Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kameo, Yutaka; Sato, Soichi; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Nagai, Takayuki; Niibori, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; et al.
Introduction to Dismantling and Decommissioning Chemistry, 251 Pages, 2024/09
This book focuses on the dismantling and decommissioning of nuclear facilities and reactors that have suffered severe accidents. In Part 1, we introduce basic aspects ranging from fuel chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiation chemistry, corrosion, and decontamination chemistry to waste treatment and disposal. Then, Part 2 covers the chemistry involved in the decommissioning of various nuclear facilities, and discusses what chemical approaches are necessary and possible for the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, how decommissioning should be carried out, and what kind of research and development and also human resource development are required for this.
Furuno, Akiko; Omori, Ryuta*; Tateoka, Hisanori*; Minakawa, Yuya*; Kurihara, Toshiyuki; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Tomita, Yutaka
Pure and Applied Geophysics, 14 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) Okinawa radionuclide monitoring station (JPP37) is located on a hill facing the East China Sea at the center of the main island of Okinawa. It occasionally detects Cs-137, although no nuclear facilities are located on the island. This study focused on the detection of Cs-137 at JPP37 and examined the ratio of simultaneous detections at nearby stations of the International Monitoring System (IMS) of the CTBTO and the relationship with Asian dust from inland East Asia. The detection of Cs-137 in JPP37 from 2020 to 2023, which motivated this study, was high in spring. Among the nine IMS radionuclide stations in East Asia, the detections in Beijing, Lanzhou, and Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, were also high in spring. This suggested a high association with the detection of Asian dust in East Asia. Thus, we confirmed the detection of Cs-137 at nine nearby IMS stations when Asian dust was observed at any of the sites in Japan. In addition, we observed that the detection rates were high in Takasaki, Beijing, Lanzhou, and Ulaanbaatar. It can be inferred that the Cs-137 observed mainly in spring at the IMS particulate radionuclide stations in the East Asian region around Japan were likely to pick up the effects of global fallout conveyed by Asian dust. Thereafter, we conducted a preliminary source estimation analysis for Asian dust arrival near Japan. Atmospheric dispersion simulations explained the detection of Cs-137 at nearby IMS particulate radionuclide stations, assuming that Cs-137 was emitted from the desert, the source of the Asian dust.
Nagata, Shuhei*; Ogawa, Yusuke*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Mitsui, Seiichiro
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.21 - 22, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:187 Percentile:99.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology)Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:87.69(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.58(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Iguchi, Masahide; Morimoto, Masaaki; Chida, Yutaka*; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Nakajima, Hideo; Nakahira, Masataka; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Yamamoto, Akio*; Miyake, Takashi*; Sawa, Naoki*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 24(3), p.3801004_1 - 3801004_4, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.10(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Tokuhisa, Atsushi*; Arai, Junya*; Jochi, Yasumasa*; Ono, Yoshiyuki*; Kameyama, Toyohisa*; Yamamoto, Keiji*; Hatanaka, Masayuki*; Gerofi, B.*; Shimada, Akio*; Kurokawa, Motoyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.899 - 904, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:28.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nakanishi, Chika; Sato, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kakefuda, Toyokazu; Katata, Genki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Ikeda, Takeshi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2013-030, 105 Pages, 2013/10
North Korea carried out the third nuclear test in February 2013. Due to the request of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) and Nuclear Science and Engineering Directorate (NSED) of JAEA predicted the atmospheric dispersion of radionuclide by WSPEEDI-II for the purpose of contributing to the environmental monitoring plan. From February 12 to 22, they provided daily reports on the prediction to the MEXT and the Ministry of Defense. MEXT has published these reports on the website. Since April 2012, NEAT and NSED had prepared to predict by the framework for the prediction around the clock during 10months until February 2013. This report described this experience and pointed issues out on this system.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sakoda, Akihiro*; Yoshimoto, Masaaki*; Toyota, Teruaki*; Yamamoto, Yuki*; Ishimori, Yuu; Hanamoto, Katsumi*; Kawabe, Atsushi*; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Radiation Safety Management, 10(1), p.1 - 7, 2011/12
We examined the effect of continuous radon inhalation on acute alcohol-induced oxidative damage of mouse liver and brain. Assay of antioxidative functions indicated that lipid peroxide levels in both the liver and brain of the alcohol-treated mice were significantly higher than those of the saline-treated mice. However, the lipid peroxide level in the liver, but not in the brain, of alcohol-treated mice was significantly decreased by radon inhalation whereas that in the brain of saline-treated mice, but not in the liver of saline-treated mice, was significantly increased by radon inhalation. These findings suggest that radon inhalation inhibits alcohol-induced oxidative damage of liver due to activation of antioxidative functions and that radon inhalation exert only a week effect on the brains in comparing with the livers. They further suggest that alcohol administration protects against oxidative damage of the brain that is induced by radon inhalation.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kojima, Atsushi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Hemsworth, R. S.*; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tanaka, Masanobu*; Tanaka, Yutaka*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
At JAEA, a multi-aperture multi-grid accelerator has been developed for the ITER neutral beam system. A target is H ion beam acceleration of 0.5 A (200 A/m
ion beam acceleration of 0.5 A (200 A/m ) at 1 MeV. In real accelerators, it was found that the voltage holding was about a half of that obtained in an ideal small electrode. After applying necessary gap length and radii of edges of grid supports to lower local electric field concentrations, the accelerator succeeded in sustaining 1 MV for 4000 s. As a result, beam parameters were increased to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m
) at 1 MeV. In real accelerators, it was found that the voltage holding was about a half of that obtained in an ideal small electrode. After applying necessary gap length and radii of edges of grid supports to lower local electric field concentrations, the accelerator succeeded in sustaining 1 MV for 4000 s. As a result, beam parameters were increased to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m ) at perveance matched condition from 796 kV, 0.32 A (140 A/m
) at perveance matched condition from 796 kV, 0.32 A (140 A/m ) reported in FEC2008. In the beam acceleration, the beamlet deflections due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion caused direct interceptions, that resulted in limitations in the beam energy and current. Compensation of these beamlet deflections has been tested applying aperture offset and field shaping plate, which were examined in a three-dimensional beam analysis.
