Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Kudo, Takuto*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Sentoku, Sawako*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.1797_1 - 1797_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The amount of C in steel, which is critical in determining its properties, is strongly influenced by steel production technology. We propose a novel method of quantifying the bulk C content in steel non-destructively using muons. This revolutionary method may be used not only in the quality control of steel in production, but also in analyzing precious steel archaeological artifacts. A negatively charged muon forms an atomic system owing to its negative charge, and is finally absorbed into the nucleus or decays to an electron. The lifetimes of muons differ significantly, depending on whether they are trapped by Fe or C atoms, and identifying the elemental content at the muon stoppage position is possible via muon lifetime measurements. The relationship between the muon capture probabilities of C/Fe and the elemental content of C exhibits a good linearity, and the C content in the steel may be quantitatively determined via muon lifetime measurements. Furthermore, by controlling the incident energies of the muons, they may be stopped in each layer of a stacked sample consisting of three types of steel plates with thicknesses of 0.5 mm, and we successfully determined the C contents in the range 0.20 - 1.03 wt% depth-selectively, without sample destruction.
Kadowaki, Masanao; Nagai, Haruyasu; Yoshida, Toshiya*; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Sawa, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(10), p.1194 - 1207, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study develops an estimation method using machine learning for uncertainty in forecasted plume directions. Bayesian machine learning was used in the machine learning approach. A three-day forecast simulation was conducted every day from 2015-2020, considering a hypothetical release of  Cs from a nuclear facility to create training and test datasets for the machine learning. The findings reveal that the rate of good predictability was greater than 50% even in the forecast 36 h later when investigating the effectiveness of the Bayesian model on uncertainty estimation. Additionally, the frequency of miss prediction of higher uncertainty was low (0.9%-7.9%) throughout the forecast period. However, the rate of over-prediction of uncertainty increased with forecast time up to 31.2%, which is acceptable as a conservative estimation. These results show that the Bayesian model used in this study effectively estimates the uncertainty of plume directions predicted through atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Cs from a nuclear facility to create training and test datasets for the machine learning. The findings reveal that the rate of good predictability was greater than 50% even in the forecast 36 h later when investigating the effectiveness of the Bayesian model on uncertainty estimation. Additionally, the frequency of miss prediction of higher uncertainty was low (0.9%-7.9%) throughout the forecast period. However, the rate of over-prediction of uncertainty increased with forecast time up to 31.2%, which is acceptable as a conservative estimation. These results show that the Bayesian model used in this study effectively estimates the uncertainty of plume directions predicted through atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.08(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Yoshida, Kenta*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Shimodaira, Masaki
Materia, 62(3), p.154 - 158, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kamiya, Tomohiro; Ono, Ayako; Tada, Kenichi; Akie, Hiroshi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/11
JAEA started to develop the advanced reactor analysis code JAMPAN (JAEA advanced multi-physics analysis platform for nuclear systems). The current version of JAMPAN handles the continuous energy Monte Carlo code MVP and the detailed thermal-hydraulics analysis code for multiphase and multicomponent JUPITER. JAMPAN is designed to consider the extensibility and it does not depend on the analysis codes. All calculations in JAMAPAN are not directly connected. JAMPAN has data containers, and all input and output data of each analysis code are set in these data containers. JAMPAN will easily exchange the calculation codes and add the other calculations, e.g., structure calculation and irradiation calculation since the input and the output format of each code has no impact on the other calculation codes. The 4 by 4 pin-cell geometry was used as the demonstration calculation of JAMPAN and the physically reasonable calculation results were obtained.
Sakashita, Satoshi; Okui, Masahiro; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Uezu, Yasuhiro; Okuda, Eiichi
JAEA-Review 2022-012, 42 Pages, 2022/06
In this report, results of investigating fire alarm detectors status in order to understand the actual situation of false alarm occurrence and measures to systematically update of them. Based on results of this investigation, measures to systematically update of detectors were taken in order to reduce false fire alarm reports in a harsh environment and aged detectors. Numbers of detectors, false alarms were investigated. Furthermore, causes of their occurrence were investigated for three years (2018-2020). As a result of this investigation, it was found that most of the 34,400 fire alarm detectors in JAEA have been used for more than 20 years. In the last 3 years, 65 false alarms have been reported, 60% of which were found to have been used where the environment should be improved. It was also found that there are many cases where false alarms are reported from a detector within 14 years after installation. Based on the above, three basic policies were formulated. First of all, database will be built for fire alarm maintenance and inspection, secondly, installation location of fire alarm will be improved, and finally, detectors will be updated with reference to the manufacture's plan. According to the three basic policies, it is considered that the reports of false fire alarms will be able to reduced.
 TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloy
TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloyChen, J.*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Shimada, Yusuke*; Inoue, Koji*; Konno, Toyohiko*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.468 - 474, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ electron irradiation using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) was performed to visualize the Frank loop evolution in aluminium-copper (Al-Cu) alloy with an atomic-scale spatial resolution of 0.12 nm. The  HRTEM observation along the [110] direction of the FCC-Al lattice, Frank partial dislocation bounding an intrinsic stacking fault exhibited an asymmetrical climb along the
HRTEM observation along the [110] direction of the FCC-Al lattice, Frank partial dislocation bounding an intrinsic stacking fault exhibited an asymmetrical climb along the  112
112 direction opposed to those in the reference pure Al under an electron irradiation, with a corresponding displacement-per-atom rate of 0.055-0.120 dpa/s. The asymmetrical climb of the partial dislocation was described as pinning effects due to Cu-Cu bonding in Guinier-Preston zones by a molecular dynamics simulation.
direction opposed to those in the reference pure Al under an electron irradiation, with a corresponding displacement-per-atom rate of 0.055-0.120 dpa/s. The asymmetrical climb of the partial dislocation was described as pinning effects due to Cu-Cu bonding in Guinier-Preston zones by a molecular dynamics simulation.
