Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kobayashi, Naoki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Furukawa, Hazuki*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Koda, Yuya; Matsuno, Hiroki; Matsushima, Akira; Kubota, Shintaro; Toda, Keisuke; Nakamura, Yasuyuki
JAEA-Review 2024-003, 38 Pages, 2024/06
"Fugen Decommissioning Engineering Center", in planning and carrying out our decommissioning technical development, organizes "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning" which consists of the members well-informed, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened domestic and international, as the central place in research and development base of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report consists of presentation paper are "The current status of Fugen decommissioning", "Regarding dismantling and decontamination of steam drums", "Knowledge of radiation management in dismantling contaminated equipment", "Achievements and considerations for identifying and separating contaminated parts of nonradioactive waste" and "Regarding technology development plans for nuclear reactor dismantling" which is presented in the 41st Technical Special Committee on Fugen Decommissioning.
Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:48.53(Chemistry, Physical)Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.36(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Kikuchi, Shin; Nakamura, Kinya*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(4), p.20-00542_1 - 20-00542_13, 2021/08
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B
C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B
C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B
C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B
C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2021/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a CDA computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2019. Specific results in this paper are the validation of physical model describing B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a CDA computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2019. Specific results in this paper are the validation of physical model describing B C-SS eutectic reaction in the CDA analysis code, SIMMER-III, through the numerical analysis of the B
C-SS eutectic reaction in the CDA analysis code, SIMMER-III, through the numerical analysis of the B C-SS eutectic melting experiments in which a B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments in which a B C block was placed in a SS pool.
C block was placed in a SS pool.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:95.97(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,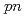 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Kikuchi, Shin; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nakamura, Kinya*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2020/08
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B
C) and stainless steel (SS) may take place. Thus, kinetic behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the important phenomena to be considered when evaluating the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In this study, for the first step to obtain the fundamental information on kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B
C-SS eutectic melting, the thermal analysis using the pellet type samples of B C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B
C and Type 316L SS as different experimental technique was performed. The differential thermal analysis endothermic peaks for the B C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B
C-SS eutectic melting appeared from 1483K to 1534K and systematically shifted to higher temperatures when increasing heating rate. Based on this kinetic feature, apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor for the B C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
C-SS eutectic melting were determined by Kissinger method. It was found that the kinetic parameters obtained by thermal analysis were comparable to the literature values.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.418 - 427, 2019/09
Eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Seto, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 562, p.148 - 154, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.46(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawamura, Seiko; Ito, Shinichi*; Nakajima, Kenji
JAEA-Review 2017-031, 107 Pages, 2018/02
The joint user meeting for four direct-geometry neutron spectrometers in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC, "DIRECTION 2017", was held at the Ibaraki Quantum Beam Research Center building on October 16th - 17th, 2017. This meeting was purposed to encourage the user activities on the four instruments 4SEASONS (BL01), HRC (BL12), AMATERAS (BL14), and POLANO (BL23), and was jointly organized by J-PARC MLF, KEK-IMSS, and CROSS. In this meeting, recent research activities using these instruments were reported in addition to the current status of the instruments, the sample environments, and software. This report compiles the presentation materials and their abstracts.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
 Pt
PtIbuka, Soshi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Ito, Shinichi*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Imai, Motoharu*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 868(1), p.012017_1 - 012017_6, 2017/07
Spin wave dispersion of the metallic antiferromagnet Mn Pt was investigated just above the order-order transition temperature by using the inelastic neutron scattering technique. The spin wave dispersion at
Pt was investigated just above the order-order transition temperature by using the inelastic neutron scattering technique. The spin wave dispersion at  = 400 K along [100], [110] and [111] directions was isotropic within the measurement accuracy. These results show that large reduction of the stiffness constant with increasing temperature, and indicate the itinerancy of the magnetic moments.
= 400 K along [100], [110] and [111] directions was isotropic within the measurement accuracy. These results show that large reduction of the stiffness constant with increasing temperature, and indicate the itinerancy of the magnetic moments.
Seto, Hideki; Ito, Shinichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Shibata, Kaoru; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; General Subjects, 1861(1), p.3651 - 3660, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.18(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)J-PARC, Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex provides short pulse proton beam at a repetition rate 25 Hz and the maximum power is expected to be 1 MW. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments have already been operated or under construction / commissioning. There are 6 inelastic / quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectrometers and the complementary use of these spectrometers will open new insight for life science.
