. By these improvements, the imaging time of mouse is expected to be reduced from several hours with to  20 minutes for lots of kinds of RIs with the energy band from 0.1-2 MeV.
20 minutes for lots of kinds of RIs with the energy band from 0.1-2 MeV.
To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ochi, Atsuhiko*; Tanimori, Toru*
no journal, ,
Neutron scattering experiments using high intensity pulsed neutrons will be carried out in Materials and Life Science Facility at J-PARC. Detectors using in the facility require features such as a good spatial resolution, high detection efficiency, fast response, etc. We have developed a 2D position sensitive neutron detector system consist of micro-pattern detector array such as microstrip and miltiwire detector array. In this presentation, characteristics of the 2D micro-pixel gas chamber system under Cf-252 neutron irradiation are reported. Detection area used in this experiment is 50 50 mm
50 mm and pitches of both axes, anodes and cathodes, are 0.4 mm. Irradiation were carried out with a mixture gas of helium-3 and carbon tetrafluoride. It can be seen that signal pulse peaks of neutrons can be identified and these pulse peaks is discriminated easily from background noises. Here, degradation of gas gain arisen from a charge up effect was not observed in our system.
and pitches of both axes, anodes and cathodes, are 0.4 mm. Irradiation were carried out with a mixture gas of helium-3 and carbon tetrafluoride. It can be seen that signal pulse peaks of neutrons can be identified and these pulse peaks is discriminated easily from background noises. Here, degradation of gas gain arisen from a charge up effect was not observed in our system.
To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Sakasai, Kaoru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ochi, Atsuhiko*; Tanimori, Toru*
no journal, ,
Neutron scattering experiments involving high-intensity and wide-energy pulsed neutrons are expected to be conducted at the MLF in the J-PARC. These experiments require neutron detectors with features such as a two-dimensional detection area, good spatial resolution, high detection efficiency, and a fast response time. In this study, a gas-based neutron detection system with individual readout method and consisting of a micro-pixel detector head was developed, and preliminary experiments were conducted under neutrons irradiation. To examine the operation of the detector system, the total projection ranges of the secondary particles emitted by the nuclear reaction between neutrons and  He nuclei are measured and compared with the values obtained from a Monte Carlo simulation. Since the measured projection ranges of the secondary particles agree with the ranges obtained from the Monte Carlo simulation, it is concluded that the operation of the developed system is satisfactory.
He nuclei are measured and compared with the values obtained from a Monte Carlo simulation. Since the measured projection ranges of the secondary particles agree with the ranges obtained from the Monte Carlo simulation, it is concluded that the operation of the developed system is satisfactory.
Harada, Masahide; Parker, J.*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Kubo, Hidetoshi*; Tanimori, Toru*; Shinohara, Takenao; Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Harada, Masahide; Parker, J.*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Kubo, Hidetoshi*; Tanimori, Toru*; Shinohara, Takenao; Maekawa, Fujio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English