Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Shibata, Motoki*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*
Soft Matter, 19(11), p.2082 - 2089, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Arima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Shibata, Motoki*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; et al.
Langmuir, 38(41), p.12457 - 12465, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) structural analysis of an aligning agent additive for the alignment of nematic liquid crystals on solid substrates
structural analysis of an aligning agent additive for the alignment of nematic liquid crystals on solid substratesNemoto, Fumiya*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Hino, Masahiro*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Seto, Hideki*
Soft Matter, 18(3), p.545 - 553, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1039 - 1054, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been performed in simulated Boiling Water Reactor water conditions at  288
288 C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at
C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at  12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at
12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at 
 2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Seto, Yusuke*; Nagai, Takaya*; Utsumi, Wataru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 780, p.55 - 67, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:98.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)PLANET is a time-of-flight (ToF) neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature experiments. The large six-axis multi-anvil high-pressure press designed for ToF neutron diffraction experiments enables routine data collection at high pressures and high temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000 K, respectively. To obtain clean data, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators to eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell assembly. The high performance of the diffractometer for the resolution (
 /
/
 0.6%) and the accessible
0.6%) and the accessible  -spacing range (0.2-8.4
-spacing range (0.2-8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.

Matsuoka, Takahiro*; Fujihisa, Hiroshi*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Mitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo; Seto, Makoto*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Machida, Akihiko; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 107(2), p.025501_1 - 025501_4, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:77.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Europium-hydride EuH exposed to high-pressure H
exposed to high-pressure H conditions has been found to exhibit structural and valence changes,
conditions has been found to exhibit structural and valence changes, 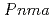 (
( =2, divalent)
=2, divalent) 
 63/
63/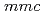 (
( =2, 7.2-8.7 GPa)
=2, 7.2-8.7 GPa) 
 4/
4/ (
(
 2, 8.7-9.7 GPa)
2, 8.7-9.7 GPa) 
 4/
4/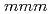 (
(
 2, 9.7 GPa-, trivalent). Having trivalent character and distorted cubic fcc structure, the
2, 9.7 GPa-, trivalent). Having trivalent character and distorted cubic fcc structure, the  4/
4/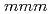 structure is the
structure is the  -phase which has been commonly observed for other rare-earth metal hydrides. Our study clearly demonstrates that EuH
-phase which has been commonly observed for other rare-earth metal hydrides. Our study clearly demonstrates that EuH is no longer an "irregular" member of the rare earth metal hydrides.
is no longer an "irregular" member of the rare earth metal hydrides.
Oka, Toshitaka; Oshima, Akihiro*; Motohashi, Ryota*; Seto, Naoto*; Watanabe, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Ryoji*; Saito, Koki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Washio, Masakazu*; et al.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 80(2), p.278 - 280, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.75(Chemistry, Physical)The chemical structures of various ion-beam irradiated isotactic-polypropylene samples were studied. Results of micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy suggest not only the linear energy transfer, but also the fluence is effective in local transformation of the isotactic-polypropylene.
Yasuo, Kiyoshi; Seto, Nobuhiko; Watahiki, Seiichi; Fukuari, Yoshihiro
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-5-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.385 - 387, 2008/07
The nitric acid solution including nuclear fuel material is transferred by the three way valve called VCV (VCV: vide-casse-vide in Fr.) using vacuum in the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. The reliability of initial three way valve was not obtained because failure occurred by use for one or two years. The cause of failure was damage of the plastic diaphragms in the moving parts. Then, the new three way valve with stainless-steel bellows was developed. there is no failure in moving parts, reliability improved significantly.
Yamada, Toshiro*; Morikawa, Hiroshi*; Ishida, Masatoshi*; Seto, Yutaka*; Yamamoto, Yoshifumi*; Sawamoto, Yoshikazu*
JNC TJ8410 98-002, 124 Pages, 1998/11
On the 11st of March 1997, a fire and explosion occurred in a Bituminization Demonstraion Facility. It subsequently became necessary to estimate the explosive force of this event. To this end, this report evaluates the static yield and ultimate strength of the main structural walls and floors of this facility. A simple method and a Finite Element Method (FEM) were considered to evaluate the yield and ultimate strength of reinforced concrete (RC) slabs. Using the simple method, the yield strength can be estimated effectively by solution of fundamental differential equations. The ultimate strength of RC slabs is tried to estimate using a modified yield line theory which is taken an arch effect created within RC slabs into account. However, this method is difficult to apply to slabs with complicated boundary conditions. In this case, FEM is necessary. The validity of the simple method is verified by analyzing some slabs using both methods and comparing the results. Previous experimental results and some RC slabs in the Asphalt Bituminization Facility were evaluated on the basis of yield and ultimate strength using both methods, and the validity of both methods were verified. Especially, in simulating previous experiments, the error in the estimated values of the ultimate strength using simple method to experimental values were within 30%. The estimated values of the ultimate strength using the FEM were 15% larger than the experimental values. As a result, the simple method taking arch effect into account was verified to some extent.
