Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:98.62(Multidisciplinary Sciences)
Jin, H.*; Choi, E. S.*; Wu, H.-C.*; Curro, N. J.*; Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Taku*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Klavins, P.*; Taufour, V.*
Physical Review B, 111(3), p.035103_1 - 035103_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compounds
ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compoundsTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Nakamura, Jin*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Sato, Hideyuki*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.9_1 - 9_10, 2024/12
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
 C ions based on first-principles calculations
C ions based on first-principles calculationsSekikawa, Takuya; Matsuya, Yusuke; Hwang, B.*; Ishizaka, Masato*; Kawai, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kai, Takeshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 548, p.165231_1 - 165231_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)One of the main causes of radiation effects on the human body is thought to be damage to DNA, which carries genetic information. However, it is not fully understood what kind of molecular structural changes DNA undergoes upon radiation damage. Since it has been reported that various types of DNA damage are formed when DNA is irradiated, our group has investigated the relationship between DNA damage and various patterns of radiation-induced ionization induced by radiation. Although we have so far analyzed DNA damage in a simple system using a rigid body model of DNA, more detailed calculations are required to analyze the molecular structural changes in DNA, which are considered to be important in considering the effects on the human body. In this study, we attempted to clarify the molecular conformational changes of DNA using OpenMX, a first-principles calculation software that can discuss electronic states based on molecular structures. Specifically, we calculated the most stable structure, band dispersion, and wave function of DNA under the assumption that one and two electrons are ionized by various radiation. In the presentation, we will discuss the relationship between the energy dependence of each incident radiation type and the molecular conformational change of DNA. In addition, the radiation-induced changes in the basic physical properties of DNA (corresponding to the initial stage of DNA damage) will be discussed from the viewpoints of both radiation physics and solid state physics.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:183 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
Cicek, E.*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Fang, Z.*; Fukui, Yuji*; Mizobata, Satoshi*; Otani, Masashi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Sato, Yoshikatsu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167700_1 - 167700_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The digital feedback (DFB) setup employed in a low-level radio frequency (LLRF) control system is crucial to ensure RF field stability in accelerating cavities. To this end, a novel in-house and multi-purpose prototype DFB setup was developed for multiple applications at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Being efficient, low-cost, and compact is key to achieving a cost-effective system that fulfills the performance specifications. A field-programmable gate array (FPGA)-based design with a digital signal processing (DSP) function is used. This arrangement compensates for RF phase fluctuations and amplitude modulations by employing a proportional and integral (PI) feedback controller. The system was utilized to conduct high-power tests on the interdigital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) cavity of a muonlinac for short RF pulses. The setup was also tested on a buncher cavity (Buncher-2) in the J-PARC linac, achieving efficient performance for longer RF pulses. The stability of the RF accelerating field in the IH-DTL was achieved at  0.25% peak-to-peak (pp) in amplitude and
0.25% peak-to-peak (pp) in amplitude and  0.36 degree pp in phase. For the Buncher-2, the amplitude stability of
0.36 degree pp in phase. For the Buncher-2, the amplitude stability of  0.18% pp and phase stability of
0.18% pp and phase stability of  0.13 degree pp were obtained. This study discusses the design aspects of a cost-effective DFB system and reports high-power measurements.
0.13 degree pp were obtained. This study discusses the design aspects of a cost-effective DFB system and reports high-power measurements.
Xu, S.*; Odaira, Takumi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Seiner, H.*; Zoubkov , K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
, K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.5307_1 - 5307_8, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.79(Multidisciplinary Sciences)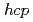 -Mg alloys based on peak asymmetry analysis
-Mg alloys based on peak asymmetry analysisEgusa, Daisuke*; Manabe, Ryo*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Sato, Shigeo*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Today Communications (Internet), 31, p.103344_1 - 103344_6, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mattan, K.*; Ono, Toshio*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Nambu, Yusuke*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review B, 105(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_8, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spin dynamics of the spin-1/2 kagome-lattice antiferromagnet Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
Uehara, Akihiro*; Shuhui, X.*; Sato, Ryotaro*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Yakumaru, Haruko*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Tanaka, Izumi*; Ishihara, Hiroshi*; et al.
