Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -,
-,  - and X-ray spectra
- and X-ray spectraOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Shen, H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The spectrum determination method (SDM) is the method to determine radioactivities by analyzing full spectral shape of  - or
- or  rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard
rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard  - and
- and  spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
Sato, Hinata; Mori, Amami; Kuno, Sorato; Horigome, Kazushi; Goto, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo
JAEA-Technology 2024-011, 56 Pages, 2024/10
Flush-out, which recovers remaining nuclear materials in the process and transfer it to a highly radioactive liquid waste storage tank, has been performed at main plant of Tokai Reprocessing Plant. The flush-out has been composed from three steps: first step is to remove of spent fuel sheared powder, second step is to collect plutonium solution stored in the process, and third step is to convert uranium solution into uranium trioxide powder. The first step of flush-out activity has been completed in 2022. Second and third steps of flush-out have been completed from March 2023 to February 2024. Process control analysis has been performed for operation of the facility, and material accountancy analysis has been performed to control the accountancy of nuclear materials. In addition, related analytical work such as pretreatment for transporting inspection samples for safeguards analysis laboratories in IAEA has been also performed. This report describes results of analytical work performed in collections of plutonium and uranium solutions in second and third steps of the flush-out, including calibration of analytical equipment, waste generation, and education and training of analytical operator.
Soyama, Kazuhiko; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Goto, Yoshiki*; Kobayashi, Yuki*; Arakawa, Shohei*; Yamamoto, Yugo*; Suba, Kenta*; Yamamura, Kazuya*
JAEA-Research 2024-006, 15 Pages, 2024/10
A neutron optics design has been conducted for a neutron magnetic microscope that utilize a Wolter type I multilayer supermirror for the purpose of magnetic fields imaging in magnetic materials. Ray trace simulation was performed for a magnifying imaging optical system with a magnification rate of 12.5 times. Based on classical model of Lamor precession, depolarization due to magnetic domains was simulated, and the effect of slope errors on the Wolter mirror created by the replica method on the spatial resolution of the microscope was investigated. As a result, reference data about the shape error required to obtain spatial resolution on the order of micrometers was obtained.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Horigome, Kazushi; Goto, Yuichi; Taguchi, Shigeo
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
Flush-out activities of Tokai Reprocessing Plant were completed in February, 2024. Since it contained remaining nuclear materials in main process of the facility, purpose of activities was to flush-out them and to rinse with nitric acid solution. This paper describes analysis of nuclear materials related to flush-out activities.
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)High-pressure responses of the O-D F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)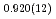 F
F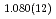 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
Kinase, Akari; Goto, Katsunori*; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-004, 60 Pages, 2024/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3 and stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc, 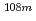 Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Oshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Sano, Yuichi*; Asai, Masato; Haraga, Tomoko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.871 - 882, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:27.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)Previously we reported a simple algorithmic method of spectral determination method (SDM), which is based on the first principle that a  -ray spectrum obtained for a sample is a linear superposition of individual spectra of the radioactive nuclides included in the sample and demonstrated that the method is valid for
-ray spectrum obtained for a sample is a linear superposition of individual spectra of the radioactive nuclides included in the sample and demonstrated that the method is valid for  -ray determination. Here we apply it to the spectra obtained by liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In LSC measurements quenching is generally observed and we at first developed its correction method to standard spectra. The SDM code reported in the previous investigation is used to analyze the LSC spectra. Based on the analyses done by using the measured spectra, we concluded that the SDM method is valid in the LSC spectra similarly to the
-ray determination. Here we apply it to the spectra obtained by liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In LSC measurements quenching is generally observed and we at first developed its correction method to standard spectra. The SDM code reported in the previous investigation is used to analyze the LSC spectra. Based on the analyses done by using the measured spectra, we concluded that the SDM method is valid in the LSC spectra similarly to the  -ray spectra studied in the previous investigation.
-ray spectra studied in the previous investigation.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*
AIP Advances (Internet), 14(5), p.055034_1 - 055034_6, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)This study examines the utilization of Fukushima weathered biotite(WB)as an alternative to conventional thermoelectric materials traditionally derived from rare and toxic substances. WB underwent milling, classification, and subsequent heat treatment via molten-salt treatment to produce crystals exhibiting conductivity akin to semiconductors within from 650 C to 850
C to 850 C range. Evaluation of WB and the derived crystal's electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient showcased their viability for high-temperature thermoelectric applications. Consequently, WB attained a dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) of 0.015, signaling its potential as a thermoelectric material that surpasses 650
C range. Evaluation of WB and the derived crystal's electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient showcased their viability for high-temperature thermoelectric applications. Consequently, WB attained a dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) of 0.015, signaling its potential as a thermoelectric material that surpasses 650 C.
C.
Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00461_1 - 23-00461_10, 2024/04
Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ambai, Hiromu; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00407_1 - 23-00407_8, 2024/04
Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Shibata, Taiju
IAEA-TECDOC-2040, p.133 - 136, 2023/12
Japan has developed back-end technologies to establish a multi-recycling fuel cycle with fast breeder reactors (FBRs) to ensure energy resources. Even though the development of FBR has been retreated to one of fundamental research, the reprocessing technologies for uranium fuel and disposal technologies had been completed for Light Water Reactor (LWR) fuel cycle on the process. These technologies were inherited to utilities and are about to be practical. Now, Japan had been completed High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) a prototype and research reactor, a commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) design Gas Turbine High Temperature Reactor 300 (GTHTR300) with related reprocessing technologies, and is planning domestic demonstration reactor project. In this context, a representative fuel cycle policy is reprocessing in Japan. However, Japan has investigated various fuel cycle scenarios to expand the usage of the commercial HTGR. Then, we would like to introduce the scenarios and development status of related technologies in the present study.