Oka, Toshitaka; Oshima, Akihiro*; Motohashi, Ryota*; Seto, Naoto*; Watanabe, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Ryoji*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Washio, Masakazu*; Hama, Yoshimasa*
no journal, ,
Domura, Kazuyuki; Morimoto, Kenji; Seto, Nobuhiko; Iwasaki, Shogo; Fukuari, Yoshihiro; Inami, Shinichi
no journal, ,
A leak occurred from the sea release pipe buried in the bottom of the sea of the Tokai reprocessing plant. The plumbing of the leak point was cut to investigate the cause of the leak and was collected ashore. Then the investigations such as surface observation and other analyses were performed. As a result of this investigation, the plumbing was scratched at the time of construction from the outside. In the service of approximately 17 years, a damaged part changed with age, and it was estimated that it led to a crack. It was estimated for the leak of the plumbing that hydrogen produced with electrolytic protection caused hydrogen embrittlement cracking and hydrogen induced cracking. This paper reports the details of the investigations.

Matsuoka, Takehiro*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Fujihisa, Hiroshi*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Mitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo; Machida, Akihiko; Aoki, Katsutoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Europium-hydride EuH exposed to high-pressure H
exposed to high-pressure H conditions has been studied by X-ray diffraction and M
conditions has been studied by X-ray diffraction and M ssbauer spectroscopy measurements up to 50 GPa using synchrotron radiation. We report new structural and valence transitions, Pnma(x=2, divalent)
ssbauer spectroscopy measurements up to 50 GPa using synchrotron radiation. We report new structural and valence transitions, Pnma(x=2, divalent)  P63/mmc(x=2, 7.2-8.7GPa)
P63/mmc(x=2, 7.2-8.7GPa)  I4/m(x
I4/m(x 2, 8.7-9.7 GPa)
2, 8.7-9.7 GPa)  I4/mmm(x
I4/mmm(x 2, 9.7 GPa, trivalent). The phase of I4/mmm having trivalent character is a small distortion from cubic fcc structure which has been commonly observed for
2, 9.7 GPa, trivalent). The phase of I4/mmm having trivalent character is a small distortion from cubic fcc structure which has been commonly observed for  -phase of all other trivalent rare-earth metal hydrides. Our study clearly demonstrates the first observation of
-phase of all other trivalent rare-earth metal hydrides. Our study clearly demonstrates the first observation of  -phase of EuH
-phase of EuH and suggest that the material is no longer an irregular member of the rare earth metal hydrides RH
and suggest that the material is no longer an irregular member of the rare earth metal hydrides RH systems.
systems.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to investigate effects of environmental mitigation and water radiolysis caused by  -rays from radioactive material on irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior for highly irradiated material, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at 563 K) are performed. The specimens made of 316L stainless steels are irradiated with neutrons up to
-rays from radioactive material on irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior for highly irradiated material, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at 563 K) are performed. The specimens made of 316L stainless steels are irradiated with neutrons up to  12 dpa in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). One of the specimens is annealed at 973 K for 1 hour to show almost recovered mechanical and micro-chemical properties corresponding to the unirradiated material. For low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition, the crack growth rate (CGR) is suppressed by about one order of magnitude in high stress intensity factor (K) condition. This result indicates that environmental mitigation for crack growth can be found even under severe conditions on material and stress factors. The effects of water radiolysis on the CGRs are discussed.
12 dpa in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). One of the specimens is annealed at 973 K for 1 hour to show almost recovered mechanical and micro-chemical properties corresponding to the unirradiated material. For low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition, the crack growth rate (CGR) is suppressed by about one order of magnitude in high stress intensity factor (K) condition. This result indicates that environmental mitigation for crack growth can be found even under severe conditions on material and stress factors. The effects of water radiolysis on the CGRs are discussed.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at  563 K) were performed using neutron-irradiated specimens made of 316L stainless steels, and the oxide film properties and locally deformed structures near the crack tip have been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) of the materials was lowered by deaeration and hydrogen injection into feed water, apparent suppression of oxidation inside the cracks was observed as well as suppression of the crack growth rate (CGR). In the presentation, the TEM results of the locally deformed structures along the cracks are also reported, and the relation among the CGR, oxide film properties, and locally deformed structures is discussed.
563 K) were performed using neutron-irradiated specimens made of 316L stainless steels, and the oxide film properties and locally deformed structures near the crack tip have been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) of the materials was lowered by deaeration and hydrogen injection into feed water, apparent suppression of oxidation inside the cracks was observed as well as suppression of the crack growth rate (CGR). In the presentation, the TEM results of the locally deformed structures along the cracks are also reported, and the relation among the CGR, oxide film properties, and locally deformed structures is discussed.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests using compact tension (CT) specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) were performed in simulated BWR environments (at  288
288 C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than
C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than 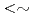 1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than
1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than 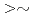 2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.
2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.