Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Plante, I.*; Liu, C.*; 小西 輝昭*; 宇佐美 徳子*; 舟山 知夫; Azzam, E.*; 村上 健*; 鈴木 雅雄*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 91(1), p.62 - 70, 2015/01
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:93.49(Biology)放射線がん治療の実施にあたり、放射線誘発バイスタンダー効果が治療域周辺の正常細胞に健康影響リスクを及ぼすかどうかは重要な問題である。そこで、本研究では、バイスタンダー効果が誘導された細胞の子孫細胞における有害影響の伝播に、照射した放射線の線質と、ギャップジャンクションを介した細胞間情報伝達機構が果たす役割について解析を行った。実験では、コンフルエントに培養したヒト正常線維芽細胞試料に対し、LETの異なるマイクロビームで、その全体の0.036 0.4%の細胞のみに照射を行い、バイスタンダー効果を誘導した。この細胞を照射後20世代にわたって培養し回収した後に、微小核形成、
0.4%の細胞のみに照射を行い、バイスタンダー効果を誘導した。この細胞を照射後20世代にわたって培養し回収した後に、微小核形成、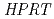 遺伝子への変異誘発、及びタンパク質酸化を指標に解析を行った。その結果、バイスタンダー細胞の子孫細胞における有害影響の伝播は、照射した放射線のLETによって違いがあることが明らかになった。
遺伝子への変異誘発、及びタンパク質酸化を指標に解析を行った。その結果、バイスタンダー細胞の子孫細胞における有害影響の伝播は、照射した放射線のLETによって違いがあることが明らかになった。
鈴木 雅雄*; Autsavapromporn, N.*; 宇佐美 徳子*; 舟山 知夫; Plante, I.*; 横田 裕一郎; 武藤 泰子*; 鈴木 芳代; 池田 裕子; 服部 佑哉; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(Suppl.1), P. i54, 2014/03
It is essentially important for evaluating risk such a low-dose-rate exposure as the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants to examine bystander effects induced by low-LET electromagnetic radiations, such as X or  rays. We have been studying the cellular responses in normal human fibroblasts by targeted cell nucleus irradiations with monochromatic X-ray microbeams (5.35 keV) produced by Photon Factory in High Energy Accelerator Research Organization. The results indicated that the bystander effect in cell- killing effect was observed in the targeted cell nucleus irradiation, not in the random irradiation containing both cell nucleus and cytoplasm by Poisson distribution. The results suggest that energy deposition in cytoplasm is an important role of inducing bystander effects in case of low-LET radiations. We have also been investigating high-LET-radiation induced bystander effects using the heavy-ion microbeams at Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Only 0.04% of the total numbers of normal human fibroblasts were irradiated with C-ion (220 MeV), Ne-ion (260 MeV) and Ar-ion (460 MeV) microbeams collimated at 20 micro meter in diameter. Cell-killing effect and gene mutation at HPRT locus in the cells irradiated with C ions were higher beyond our expectations and returned the estimated values that only 0.04% of the total cells were irradiated when using the specific inhibitor of gap junctions. On the other hand, no induced biological effects were observed in Ne and Ar ions whether the inhibitor was applied or not. The result suggested that the C-ion microbeam was capable of inducing bystander cellular effects via gap junction mediated cell-cell communication. There is clear evidence that bystander cellular effects are dependent on radiation quality.