) reported in FEC2008. In the beam acceleration, the beamlet deflections due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion caused direct interceptions, that resulted in limitations in the beam energy and current. Compensation of these beamlet deflections has been tested applying aperture offset and field shaping plate, which were examined in a three-dimensional beam analysis.
 Si
Si
Matsuda, Tatsuma; Dung, N. D.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeda, Shugo*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Ishikura, Tatsuro*; Endo, Toyoaki*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Physica Status Solidi (B), 247(3), p.757 - 759, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.28(Physics, Condensed Matter)We succeeded in growing high-quality single crystals of a heavy electron compound YbCu Si
Si . The electronic specific heat coefficient
. The electronic specific heat coefficient  is determined to be 150 mJ/K
is determined to be 150 mJ/K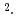 mol, which is consistent with the
mol, which is consistent with the  value of the electrical resistivity from Kadowaki-Woods relation. We succeeded in observing the de Haas-van Alphen (dHvA) oscillations. The dHvA frequencies and large cyclotron effective masses in YbCu
value of the electrical resistivity from Kadowaki-Woods relation. We succeeded in observing the de Haas-van Alphen (dHvA) oscillations. The dHvA frequencies and large cyclotron effective masses in YbCu Si
Si are highly different from those in a non-4
are highly different from those in a non-4 reference compound YCu
reference compound YCu Si
Si . From these dHvA results, the heavy electron state of YbCu
. From these dHvA results, the heavy electron state of YbCu Si
Si is characterized by the large contribution of 4
is characterized by the large contribution of 4 -electrons to the volume of the Fermi surface and also to the strong enhancement of effective mass caused by the spin fluctuations.
-electrons to the volume of the Fermi surface and also to the strong enhancement of effective mass caused by the spin fluctuations.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*
JAEA-Research 2009-050, 57 Pages, 2010/01
It is important to understand EDZ in assessing performance of repository and designing of plug. It is known that it remains possible that the large-scale EDZ is generated due to strain localization from boring investigations and tunnel excavation analyses and rock properties changes with increase of depth. Excavation analysis of vertical shaft in sedimentary rock taken into account strain softening, depth variation of rock properties and the actual construction procedure had been done in order to understand EDZ of Horonobe URL. The large-scale EDZ due to strain localization was generated around the border between Koetoi formation and Wakkanai formation. From result obtained from excavation analysis, scale of EDZ obtained from excavation analysis is from 60 cm to 120 cm. And it was estimated that seismic velocity changed by 20 percent, elastic modulus changed by 30 percent and hydraulic conductivity changed by 0.1 m/s order.
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya
Dai-12-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.933 - 940, 2008/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is planning to conduct researches into geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes in the Horonobe site located in Hokkaido, Japan. As part of the underground research facilities, two 500m-long vertical shafts have been constructed in tertiary sedimentary rocks since 2005. The surrounding rocks are known to exhibit strain-softening characteristics, necessitating appropriate modelling in the stability analysis. In addition the rocks physical properties often vary with depth. This study shows the results of three-dimensional numerical analysis of the ventilation shaft, taking the construction sequence and the variation of rock properties with depth into consideration.
 Si
Si
Nguyen, D.; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Ikeda, Shugo*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeda, Yuji*; Endo, Toyoaki*; Doi, Yusuke*; Settai, Rikio*; Harima, Hisatomo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(9), p.094702_1 - 094702_6, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:63.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have succeeded in growing a high-quality single crystal of a non-4 reference compound YCu
reference compound YCu Si
Si for a heavy-fermion superconductor CeCu
for a heavy-fermion superconductor CeCu Si
Si , and observed the de Haas-van Alphen (dHvA) oscillation. The detected dHvA branches in YCu
, and observed the de Haas-van Alphen (dHvA) oscillation. The detected dHvA branches in YCu Si
Si indicate that the Fermi surfaces are multiply connected, and the dHvA frequencies are in the range from 9
indicate that the Fermi surfaces are multiply connected, and the dHvA frequencies are in the range from 9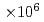 to 2
to 2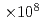 Oe. These dHvA branches are found to be well explained by the results of energy band calculations. The corresponding cyclotron masses are light, ranging from 0.4 to 1.5
Oe. These dHvA branches are found to be well explained by the results of energy band calculations. The corresponding cyclotron masses are light, ranging from 0.4 to 1.5 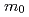 , and are consistent with the electronic specific heat coefficient of 2.2 mJ/K
, and are consistent with the electronic specific heat coefficient of 2.2 mJ/K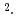 mol.
mol.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.