Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kamikawa, Yutaka; Suzuki, Makoto; Agake, Toshiki; Murakami, Takahiko; Morita, Yusuke; Shiina, Hidenori; Fukushima, Manabu; Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ouchi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-030, 57 Pages, 2024/03
Owing to the publication of the latest data about aircraft crashes by Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), it was necessary to re-evaluate the probabilities of aircraft crashes for Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI). By using of the assessment method provided in "Regulatory Guide of the Assessment Standard for Probability of Airplane Crash on a Nuclear Power Reactor Facility", we re-evaluated the probabilities of aircraft crashes against the nuclear facilities in NSRI. As a result of the evaluations, the sum of the probabilities of aircraft crashes against Waste Treatment Facilities (maximum probability among all nuclear facilities in NSRI) is 5.68 10
10 (times/(reactor
(times/(reactor  year)) which is lower than 10
year)) which is lower than 10 (times/(reactor
(times/(reactor  year)) that is the assessment criterion whether aircraft crashes is considered to be "anticipated external human induced events" in design basis or not.
year)) that is the assessment criterion whether aircraft crashes is considered to be "anticipated external human induced events" in design basis or not.
 -methyltransferase involved in flower coloration
-methyltransferase involved in flower colorationAkita, Yusuke; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; et al.
Planta, 234(6), p.1127 - 1136, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:75.6(Plant Sciences) spp., generated by ion-beam irraidation
spp., generated by ion-beam irraidationKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 65, 2011/01
no abstracts in English
 spp., generated by ion-beam irradiation
spp., generated by ion-beam irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
Plant Biotechnology, 26(5), p.565 - 569, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:66.54(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Fragrant cyclamen cultivar (

 ), that bloomed purple flower containing malvidin 3,5-diglucoside as the major anthocyanin, was irradiated with a 320-MeV carbon-ion beam at 0-16 Gy to increase flower color variation by mutation. Some of the M2 plants derived from self-pollination of M1 plants irradiated at 2 Gy were flower-color mutants that retained desirable flower shape, flower size, and leaf color. One of the mutants bloomed novel red-purple flowers, the major anthocyanin of which was delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside. Because the major anthocyanins in flowers of
), that bloomed purple flower containing malvidin 3,5-diglucoside as the major anthocyanin, was irradiated with a 320-MeV carbon-ion beam at 0-16 Gy to increase flower color variation by mutation. Some of the M2 plants derived from self-pollination of M1 plants irradiated at 2 Gy were flower-color mutants that retained desirable flower shape, flower size, and leaf color. One of the mutants bloomed novel red-purple flowers, the major anthocyanin of which was delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside. Because the major anthocyanins in flowers of  spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.
spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.
 x
x  ) by ion beam re-irradiation
) by ion beam re-irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
One of the fragrant cyclamens, Kaori-no-mai, blooms purple flowers containing malvidin 3,5-diglucoside as the major anthocyanin. Here, we irradiated etiolated petioles of Kaori-no-mai with a 320-MeV carbon-ion beam to increase flower color variation by mutation. Some of the M2 plants derived from self-pollination of M1 plants were flower-color mutan. One of the mutants bloomed novel red-purple flowers, the major anthocyanin of which was delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside. The major anthocyanins in flowers of  spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, therefore, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.
spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, therefore, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.
Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Akita, Yusuke; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

 )
)Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

 )
)Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

 )
)Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
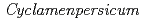

 ) by ion beam irradiation
) by ion beam irradiationKameari, Naoko*; Okubo, Naomi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
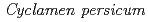

 ) by ion beam re-irradiation
) by ion beam re-irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
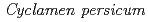

 ) by ion beam irradiation
) by ion beam irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akita, Yusuke; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
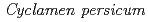

 ) by ion-beam irradiation and analysis of their flower pigments
) by ion-beam irradiation and analysis of their flower pigmentsKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 "Golden Boy"
"Golden Boy" 
 ) by ion-beam irradiation
) by ion-beam irradiationKameari, Naoko*; Akita, Yusuke; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Tanaka, Atsushi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Usui, Yoshiya*; Ueshima, Makoto*; Hase, Hideaki*; Ichihara, Hiroshi*; Aizawa, Koki*; Koyama, Takao*; Sakanaka, Shinya*; Ogawa, Tsutomu*; Yamaya, Yusuke*; Nishitani, Tadashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
In the back-arc area of the southern Tohoku region, there are several quaternary volcanos and active faults that have the potential to cause M7-class inland earthquakes. In the vicinity of some of the volcanoes, deep low-frequency earthquakes occur, implying the transfer of melt or aqueous fluid. So as to reveal the magma supply system around the area, it is important to reveal the distribution of the subsurface fluid. Also, understanding the fluid distribution helps elucidate the earthquake generation process. To delineate the subsurface electrical resistivity structure, the authors estimated the resistivity structure in the area by performing magnetotelluric surveys and generating the 3-D resistivity structure model with high resolution. In this study, the authors show the resultant electrical resistivity structure and discuss the subsurface fluid distribution as well as its relationship with the volcanic and seismic activities around the study area.