Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics)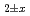 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
 based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation result
based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation resultWatanabe, Masashi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Suzuki, Kiichi; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 105(3), p.2248 - 2257, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.33(Materials Science, Ceramics)Properties of CeO were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Sawada, Shinichi*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(35), p.19141 - 19152, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.42(Chemistry, Physical) Al
Al (O
(O D
D )
) , with temperature at high pressure
, with temperature at high pressureKyono, Atsushi*; Kato, Masato*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 46(5), p.459 - 469, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To reveal the decomposition mechanism with temperature under high-pressure, crystal structure of a hydrogrossular, katoite Ca Al
Al (O
(O D
D )
) has been studied by in-situ neutron diffraction at 8 GPa. Although unusual expansion behavior was discerned at 200-400
has been studied by in-situ neutron diffraction at 8 GPa. Although unusual expansion behavior was discerned at 200-400 C, the unit cell was continuously expanded up to 850
C, the unit cell was continuously expanded up to 850 C. At 900
C. At 900 C, katoite was decomposed, indicating that pressure strongly increases dehydration temperature from 300
C, katoite was decomposed, indicating that pressure strongly increases dehydration temperature from 300 C to 900
C to 900 C. On release of pressure, the katoite reappear together with corundum and portlandite. At 8 GPa, CaO
C. On release of pressure, the katoite reappear together with corundum and portlandite. At 8 GPa, CaO and AlO
and AlO polyhedra expand with temperature up to 850
polyhedra expand with temperature up to 850 C by about 8% and 13%, respectively. On the other hand, tetrahedral interstices are isotopically squeezed by about 10%: due to the expansion of above polyhedra. The neighboring D-D distance remains almost unchanged in this temperature range, while the O-D bond distance shrinks drastically just before decomposition. This finding suggests that the shortening of O-D distance caused by the D-D repulsion destabilizes the O-D bond, which induces the thermal decomposition of katoite.
C by about 8% and 13%, respectively. On the other hand, tetrahedral interstices are isotopically squeezed by about 10%: due to the expansion of above polyhedra. The neighboring D-D distance remains almost unchanged in this temperature range, while the O-D bond distance shrinks drastically just before decomposition. This finding suggests that the shortening of O-D distance caused by the D-D repulsion destabilizes the O-D bond, which induces the thermal decomposition of katoite.

Kato, Masato; Nakamura, Hiroki; Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Machida, Masahiko
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 375, p.57 - 70, 2017/05
The basic properties of PuO were reviewed, and the equilibrium defects in PuO
were reviewed, and the equilibrium defects in PuO were evaluated from the experimental data of the oxygen potential and electrical conductivity as well as the Ab-initio calculation results. Consistency among various properties was confirmed, and the mechanistic models for thermal property representations were derived.
were evaluated from the experimental data of the oxygen potential and electrical conductivity as well as the Ab-initio calculation results. Consistency among various properties was confirmed, and the mechanistic models for thermal property representations were derived.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(5), p.053602_1 - 053602_5, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Plutonium dioxide (PuO ) is a key ingredient of mixed oxide (MOX) and advanced nuclear fuels. Its thermophysical data is crucial in understanding the high-temperature behaviors of nuclear fuels. In particular, the high-temperature heat capacity is of great importance for their safety and performance analyses. Here, we evaluate the main contributions to the heat capacity of PuO
) is a key ingredient of mixed oxide (MOX) and advanced nuclear fuels. Its thermophysical data is crucial in understanding the high-temperature behaviors of nuclear fuels. In particular, the high-temperature heat capacity is of great importance for their safety and performance analyses. Here, we evaluate the main contributions to the heat capacity of PuO from 0 to 1400 K through suitable first-principles calculations. Consequently, we successfully obtain a temperature dependence in good agreement with experimental measurements. This success mainly results from accurate calculations of the Schottky heat capacity caused by the excited levels of
from 0 to 1400 K through suitable first-principles calculations. Consequently, we successfully obtain a temperature dependence in good agreement with experimental measurements. This success mainly results from accurate calculations of the Schottky heat capacity caused by the excited levels of  -electrons of Pu. Our calculations resolve the mystery of why previous works failed to reproduce the measurement data. This study extends the possibility of performing simulation-based nuclear-fuel research instead of difficult measurements.
