Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Seiichi*; Ando, Tatsuhiko*; Watanabe, Aya*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 79, 2015/03
So far, we clarified that X-ray irradiation induced cell killing by bystander effect mediated-secreted factor. This phenomenon was related with sphingomyelinase (SMase). In this study we analyzed mechanism of secreted SMase from irradiated cells after irradiation. SMase was detected in the culture medium after irradiation by SDS-PAGE. Then, SMase was detected in the exosome of culture medium, but not out of exosome after irradiation. This result indicates that SMase was secreted as exosome from the irradiated cells.

Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.21 - 25, 2012/10
High linear energy transfer (LET) radiation is important cosmic rays that has neurobiological effects: it is known to induce conditioned taste aversion, and suppress neurogenesis that may underlie cognitive impairment. However, the impact of high-LET radiation on other learning effects remains largely unknown. Here, we focus on kinetics of the radiation response for the salt chemotaxis learning (SCL) behavior in the nameatode,  , because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET
, because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET  -irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation (
-irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of
m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of 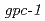 mutant showed that the G-protein
mutant showed that the G-protein  subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C.
subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C. 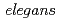 .
.
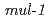 , induced by ionizing radiation in
, induced by ionizing radiation in 
Kimura, Takafumi*; Takanami, Takako*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Higashitani, Atsushi*
Radiation Research, 178(4), p.313 - 320, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:41.71(Biology)Here, we found that exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) induce certain innate immune response gene of 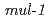 in the intestine. Pre-treatment with IR before seeding on
in the intestine. Pre-treatment with IR before seeding on 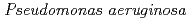 lawn plate, significantly increased survival rate in the nematode. IR induction of
lawn plate, significantly increased survival rate in the nematode. IR induction of 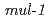 gene was highly dependent on the ELT-2 transcription factor and p38 MAPK. Moreover, the insulin/IGF-1 signal pathway works as an enhancer of induction of this gene. Silencing of the
gene was highly dependent on the ELT-2 transcription factor and p38 MAPK. Moreover, the insulin/IGF-1 signal pathway works as an enhancer of induction of this gene. Silencing of the 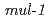 gene led to growth retardation after IR irradiation. Finally, we describe the cross-tolerance between the responses to radiation exposure and innate immune system.
gene led to growth retardation after IR irradiation. Finally, we describe the cross-tolerance between the responses to radiation exposure and innate immune system.
 against high-LET radiation exposure
against high-LET radiation exposureSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.7 - 11, 2012/07
Here, we investigated the resistance to high-LET radiation exposure for two behaviors of the nematode,  , which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation (
, which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of
m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of  is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
 to extreme environments
to extreme environmentsHorikawa, Daiki*; Yamaguchi, Ayami*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Tanaka, Daisuke*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yukuhiro, Fumiko*; Kuwahara, Hirokazu*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; et al.
Astrobiology, 12(4), p.283 - 289, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.44(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We examined the hatchability of hydrated and anhydrobiotic eggs of the tardigrade  to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
Watanabe, Ritsuko; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Saito, Kimiaki; Furusawa, Yoshiya*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.186 - 190, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:75.56(Environmental Sciences)Microscopic energy deposition pattern in an ion track is thought to affect on the spatial distribution of DNA damage as well as the damage spectrum. In this study, we focus on the intra-track spatial distribution of DNA damage in cellular condition based on the energy deposition pattern for each ion obtained by the detailed Monte Carlo track structure simulation. The estimation was performed for C and Ne ions with similar LET around 440 keV/ m. As a result, radial DNA damage distribution shows different pattern for C and Ne ions. That is, DSBs or non-DSB type clustered damage are formed in the limited central area while the isolated damages as SSBs and base lesions are spread in larger area. Such tendency is more clearly shown for Ne ions than C ions. This result shows good agreement with the previously obtained experimental observation at TIARA, which indicates the different types of DNA damage shows different distribution pattern around C and Ne projectiles in cell nuclei.
m. As a result, radial DNA damage distribution shows different pattern for C and Ne ions. That is, DSBs or non-DSB type clustered damage are formed in the limited central area while the isolated damages as SSBs and base lesions are spread in larger area. Such tendency is more clearly shown for Ne ions than C ions. This result shows good agreement with the previously obtained experimental observation at TIARA, which indicates the different types of DNA damage shows different distribution pattern around C and Ne projectiles in cell nuclei.