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 53, p.223 - 229, 2022/03
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Mamoru*; Shiota, Daiko*; Tao, Chihiro*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Ishii, Takako*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Koga, Kiyokazu*; Kubo, Yuki*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.108_1 - 108_20, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.42(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We surveyed the relationship between the scale of space weather events and their occurrence rate in Japan and we discussed the social impact of these phenomena during the Project for Solar-Terrestrial Environment Prediction (PSTEP). The information was compiled for domestic users of space weather forecasts for appropriate preparedness against space weather disasters. This paper gives a comprehensive summary of the survey, focusing on the fields of electricity, satellite operations, communication and broadcasting, satellite positioning usage, aviation, human space activity, and daily life on the Earth's surface, using the cutting-edge knowledge of space weather. Quantitative estimations of the economic impact of space weather events on electricity and aviation are also given.
 anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca
anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca ReO
ReO Cl
Cl
Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Hirai, Daigoro*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Murasaki, Ryo*; Kogane, Satoshi*; Kimata, Motoi*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Hiroi, Zenji*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(4), p.043121_1 - 043121_11, 2020/12
The spin excitations of the  =
=  anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca
anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca ReO
ReO Cl
Cl were investigated by inelastic neutron-scattering experiments. The spin excitation spectrum exhibits sharp dispersive modes in addition to a spinonlike continuum. The consistency with the simulated spectrum based on the random-phase approximation is better for Ca
were investigated by inelastic neutron-scattering experiments. The spin excitation spectrum exhibits sharp dispersive modes in addition to a spinonlike continuum. The consistency with the simulated spectrum based on the random-phase approximation is better for Ca ReO
ReO Cl
Cl than for Cs
than for Cs CuCl
CuCl , indicating that the spin system in the former remains closer to a Tomonaga-Luttinger liquidlike disordered state.
, indicating that the spin system in the former remains closer to a Tomonaga-Luttinger liquidlike disordered state.
 Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.17(Physics, Nuclear)Oikawa, Kenichi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Omae, Kazuma*; Pham, A.*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harjo, S.; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.207 - 213, 2020/02
Sato, Yuki; Kawase, Keiichi; Iijima, Kazuki; Kobayashi, Takuya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(1), p.37 - 41, 2020/01
, 62(1), p.37 - 41, 2020/01
This series articles introduce JAEA R&D. This time, we will introduce about Fukushima Daiichi decommissioning and Fukushima remediation (2).
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.16(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sato, Seiji; Matsumoto, Takumi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(3-4), p.311 - 314, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.32(Environmental Sciences)There has been significant concern about an increase of exposure dose in living sphere due to the accumulation of radiocesium discharged from contaminated mountainous forest in Fukushima. In this study, we investigated the history of radiocesium deposition on some floodplains in Fukushima. Radiocesium concentrations of river suspended particles and air dose rates at floodplains were also observed continuously. In many situations, annual sediment accumulation at floodplains was only several kg m and its radiocesium concentration was gradually decreasing in line with that of suspended particle. Simultaneously, air dose rates on floodplains were decreasing with time. In 2015 with heavy flood discharge, several hundred kg m
and its radiocesium concentration was gradually decreasing in line with that of suspended particle. Simultaneously, air dose rates on floodplains were decreasing with time. In 2015 with heavy flood discharge, several hundred kg m of sediment accumulation and sharply decrease of air dose rate was observed at rivers without reservoir. Conversely, radiocesium accumulation at floodplain was significant reduced due to deposition on upstream reservoir.
of sediment accumulation and sharply decrease of air dose rate was observed at rivers without reservoir. Conversely, radiocesium accumulation at floodplain was significant reduced due to deposition on upstream reservoir.
Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Tanaka, Kimihito*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Sato, Taku*; Sugiyama, Haruki*; Uekusa, Hidehiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Tanaka, Hidekazu*
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2096_1 - 2096_8, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:73.92(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Search for topological materials has been actively promoted in the field of condensed matter physics for their potential application in energy-efficient information transmission and processing. Recent studies have revealed that topologically invariant states, such as edge states in topological insulators, can emerge not only in a fermionic electron system but also in a bosonic system, enabling nondissipative propagation of quasiparticles. Here we report the topologically nontrivial triplon bands measured by inelastic neutron scattering on the spin-1/2 two-dimensional dimerized antiferromagnet Ba CuSi
CuSi O
O Cl
Cl . The excitation spectrum exhibits two triplon bands that are clearly separated by a band gap due to a small alternation in interdimer exchange interaction, consistent with a refined crystal structure. By analytically modeling the triplon dispersion, we show that Ba
. The excitation spectrum exhibits two triplon bands that are clearly separated by a band gap due to a small alternation in interdimer exchange interaction, consistent with a refined crystal structure. By analytically modeling the triplon dispersion, we show that Ba CuSi
CuSi O
O Cl
Cl is the first bosonic realization of the coupled Su-Schrieffer-Heeger model, where the presence of topologically protected edge states is prompted by a bipartite nature of the lattice.
is the first bosonic realization of the coupled Su-Schrieffer-Heeger model, where the presence of topologically protected edge states is prompted by a bipartite nature of the lattice.
Ishikawa, Hirotaku*; Kai, Tetsuya; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(2), p.221 - 227, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)