Tobita, Minoru*; Goto, Katsunori*; Omori, Takeshi*; Osone, Osamu*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-011, 32 Pages, 2023/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to the study of radioactivity concentration evaluation methods for radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3, JRR-4 and JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 23 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Takayama, Yusuke; Yamamoto, Yoichi*; Goto, Takahiro*
Jiban Kogaku Janaru (Internet), 18(3), p.317 - 330, 2023/09
It has been reported that the deformation greatly increased in the secondary consolidation process in the past long-term consolidation test of 1.8 years on Na-type bentonite/sand mixed soil. Therefore, we analyzed potential contributing factors in this behavior. A long-term consolidation test for about 10 years on bentonite and kaolinite was started using the test equipment with countermeasures against these factors. In this paper, the secondary consolidation behavior of bentonite was investigated based on the long-term consolidation test data for 2.7, 3.7 and 4 years. The results were generally consistent with the conventional findings on soil mechanics that the deformation due to secondary consolidation progresses linearly with respect to logarithm of time. This test will be continued for about 10 years and longer-term secondary consolidation behavior will be investigated.
Ishibashi, Atsushi; Masui, Kenji; Goto, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Ishikawa, Satoshi*; Ishikawa, Tomoya*
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-19-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.18 - 21, 2023/08
An inner-box typed hot cell for analysis of highly radioactive samples has been operated for about 40 years in Tokai Reprocessing Plant since its installation in 1980. During the operation of analytical hot cell, improvement and upgrades including auxiliary equipment have been performed, in addition to keep the equipment in proper condition through periodic inspections and maintenance. This paper describes about these efforts for analytical hot cell and its results.
Aoya, Juri; Mori, Amami; Sato, Hinata; Kono, Soma; Morokado, Shiori; Horigome, Kazushi; Goto, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo
JAEA-Technology 2023-008, 34 Pages, 2023/06
Flush-out, by which nuclear materials in the Tokai Reprocessing Plant process are recovered, has been started in June 2022 as the first step of decommissioning. Flush-out consists of removal of spent fuel sheared powder, plutonium solution, uranium solution, and the other nuclear materials. Removal of spent fuel sheared powder has been completed in September 2022. During removal of spent fuel sheared powder, uranium concentration, plutonium concentration, acid concentration, radioactivity concentration, and solution density have been analyzed for process control. For nuclear material accountancy, uranium concentration, plutonium concentration, isotope ratio, and solution density have been analyzed. Analysis work including sample pretreatment before transportation to IAEA analytical facility for safeguards, and the other operations related to Flush-out such as calibration of analytical instruments, education, and training of operators are reported.
Fukaya, Yuji; Maruyama, Takahiro; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Higuchi, Hideaki
JAEA-Research 2023-002, 19 Pages, 2023/06
A study on disposal of waste derived from commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor ("HTGR") has been performed. Because of significant difference between the reprocessing of Light Water Reactor ("LWR") and that of HTGR due to difference in structures of the fuel, adoptability of the laws relating to reprocessing waste disposal, which is enacted for LWR, to HTGR waste should be confirmed. Then, we compared the technologies and waste of reprocessing and evaluated radioactivity concentration in graphite waste by activation and contamination based on whole core burn-up calculation. As a result, it was found that SiC residue waste should be disposed of into a geological repository as 2nd class designated radioactive waste in the Designated Radioactive Waste Final Disposal Act (Act No.117 of 2000), by way of amendment of the applicable order, same as hull and end-piece of LWR, and graphite waste should be shallowly disposed of than geological disposal as 2nd class waste for pit disposal in the Act on the Regulation of Nuclear Source Material, Nuclear Fuel Material and Reactors (Act No.166 of 1957) same as a channel box of LWR.
Iyota, Muneyoshi*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Sano, Tomokazu*; Shigeta, Masaya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yumoto, Hirokatsu*; Koyama, Takahisa*; Yamazaki, Hiroshi*; Semba, Yasunori*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; et al.
Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 94, p.424 - 434, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:69.14(Engineering, Manufacturing)Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/05
Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ambai, Hiromu; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/05
Kawasaki, Kohei; Ono, Takanori; Shibanuma, Kimikazu; Goto, Kenta; Aita, Takahiro; Okamoto, Naritoshi; Shinada, Kenta; Ichige, Hidekazu; Takase, Tatsuya; Osaka, Yuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-031, 91 Pages, 2023/02
The document for back-end policy opened to the public in 2018 by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (hereafter, JAEA) states the decommissioning of facilities of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories and JAEA have started gathering up nuclear fuel material of the facilities into Plutonium Fuel Production Facilities (hereafter, PFPF) in order to put it long-term, stable and safe storage. Because we planned to manufacture scrap assemblies almost same with Monju fuel assembly using unsealed plutonium-uranium mixed-oxide (hereafter, MOX) powder held in PFPF and transfer them to storage facilities as part of this "concentration" task of nuclear fuel material, we obtained permission to change the use of nuclear fuel material in response to the new regulatory Requirements in Japan for that. The amount of plutonium (which is neither sintered pellets nor in a lidded powder-transport container) that could be handled in the pellet-manufacturing process was limited to 50 kg Pu or less in order to decrease the facility risk in this manufacture. Therefore, we developed and installed the "MOX weighing and blending equipment" corresponding with small batch sizes that functioned in a starting process and the equipment would decrease handling amounts of plutonium on its downstream processes. The failure data based on our operation and maintenance experiences of MOX fuel production facilities was reflected in the design of the equipment to further improve reliability and maintainability in this development. The completed equipment started its operation using MOX powder in February 2022 and the design has been validated through this half-a-year operation. This report organizes the knowledge obtained through the development of the equipment, the evaluation of the design based on the half-a-year operation results and the issues in future equipment development.