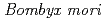 , induces the somatic mutation
, induces the somatic mutationFurusawa, Toshiharu*; Fukamoto, Kana*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Eiko*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(4), p.371 - 375, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:31.97(Biology)Using heavy-ion microbeam, we report target irradiation of selected compartments within the diapause-terminated egg and its mutational consequences in the silkworm, 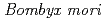 . On one hand, carbon-ion exposure of embryo to 0.5 - 6 Gy increased the somatic mutation frequency, suggesting targeted radiation effects. On the other, such increases were not observed when yolk was targeted, suggesting a lack of nontargeted bystander effect.
. On one hand, carbon-ion exposure of embryo to 0.5 - 6 Gy increased the somatic mutation frequency, suggesting targeted radiation effects. On the other, such increases were not observed when yolk was targeted, suggesting a lack of nontargeted bystander effect.
 -irradiated tobacco cultured cells
-irradiated tobacco cultured cellsYokota, Yuichiro; Wada, Seiichi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(2), p.171 - 175, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.46(Biology)The rejoining efficiency of double-strand breaks (DSBs) was quantified in tobacco protoplasts and CHO-K1 cells following  -ray irradiation in order to compare DNA reparability of higher plants with mammals. The DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts were well represented by a biphasic-exponential equation: half of initial-induced DSBs were rejoined for 1 h and the others were almost rejoined within 4 h. We found that the DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts at 27
-ray irradiation in order to compare DNA reparability of higher plants with mammals. The DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts were well represented by a biphasic-exponential equation: half of initial-induced DSBs were rejoined for 1 h and the others were almost rejoined within 4 h. We found that the DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts at 27 C are the same as those of CHO-K1 cells at 37
C are the same as those of CHO-K1 cells at 37 C. These findings indicate that the DSB rejoining efficiency of tobacco protoplasts and CHO-K1 cells are comparable at their respective cell cultivation temperatures, suggesting that DSB rejoining efficiency is little responsible for the higher radiation-tolerance of tobacco protoplasts.
C. These findings indicate that the DSB rejoining efficiency of tobacco protoplasts and CHO-K1 cells are comparable at their respective cell cultivation temperatures, suggesting that DSB rejoining efficiency is little responsible for the higher radiation-tolerance of tobacco protoplasts.

Miyazawa, Yutaka*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Morohashi, Keita*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 49(4), p.373 - 379, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:64.75(Biology)We examined the role of root cap and elongation zone cells in root hydrotropism using heavy-ion and laser microbeam. Heavy-ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporary suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy-ion broad-beam irradiation suppressed 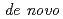 expression of
expression of 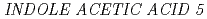 gene, but not
gene, but not 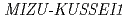 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that
gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that 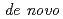 gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
 ; A New model animal for astrobiology
; A New model animal for astrobiologyHorikawa, Daiki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Abe, Wataru*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Yukuhiro, Fumiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Astrobiology, 8(3), p.549 - 556, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:91.30(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report the successful rearing of the herbivorous tardigrade,  , by supplying the green alga
, by supplying the green alga 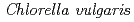 as food. The life span was 35 d, deposited eggs required 5.7 d to hatch, and animals began to deposit eggs 9 d after hatching. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle in egg, juvenile, and adult stages. Furthermore, the reared adults in an anhydrobiotic state were tolerant of temperatures of 90
as food. The life span was 35 d, deposited eggs required 5.7 d to hatch, and animals began to deposit eggs 9 d after hatching. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle in egg, juvenile, and adult stages. Furthermore, the reared adults in an anhydrobiotic state were tolerant of temperatures of 90 C and -196
C and -196 C and exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile or irradiation with 4000 Gy
C and exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile or irradiation with 4000 Gy  He ions. Based on their life history traits and tolerance to extreme stresses,
He ions. Based on their life history traits and tolerance to extreme stresses, 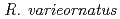 might be a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
might be a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
 to high-LET carbon ion beam irradiation
to high-LET carbon ion beam irradiationSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 111, 2008/03
We investigated the high LET carbon ions induced response of salt chamotaxis learning in  . The performance of the salt chemotaxis learning was normal even after the exposure at the dose of 100 - 500 Gy. Also, the normal chemotaxis to benzaldehyde was normal, whereas the salt chemotaxis learning was affected by carbon irradiation. These results suggest the specific effect of carbon ions on the neuron network in
. The performance of the salt chemotaxis learning was normal even after the exposure at the dose of 100 - 500 Gy. Also, the normal chemotaxis to benzaldehyde was normal, whereas the salt chemotaxis learning was affected by carbon irradiation. These results suggest the specific effect of carbon ions on the neuron network in  .
