Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Johansen, M. P.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; Mori, Airi; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*; McGinnity, P.*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 287, p.107706_1 - 107706_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*; Ito, Tatsuya; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0Lin, Z. M.*; Liu, B. X.*; Ming, K. S.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F. X.*; Zheng, S. J.*
Scripta Materialia, 263, p.116692_1 - 116692_7, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1Aoyama, Takahito; Choudhary, S.*; Pandaleon, A.*; Burns, J. T.*; Kokaly, M.*; Restis, J.*; Ross, J.*; Kelly, R. G.*
Corrosion, 81(6), p.609 - 621, 2025/06
Sugita, Yutaka; Ono, Hirokazu; Beese, S.*; Pan, P.*; Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Jove-Colon, C.*; Lopez, C. M.*; Liang, S.-Y.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100668_1 - 100668_21, 2025/06
The international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2023 focused on the Horonobe EBS experiment in the Task D, which was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (or thermo-hydro) interactions in bentonite based engineered barriers. One full-scale in-situ experiment and four laboratory experiments, largely complementary, were selected for modelling. The Horonobe EBS experiment is a temperature-controlled non-isothermal experiment combined with artificial groundwater injection. The Horonobe EBS experiment consists of the heating and cooling phases. Six research teams performed the THM or TH (depended on research team approach) numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws.
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Wilson, J.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Tachi, Yukio; Kawama, Daisuke*
Applied Clay Science, 275, p.107862_1 - 107862_15, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0High-Level Radioactive Waste (HLW) repositories include iron or steel-based containers/overpack and bentonite buffers. Over the last 25 years or so, research efforts have attempted to elucidate the nature of iron-bentonite interactions, especially the potential for the deleterious alteration of the swelling clay component (smectite), to iron-rich layer silicates, some of which lack the capacity for intracrystalline swelling. This could result in a reduction or loss in swelling pressure in the bentonite buffer which is designed to protect waste containers from shear forces and also acts to restrict water and solute transport, as part of an engineered barrier system. Most data on iron-bentonite interactions come from experimental and geochemical modelling studies, as natural analogue data are lacking. The data suggests that there is the potential for the development of an iron-rich bentonite alteration zone with smectite (generally present as the aluminous montmorillonite type) undergoing alteration to iron-rich solids, including layer silicates and steel corrosion products such as green rust or magnetite. The evidence available is complex, arguably incomplete, with many potential complex couplings. Many uncertainties remain despite efforts taken over the last 25 years, but plausible scenarios for iron-bentonite interactions have been identified and possible implications for buffer properties have been suggested.
Mori, Airi; Johansen, M. P.*; McGinnity, P.*; Takahara, Shogo
Communications Earth & Environment (Internet), 6, p.356_1 - 356_11, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0Hartzell, S.*; Parisi, A.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Beltran, C. J.*; Furutani, K. M.*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 70(10), p.105010_1 - 105010_19, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ono, Masato; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.235 - 242, 2025/05
Kato, Masaru*; Zheng, J.*; Deng, Y.*; Saito, Fumie*; Unuma, Yuki*; Oka, Sayuki*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Yagi, Ichizo*
ACS Catalysis, 15(10), p.7710 - 7719, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH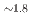 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH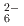 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH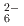 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (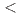 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.
Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 7 of others*
Acta Materialia, 288, p.120840_1 - 120840_14, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 3 of others*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
Pandian, K.*; Neikter, M.*; Ekh, M.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Woracek, R.*; Hansson, T.*; Pederson, R.*
JOM, 77(4), p.1803 - 1815, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Joung, S.*; Ji, Y.-Y.*; Choi, Y.*; Lee, E.*; Ji, W.*; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 20(4), p.P04027_1 - P04027_10, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0