Yoshida, Toshiya; Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Sawa, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(1), p.55 - 66, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)Atmospheric transport, dispersion, and deposition models (ATDMs) can support decision-making during nuclear emergencies; however, uncertainties in the ATDM results need to be carefully evaluated. To investigate the uncertainties derived from meteorological forecast inputs, we conducted three-day forecast simulations every day for one year with hypothetical releases of radionuclides (one-hour releases every 6 h) from a nuclear facility. The forecast outputs were compared with the analysis outputs during the same period. The difference between the outputs is treated as the uncertainty in the forecasts and is represented as an angle based on the discrepancy in the plume directions between the analysis and forecast outputs. Using meteorological inputs made by Japan Meteorological Agency, the discrepancy angle (Ang) increased by approximately 10 per day on an annual average basis. Meanwhile, the Ang values were occasionally 4-5 times higher than the annual average during short time periods. Since the Ang time series show seasonal and diurnal changes, the statistical characteristics likely depend on the geographical and meteorological conditions, as well as the types of meteorological inputs. Additionally, a main factor in the uncertainty is the wind-direction difference between the analysis and forecast outputs on scales of more than or less than 100 km.
per day on an annual average basis. Meanwhile, the Ang values were occasionally 4-5 times higher than the annual average during short time periods. Since the Ang time series show seasonal and diurnal changes, the statistical characteristics likely depend on the geographical and meteorological conditions, as well as the types of meteorological inputs. Additionally, a main factor in the uncertainty is the wind-direction difference between the analysis and forecast outputs on scales of more than or less than 100 km.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.66(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
 layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O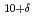 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopyIdeta, Shinichiro*; Johnston, S.*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Mori, Michiyasu; Anzai, Hiroaki*; Ino, Akihiro*; Arita, Masashi*; Namatame, Hirofumi*; Taniguchi, Masaki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.217004_1 - 217004_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.12(Physics, Multidisciplinary) (001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Takayanagi, Shuhei*; Ojima, Shoki*; Maeda, Motoyasu*; Origuchi, Naoki*; Ogawa, Arata*; Ikeda, Natsuki*; Aoyagi, Yoshihide*; Kabutoya, Yuito*; et al.
Langmuir, 37(42), p.12313 - 12317, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.17(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
(001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
Koyama, Shinichi; Nakagiri, Toshio; Osaka, Masahiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Takano, Masahide; et al.
Hairo, Osensui Taisaku jigyo jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 144 Pages, 2021/08
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy and Thermal Behavior Estimation of Fuel Debris))" in 2020JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:96.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
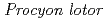 )
)Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iwasaki, Tsugumi*; Murata, Kosuke*; Yamashiro, Hideaki*; Goh, V. S. T.*; Nakayama, Ryo*; Fujishima, Yohei*; Ono, Takumi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; et al.
Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 56(3), p.484 - 497, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:85.28(Agriculture, Dairy & Animal Science)We have established an archive system of livestock and wild animals from the surrounding ex-evacuation zone. Wildlife within the alert zone have been exposed to low-dose-rate (LDR) radiation for a long and continuous time. In this study, we analysed the morphological characteristics of the testes and in vitro fertilization (IVF) capacity of cryopreserved sperm of raccoons from the ex-evacuation zone of the FDNPP accident. This study revealed that the chronic and LDR radiation exposure associated with the FDNPP accident had no adverse effect on the reproductive characteristics and functions of male raccoons.
Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; Minato, Futoshi; Chiba, Satoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(2), p.151 - 165, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:77.77(Nuclear Science & Technology) -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:96.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,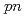 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Yoshida, Yasuhito*; Nakagawa, Ryo*; Yazawa, Shinya*; Kumada, Masashi*; Sato, Daisuke*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Chaumeix, N.*; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 16(2), p.21-00044_1 - 21-00044_13, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.36(Thermodynamics)The effects of addition of CO and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO
and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co
addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co or H
or H O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
 WB-STEM observation of dislocation loop behavior in reactor pressure vessel steel during post-irradiation annealing
WB-STEM observation of dislocation loop behavior in reactor pressure vessel steel during post-irradiation annealingDu, Y.*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Milan, K. J.*; Gerard, R.*; Onuki, Somei*; et al.
Materialia, 12, p.100778_1 - 100778_10, 2020/08
In order to ensure the integrity of the reactor pressure vessel in the long term, it is necessary to understand the effects of irradiation on the materials. In this study, irradiation-induced dislocation loops were observed in neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel specimens during annealing using our newly developed WB-STEM. It was confirmed that the proportion of 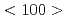 loops increased with increasing annealing temperature. We also succeeded in observing the phenomenon that two
loops increased with increasing annealing temperature. We also succeeded in observing the phenomenon that two 
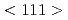 loops collide into a
loops collide into a 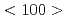 loop. Moreover, a phenomenon in which dislocation loops decorate dislocations was also observed, and the mechanism was successfully explained by molecular dynamics simulation.
loop. Moreover, a phenomenon in which dislocation loops decorate dislocations was also observed, and the mechanism was successfully explained by molecular dynamics simulation.