Uto, Hiroyasu; Takase, Haruhiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tobita, Kenji; Mori, Kazuo; Kudo, Tatsuya; Someya, Yoji; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hoshino, Kazuo; Nakamura, Makoto; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 103, p.93 - 97, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Conceptual design of in-vessel component including conducting shell has been investigated in Broader Approach (BA) DEMO design activities, in order to propose feasible DEMO reactor from plasma vertical stability and engineering viewpoint. The conducting shell for the plasma vertical stability will be incorporated behind blanket module, while the location must be close to the plasma surface as possible for the plasma stabilization. We evaluated dependence of the plasma vertical stability on the conducing shell parameters by using a 3-dimensional eddy current analysis code (EDDYCAL). The calculation results showed that the conducting shell requires more than 0.01 m thickness of Cu-alloy on DEMO. On the other hand, the electromagnetic force at the plasma disruption is a few times larger than no conducting shell case because of larger eddy current on conducting shell. The engineering design issues of in-vessel components for plasma vertical stability are presented.
Someya, Yoji; Tobita, Kenji; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tokunaga, Shinsuke; Hoshino, Kazuo; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Makoto; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1872 - 1875, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:96.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)Blanket concept with simplified interior for mass production has been developed with a mixed bed of Li TiO
TiO and Be
and Be Ti pebbles, a coolant condition of 15.5 MPa and 290-325
Ti pebbles, a coolant condition of 15.5 MPa and 290-325 C and cooling tubes only without any partitions. A neutronics analysis ensured the blanket concept meets a self-sufficient supply of tritium. However, this concept is vulnerable to the inner pressure. A plant availability for DEMO may drop to a lower value, because a potential of resume operations after an accident such as a coolant leakage in blanket is not considered. The blanket design will be revisited for the availability. Considering the continuity with the ITER-TBM option of Japan and the engineering feasibility of fabrication, our design study focuses on a water-cooled solid breeding blanket using the mixed pebbles bed. A breakage of the blanket casing should be avoided not to contaminate the plasma chamber with water and breeding materials. A water-cooled solid blanket with inner pressure tightness is estimated by the ANSYS code. As a results, the pressure tightness of 8 MPa (water vapor pressure at 300
C and cooling tubes only without any partitions. A neutronics analysis ensured the blanket concept meets a self-sufficient supply of tritium. However, this concept is vulnerable to the inner pressure. A plant availability for DEMO may drop to a lower value, because a potential of resume operations after an accident such as a coolant leakage in blanket is not considered. The blanket design will be revisited for the availability. Considering the continuity with the ITER-TBM option of Japan and the engineering feasibility of fabrication, our design study focuses on a water-cooled solid breeding blanket using the mixed pebbles bed. A breakage of the blanket casing should be avoided not to contaminate the plasma chamber with water and breeding materials. A water-cooled solid blanket with inner pressure tightness is estimated by the ANSYS code. As a results, the pressure tightness of 8 MPa (water vapor pressure at 300 C) can be compatible with the self-sufficient production of tritium when the blanket is as thick as about 0.9 m and the ribs are arranged in the radial direction. Therefore, the blanket concept with pressure tightness of 8 MPa is adopted with depressurization system as which a tritium recovery system such as helium purge-gas line is posteriorly arranged in blanket to serve. On the other hand, a handling of decay heat is a serious problem at an accident such as LOCA. Coolant flow is divided into the blanket to secure heat removal for the safety. Finally, the blanket segmentation with the shape and dimension of blanket and routing of coolant flow has also been proposed. Moreover, overall TBR is estimated with torus configuration based in the segmentation using three-dimensional MCNP calculation.
C) can be compatible with the self-sufficient production of tritium when the blanket is as thick as about 0.9 m and the ribs are arranged in the radial direction. Therefore, the blanket concept with pressure tightness of 8 MPa is adopted with depressurization system as which a tritium recovery system such as helium purge-gas line is posteriorly arranged in blanket to serve. On the other hand, a handling of decay heat is a serious problem at an accident such as LOCA. Coolant flow is divided into the blanket to secure heat removal for the safety. Finally, the blanket segmentation with the shape and dimension of blanket and routing of coolant flow has also been proposed. Moreover, overall TBR is estimated with torus configuration based in the segmentation using three-dimensional MCNP calculation.