Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 35(1), p.103 - 106, 2010/03
A careful observation on X-ray diffraction in the ferroelectric crystals such as BaTiO reveals that a new physical picture of the ferroelectric transition in these crystals may rather be regarded as an order-disorder transition. A strong local order in the disordered phase is a characteristic feature. The model gives natural interpretation of the occurrence of a micro cluster phase in the phase transition to explain the existence of the central peak. We also observed the micro cluster phase just behind the phase transition temperature in the tetragonal phase.
reveals that a new physical picture of the ferroelectric transition in these crystals may rather be regarded as an order-disorder transition. A strong local order in the disordered phase is a characteristic feature. The model gives natural interpretation of the occurrence of a micro cluster phase in the phase transition to explain the existence of the central peak. We also observed the micro cluster phase just behind the phase transition temperature in the tetragonal phase.
 at phase transition temperature
at phase transition temperatureYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 48(9), p.09KF01_1 - 09KF01_5, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.89(Physics, Applied)We performed X-ray diffraction topography analysis on a BaTiO single crystal with high-coherence synchrotron X-rays. Since the domain configuration of the BaTiO
single crystal with high-coherence synchrotron X-rays. Since the domain configuration of the BaTiO single crystal was unstable and fluctuated with temperature, an excellent temperature control system was used for domain observation. We used a milli-Kelvin (mK)-stabilized cell, which can control BaTiO
single crystal was unstable and fluctuated with temperature, an excellent temperature control system was used for domain observation. We used a milli-Kelvin (mK)-stabilized cell, which can control BaTiO crystal temperature to within
crystal temperature to within  1 mK. By combining the coherent X-rays and the mK-stabilized cell, one can detect the domain configuration very sensitively during phase transition. The domain configuration changed markedly at the transition temperature. The low-temperature tetragonal domain fluctuated greatly before the long-range-order structure changed from tetragonal to cubic. The ferroelectric-to-paraelectric transition occurred in two steps; first, the domain configuration changed in the tetragonal phase, and then, the average structure changed to the cubic structure.
1 mK. By combining the coherent X-rays and the mK-stabilized cell, one can detect the domain configuration very sensitively during phase transition. The domain configuration changed markedly at the transition temperature. The low-temperature tetragonal domain fluctuated greatly before the long-range-order structure changed from tetragonal to cubic. The ferroelectric-to-paraelectric transition occurred in two steps; first, the domain configuration changed in the tetragonal phase, and then, the average structure changed to the cubic structure.
 crystal by synchrotron X-ray topography
crystal by synchrotron X-ray topographyYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Morimura, Ryota*; Kojima, Akira*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 32(1), p.31 - 34, 2007/03
We performed X-ray diffraction topography on a BaTiO single crystal by high-coherent synchrotron X-rays. Since the domain configuration of the BaTiO
single crystal by high-coherent synchrotron X-rays. Since the domain configuration of the BaTiO crystal was unstable and fluctuated as temperature fluctuated, an excellent temperature control system is needed for the domain observation. We used a milli-Kelvin (mK) cell, which can control a BaTiO
crystal was unstable and fluctuated as temperature fluctuated, an excellent temperature control system is needed for the domain observation. We used a milli-Kelvin (mK) cell, which can control a BaTiO crystal within
crystal within  1mK. By combining the coherent X-ray and the mK-cell, one can detect the lattice strain very sensitively around the domain boundary. The lattice strain reduced as temperature increased, and disappeared at 100
1mK. By combining the coherent X-ray and the mK-cell, one can detect the lattice strain very sensitively around the domain boundary. The lattice strain reduced as temperature increased, and disappeared at 100 C, which is much lower than the phase transition temperature of the BaTiO
C, which is much lower than the phase transition temperature of the BaTiO , and the BaTiO
, and the BaTiO crystal still remained in the ferroelectric tetragonal phase. This behavior can be interpreted by the existence of the so-called "non-strain-free style domain", which is reported firstly by Takashige et al.
crystal still remained in the ferroelectric tetragonal phase. This behavior can be interpreted by the existence of the so-called "non-strain-free style domain", which is reported firstly by Takashige et al.
 Cu
Cu O
O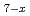 and its superconductive phase transition
and its superconductive phase transitionSuzuki, Takuya*; Takano, Hidekazu*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Kentaro*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Suzuki, Yoshio*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 36, p.249 - 257, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 30(1), p.51 - 54, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
 crystals
crystalsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Mizuki, Junichiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 43(9B), p.6821 - 6824, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:39.38(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 crystal
crystalYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(4), p.1050 - 1053, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:56.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have observed 90 domain walls in a bulk BaTiO
domain walls in a bulk BaTiO crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO
crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90
multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90 domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO
domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
 crystal
crystalYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(4), p.1050 - 1053, 2004/04
We have observed 90  C domain walls in a bulk BaTiO
C domain walls in a bulk BaTiO crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO
crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90
multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90  C domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO
C domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
Goto, Shunji*; Takeshita, Kunikazu*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Hiroaki*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Yagi, Naoto*; Isshiki, M.*; Yamazaki, H.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 467-468(Part1), p.682 - 685, 2001/07
no abstracts in English
Goto, Shunji*; Takeshita, Kunikazu*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Hiroaki*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Yagi, Naoto*; Isshiki, Maiko*; Yamazaki, H.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 467-468(Part1), p.682 - 685, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:146 Percentile:99.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Saito, Yuji; Kimura, Hiroaki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Nakatani, Takeshi*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Muro, Takayuki*; Miyahara, Tsuneaki*; Fujisawa, M.*; Soda, Kazuo*; Ueda, Shigenori*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 467-468(Part.1), p.553 - 556, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:81.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Saito, Yuji; Kimura, Hiroaki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Nakatani, Takeshi*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Muro, Takayuki*; Miyahara, Tsuneaki*; Fujisawa, M.*; Soda, Kazuo*; Ueda, Shigenori*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 71(9), p.3254 - 3259, 2000/09
Times Cited Count:188 Percentile:98.94(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 observed in Bragg reflection
observed in Bragg reflectionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Kojima, Akira*; Morimura, Ryota*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English