.
 -rays and heavy-ion beam in
-rays and heavy-ion beam in 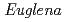
Bolige, A.*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Goto, Ken*
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 117, 2008/03
We report here how these rhythms are related to each other. First, irradiation temperatures influenced neither survival after exposure to UV,  rays, nor C ions, whereas the incubation at high temperatures (25
rays, nor C ions, whereas the incubation at high temperatures (25  C) after irradiation considerably lowered the survival particularly after
C) after irradiation considerably lowered the survival particularly after  irradiation, but not after UV irradiation at all. Secondly, although the antioxidants
irradiation, but not after UV irradiation at all. Secondly, although the antioxidants  carotene and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) increased the survival of the alga at the least resistant phase after UV C and UV B irradiation, respectively, to the level of the most resistant alga, none of these were not so effective for
carotene and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) increased the survival of the alga at the least resistant phase after UV C and UV B irradiation, respectively, to the level of the most resistant alga, none of these were not so effective for  or C ion irradiation. Finally, FITC dextran was incorporated into the alga only after C ion irradiation but not
or C ion irradiation. Finally, FITC dextran was incorporated into the alga only after C ion irradiation but not  irradiation, suggesting that C ion may perforate cell membranes to kill the alga.
irradiation, suggesting that C ion may perforate cell membranes to kill the alga.
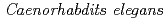
Higashitani, Atsushi*; Mori, Chihiro*; Kimura, Takafumi*; Ikenaga, Takahiko*; Takanami, Takako*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 112, 2008/03
We investigated the gene expression of  following carbon and
following carbon and  irradiation using DNA microarray analysis. We observed the 187 and 297 upregulated genes after
irradiation using DNA microarray analysis. We observed the 187 and 297 upregulated genes after  and carbon irradiation with 100 Gy, respectively, in which 51 genes were upregulated following both irradiations. On the other hand, the 358 and 388 genes were downregulated after
and carbon irradiation with 100 Gy, respectively, in which 51 genes were upregulated following both irradiations. On the other hand, the 358 and 388 genes were downregulated after  and carbon irradiation, respectively.
and carbon irradiation, respectively.
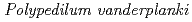
Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Fujita, Akihiko*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Okuda, Takashi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 113, 2008/03
We have shown that anhydrobiotic larvae of 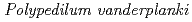 have higher tolerance against both high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation than hydrated larvae. We therefore examined effects of high-LET radiation on four kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae.
have higher tolerance against both high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation than hydrated larvae. We therefore examined effects of high-LET radiation on four kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae.
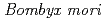
Furusawa, Toshiharu*; Suzuki, Eiko*; Nagaoka, Shunji*; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 115, 2008/03
Using heavy ion microbeam, we investigated the somatic mutation arising on the larvae in embyro and yolk in the egg of silkworm, 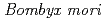 . The incidence of the somatic mutation was 12%, and the same level of mutation following the microbeam irradiation at the center of the egg. However, the microbeam irradiation to the abdomen of the silkworm larvae induced the increase of somatic mutation, 63% (3 Gy) and 80% (6 Gy).