-electrons of Pu. Our calculations resolve the mystery of why previous works failed to reproduce the measurement data. This study extends the possibility of performing simulation-based nuclear-fuel research instead of difficult measurements.
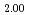
Kato, Masato; Uchida, Teppei; Matsumoto, Taku; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 451(1-3), p.78 - 81, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Linear thermal expansion of PuO was measured by dilatometry in an oxygen partial pressure-controlled atmosphere. The measured data of PuO
was measured by dilatometry in an oxygen partial pressure-controlled atmosphere. The measured data of PuO slightly increased with deviation
slightly increased with deviation  . The linear thermal expansion of PuO
. The linear thermal expansion of PuO was determined as a function of temperature and O/M ratio, and the equation for the thermal expansion coefficient was derived. Heat capacity of PuO
was determined as a function of temperature and O/M ratio, and the equation for the thermal expansion coefficient was derived. Heat capacity of PuO was evaluated using this equation. The effect of O/M ratio on heat capacity was small. In addition to the vibration and dilatational terms, it is important to analyze the Schottky term in evaluating heat capacity of PuO
was evaluated using this equation. The effect of O/M ratio on heat capacity was small. In addition to the vibration and dilatational terms, it is important to analyze the Schottky term in evaluating heat capacity of PuO .
.
 study on plutonium dioxide with spin-orbit couplings
study on plutonium dioxide with spin-orbit couplingsNakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.16 - 19, 2011/10
Plutonium dioxide is a main component of mixed oxide fuels. We perform first-principles density functional calculations on plutonium dioxides considering proper relativistic effects and strong correlations. Though this material is a paramagnetic insulator, standard calculations predict metallic states. The reason of this failure is often considered lack of strong correlations in LDA. However, even if strong correlation effects on plutonium  -orbital electrons are taken into account using the LDA+
-orbital electrons are taken into account using the LDA+ method, an insulating state cannot be obtained. In this paper, we point out that not only strong correlations but also spin-orbit couplings as relativistic effects are necessary to obtain paramagnetic insulating states. Based on this proper method, we calculate several physical properties of plutonium dioxide and compare them with other calculations and experiments. We also discuss the effects of oxygen deficiency on the electronic structures and thermal properties.
method, an insulating state cannot be obtained. In this paper, we point out that not only strong correlations but also spin-orbit couplings as relativistic effects are necessary to obtain paramagnetic insulating states. Based on this proper method, we calculate several physical properties of plutonium dioxide and compare them with other calculations and experiments. We also discuss the effects of oxygen deficiency on the electronic structures and thermal properties.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Physical Review B, 82(15), p.155131_1 - 155131_6, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We perform first-principles calculations taking account of both relativistic and strong correlation effects on plutonium dioxides in order to numerically obtain its observed ground state, i.e., the paramagnetic insulating state and properly calculate the material properties. Generally, it is known for plutonium dioxides that the standard LDA calculations give metallic states and even LDA +  considering the strong correlation on Pu
considering the strong correlation on Pu  -orbitals fails to attain the paramagnetic insulating state. In this paper, we clarify that inclusion of the spin-orbit coupling in addition to the strong correlation is responsible for the paramagnetic insulating state. Using the obtained paramagnetic insulating state, we calculate various material properties and claim that the proper state preparation is essential for quantitative evaluation of the material properties.
