Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyasaka, Satoshi*; Unome, Sota*; Tamura, Ayako*; Ito, Yoshiaki*; Ishizaki, Azusa; Sanada, Yukihisa
Nihon Rimoto Senshingu Gakkai Dai-63-Kai (Heisei-29-Nendo Shuki) Gakujutsu Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.81 - 84, 2017/11
Information of snow depth is important to improve the airborne radiation measurement in the winter. The snow depth is enable to estimate by the aerial photograph which is obtained at the same time with the radiation measurement before and after the snowfall. We attempted optimization parameters which used to make a Digital Surface Model (DSM) using Structure from Motion (SfM) method for estimation of the snow depth. As a result, to enable to measure precisely the snow depth was indicated. However, the estimated snow depth in the forest area was relatively not so accurate because fallen leaves and a tree move were prevented to measure DSM precisely.
Jiang, X.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Haruma, Toshikatsu; Takahashi, Junko*; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Jiang, Q.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Takahashi, Junko*; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
In the former open-pit mining area of Ningyo-toge mine, 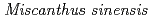 is the dominant in its vegetation and the vegetation succession has been suspended for 2 decades. The present work was conducted to understand the soil micromorphological characteristics on this unusual area. We set two sampling sites (site A and site B) at the former open-pit mining area. Site A is in
is the dominant in its vegetation and the vegetation succession has been suspended for 2 decades. The present work was conducted to understand the soil micromorphological characteristics on this unusual area. We set two sampling sites (site A and site B) at the former open-pit mining area. Site A is in 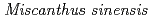 dominant vegetation, and site B is in
dominant vegetation, and site B is in 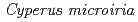 dominant vegetation. Soil samples were taken from each horizon of the soil profiles for chemical analysis at the sites, and thin sections were obtained from the soil core samples (0-5 cm, 10-15 cm, 30-35 cm depth of site A and Site B, respectively). The BC horizon of site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. And the soil thin section observation showed that the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the lower layer is not fully developed and forms a block structure. The content of the five forms of Fe and Mn are residual form
dominant vegetation. Soil samples were taken from each horizon of the soil profiles for chemical analysis at the sites, and thin sections were obtained from the soil core samples (0-5 cm, 10-15 cm, 30-35 cm depth of site A and Site B, respectively). The BC horizon of site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. And the soil thin section observation showed that the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the lower layer is not fully developed and forms a block structure. The content of the five forms of Fe and Mn are residual form  oxide-bound form
oxide-bound form  organic-bound form
organic-bound form  carbonate-bound form
carbonate-bound form  exchangeable form in this study site.
exchangeable form in this study site.
Jiang, Q.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
This study was conducted to understand the soil macro and micromorphological characteristics on the former open pit mining area of Ningyo-toge mine. The vegetation succession of the area has not progressed. Its dominant vegetation has been 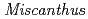 . The conclusions of this study are follows. The BC horizon of Site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. The contents of Mn, Cd, Pb, and Co were higher than the average contents in Japanese soil, but they did not reach the level of pollution. The content of acid-soluble Fe was very low in the soil, Fe mainly is the form of residual and a part of reducible form in the study site. But, the content of Mn in acid-soluble form is high, and Mn has a greater impact on vegetation. In this study site, external human factors have a large influence, mixed with a large amount of black residue and wood chips. And the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the soil in the lower layer is not fully developed and it is a block structure.
. The conclusions of this study are follows. The BC horizon of Site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. The contents of Mn, Cd, Pb, and Co were higher than the average contents in Japanese soil, but they did not reach the level of pollution. The content of acid-soluble Fe was very low in the soil, Fe mainly is the form of residual and a part of reducible form in the study site. But, the content of Mn in acid-soluble form is high, and Mn has a greater impact on vegetation. In this study site, external human factors have a large influence, mixed with a large amount of black residue and wood chips. And the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the soil in the lower layer is not fully developed and it is a block structure.