. The incidence of the somatic mutation was 12%, and the same level of mutation following the microbeam irradiation at the center of the egg. However, the microbeam irradiation to the abdomen of the silkworm larvae induced the increase of somatic mutation, 63% (3 Gy) and 80% (6 Gy).
 using heavy-ion microbeam
using heavy-ion microbeamMiyazawa, Yutaka*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Morohashi, Keita*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 116, 2008/03
We examined the role of root cap and elongation zone cells in root hydrotropism of  using heavy ion and laser microbeam. Heavy ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporarily suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy ion broad beam irradiation suppressed de novo expression of INDOLE ACETIC ACID 5 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that de novo gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
using heavy ion and laser microbeam. Heavy ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporarily suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy ion broad beam irradiation suppressed de novo expression of INDOLE ACETIC ACID 5 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that de novo gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
 /M phase after
/M phase after  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationYokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Inoue, Masayoshi*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 69, 2008/03
no abstracts in English
 to
to  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Fukamoto, Kana; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Horikawa, Daiki*; Bolige, A.*
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 110, 2008/03
We investigated the effects of  rays on the salt chemotaxis learning in
rays on the salt chemotaxis learning in  . We observed no decrease of performance of the salt chemotaxis learning following 500 Gy
. We observed no decrease of performance of the salt chemotaxis learning following 500 Gy  irradiation. Also,
irradiation. Also,  showed the normal chemotaxis to benzaldehyde, whereas the salt chemotaxis learning were affected by irradiation during learning.
showed the normal chemotaxis to benzaldehyde, whereas the salt chemotaxis learning were affected by irradiation during learning.
 He
He ion irradiation
ion irradiationUrushibara, Ayumi*; Shikazono, Naoya; O'Neill, P.*; Fujii, Kentaro; Wada, Seiichi*; Yokoya, Akinari
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 84(1), p.23 - 33, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:91.12(Biology)To characterize the complexity of radiation damage to DNA, fully hydrated plasmid DNA was irradiated with  He
He ions. From quantification of the conformational changes of the irradiated samples, the yields of single-(SSB) and double strand break (DSB) were obtained. Base lesions were visualized as additional strand breaks by treatment with base excision repair enzymes. The yield of prompt SSBs does not depend significantly on LET of the
ions. From quantification of the conformational changes of the irradiated samples, the yields of single-(SSB) and double strand break (DSB) were obtained. Base lesions were visualized as additional strand breaks by treatment with base excision repair enzymes. The yield of prompt SSBs does not depend significantly on LET of the  He
He ions, whereas the yield of prompt DSBs increases with increasing LET. The yields of isolated base lesions, revealed by enzymes as additional SSBs, decrease drastically with increasing LET. The sum of the yields of DSB and additional DSBs revealed by the enzymes increase with increasing LET of the
ions, whereas the yield of prompt DSBs increases with increasing LET. The yields of isolated base lesions, revealed by enzymes as additional SSBs, decrease drastically with increasing LET. The sum of the yields of DSB and additional DSBs revealed by the enzymes increase with increasing LET of the  He
He ions except at the highest LET investigated. These results indicate that the yields of clustered damage, revealed as DSB and non-DSB clustered damage sites, increase with increasing ionization density of radiation.
ions except at the highest LET investigated. These results indicate that the yields of clustered damage, revealed as DSB and non-DSB clustered damage sites, increase with increasing ionization density of radiation.
Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Fukamoto, Kana; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 49(1), p.71 - 82, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:78.54(Biology)Research concerning cellular responses to low dose irradiation, radiation-induced bystander effects, and the biological track structure of charged particles has recently received particular attention in the field of radiation biology. Target irradiation employing a microbeam represents a useful means of advancing this research by obviating some of the disadvantages associated with the conventional irradiation strategies. The heavy-ion microbeam system at JAEA-Takasaki can provide target irradiation of heavy charged particles to biological material at atmospheric pressure using a minimum beam size 5  m in diameter. The system can be applied to the investigation of mechanisms within biological organisms not only in the context of radiation biology, but also in the fields of general biology such as physiology, developmental biology and neurobiology, and should help to establish and contribute to the field of "microbeam biology".
m in diameter. The system can be applied to the investigation of mechanisms within biological organisms not only in the context of radiation biology, but also in the fields of general biology such as physiology, developmental biology and neurobiology, and should help to establish and contribute to the field of "microbeam biology".