-orbitals fails to attain the paramagnetic insulating state. In this paper, we clarify that inclusion of the spin-orbit coupling in addition to the strong correlation is responsible for the paramagnetic insulating state. Using the obtained paramagnetic insulating state, we calculate various material properties and claim that the proper state preparation is essential for quantitative evaluation of the material properties.
 and CeO
and CeO
Kato, Masato; Nakamura, Hiroki; Watanabe, Masashi; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
It is difficult to measure the physical properties of fuel materials, such as uranium dioxide, at a high temperature near their melting point. In such cases, fluorite is often adopted as simulated fuel materials, because of its lower melting point than that of uranium dioxide. In this presentation, we evaluate the high-temperature behavior of fluorite using machine-learning molecular dynamics whose training data are obtained by first-principles calculations. Comparing calculated results with experimental data, we confirm the reliability and effectiveness of this method and discuss the possibility of application to fuel materials.
 , 2; Machine-learning molecular dynamics study
, 2; Machine-learning molecular dynamics studyNakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
It is difficult to measure the thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials such as uranium dioxide, at high temperature just below their melting points. CaF is sometimes employed as alternative nuclear fuel materials. In this paper, we evaluate the Bredig transition and its effect on the materials properties, using machine-learning molecular dynamics trained by first-principles calculations. In particular, we investigate the dynamical structure factor measured by inelastic neutron scattering, and we explore the characteristics of the Bredig transition. We also discuss application to nuclear materials such as uranium dioxide.
is sometimes employed as alternative nuclear fuel materials. In this paper, we evaluate the Bredig transition and its effect on the materials properties, using machine-learning molecular dynamics trained by first-principles calculations. In particular, we investigate the dynamical structure factor measured by inelastic neutron scattering, and we explore the characteristics of the Bredig transition. We also discuss application to nuclear materials such as uranium dioxide.
 , 1; High temperature neutron inelastic scattering measurement
, 1; High temperature neutron inelastic scattering measurementWatanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 with machine-learning molecular dynamics
with machine-learning molecular dynamicsNakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
It is difficult to measure the thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials, such as MOX fuel materials, at high temperature just below their melting points. Solid solution of calcium fluoride and strontium fluoride, (Ca,Sr)F , is sometimes employed as alternative MOX fuel materials. In this paper, we evaluate the (Ca,Sr)F
, is sometimes employed as alternative MOX fuel materials. In this paper, we evaluate the (Ca,Sr)F dynamic structure factor measured by inelastic neutron scattering using machine-learning molecular dynamics trained by first-principles calculations. We investigate the behavior of the dynamic structure factor at the Bredig transition temperature, at which heat capacity rapidly increases. We also discuss application of the present method to MOX fuel materials.
dynamic structure factor measured by inelastic neutron scattering using machine-learning molecular dynamics trained by first-principles calculations. We investigate the behavior of the dynamic structure factor at the Bredig transition temperature, at which heat capacity rapidly increases. We also discuss application of the present method to MOX fuel materials.

Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 , 2; DFT analysis of high-temperature properties
, 2; DFT analysis of high-temperature propertiesNakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
It is difficult to measure thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials such as uranium dioxide, at high temperature just below their melting points. Employing calcium fluoride as alternative nuclear fuel materials, we aim to clarify its thermophysical properties and to understand the mechanism and behavior of nuclear fuel at high temperature. In this paper, we evaluate thermal properties of calcium fluoride using first-principles calculations and confirm the reliability of the calculations comparing with experimental data. Besides, we analyze the mechanism of the Bredig transition.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Masato; Nakamura, Hiroki; Watanabe, Masashi; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Brouwer's diagrams for PuO and CeO
and CeO were constructed based on results of oxygen potential measurement and DFT calculation. Defect concentration, oxygen diffusion coefficient and electrical conductivity were evaluated, and differences between PuO
were constructed based on results of oxygen potential measurement and DFT calculation. Defect concentration, oxygen diffusion coefficient and electrical conductivity were evaluated, and differences between PuO and CeO
and CeO were discussed.
were discussed.