rays. We have been studying the cellular responses in normal human fibroblasts by targeted cell nucleus irradiations with monochromatic X-ray microbeams (5.35 keV) produced by Photon Factory in High Energy Accelerator Research Organization. The results indicated that the bystander effect in cell- killing effect was observed in the targeted cell nucleus irradiation, not in the random irradiation containing both cell nucleus and cytoplasm by Poisson distribution. The results suggest that energy deposition in cytoplasm is an important role of inducing bystander effects in case of low-LET radiations. We have also been investigating high-LET-radiation induced bystander effects using the heavy-ion microbeams at Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Only 0.04% of the total numbers of normal human fibroblasts were irradiated with C-ion (220 MeV), Ne-ion (260 MeV) and Ar-ion (460 MeV) microbeams collimated at 20 micro meter in diameter. Cell-killing effect and gene mutation at HPRT locus in the cells irradiated with C ions were higher beyond our expectations and returned the estimated values that only 0.04% of the total cells were irradiated when using the specific inhibitor of gap junctions. On the other hand, no induced biological effects were observed in Ne and Ar ions whether the inhibitor was applied or not. The result suggested that the C-ion microbeam was capable of inducing bystander cellular effects via gap junction mediated cell-cell communication. There is clear evidence that bystander cellular effects are dependent on radiation quality.
Autsavapromporn, N.*; 鈴木 雅雄*; 舟山 知夫; 宇佐美 徳子*; Plante, I.*; 横田 裕一郎; 武藤 泰子*; 池田 裕子; 小林 克己*; 小林 泰彦; et al.
Radiation Research, 180(4), p.367 - 375, 2013/10
被引用回数:58 パーセンタイル:89.88(Biology)ヒト正常培養細胞集団のごく一部に照射を行い、照射シグナルの伝達に細胞間ギャップ結合が果たす役割を解析した。コンフルエント培養した細胞に、X線および重イオンビーム(炭素、ネオン、アルゴン)のマイクロビームを用いて照射を行い、培地へのギャップ結合阻害剤添加の有無によるバイスタンダー効果誘導の違いを比較した。X線と重イオンの双方のマイクロビーム照射によって、線量に応じた微小核形成のバイスタンダー効果誘導が認められた。ギャップ結合阻害剤の添加によって、重イオンマイクロビームによって誘導されたバイスタンダー効果は抑制されたが、X線マイクロビームによるバイスタンダー効果は抑制されなかった。この結果は、バイスタンダー効果の誘導には線質が重要であることを示す。
鈴木 雅雄*; Autsavapromporn, N.*; 舟山 知夫; 横田 裕一郎; 武藤 泰子*; 池田 裕子; 鈴木 芳代; 服部 佑哉; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦; et al.
no journal, ,
重イオンマイクロビームを照射した細胞から湧出する因子によるバイスタンダー効果誘導を明らかにする目的で、マイクロビーム照射後の細胞致死効果の時間変化を調べた。重イオンマイクロビーム照射には、日本原子力研究開発機構TIARAの細胞局部照射装置を用いた。照射後培養液を添加し、0.5, 3, 24時間インキュベーター内に保持し、それぞれのタイミングでの細胞増殖死をコロニー形成法で調べた。その結果、アルゴンイオン照射試料で、ギャップジャンクション阻害剤やDMSOの添加では抑制されないが、アスコルビン酸の添加によって抑制される何らかの因子によって、細胞致死効果を増幅するようなバイスタンダー効果が誘導されることが示唆された。
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Plante, I.*; Liu, C.*; 小西 輝明*; 宇佐美 徳子*; 舟山 知夫; Azzam, E.*; 村上 健*; 鈴木 雅雄*
no journal, ,
ヒト皮膚由来正常線維芽細胞NG1RGB株へLETの異なるマイクロビームを照射し、その子孫細胞における影響を解析した。コンフルエントに培養したNG1RGB細胞集団の0.036-0.4%にマイクロビームで1箇所あたり0.4Gy相当の照射を行い、その後、20世代継代した後に微小核形成、突然変異誘発、およびタンパク質の酸化を指標とした解析を実施した。X線とプロトンビームで照射した細胞の子孫細胞では、酸化ストレスの昂進と微小核形成および突然変異頻度の上昇が認められた。その一方、炭素イオンビームで照射した細胞の子孫細胞では、同様な影響は認められなかった。また、細胞間ギャップ結合の阻害を行うことで、プロトンでは、子孫細胞における照射効果が緩和された。