Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hasegawa, Kunio; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Udyawar, A.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 147(3), p.034501_1 - 034501_7, 2025/06
Aoyama, Takahito; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Otani, Kyohei; Igarashi, Takahiro
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111229_1 - 111229_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Be activity concentrations in Dazaifu (western Japan)
Be activity concentrations in Dazaifu (western Japan)Narazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 284, p.107612_1 - 107612_7, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Atmospheric  Be activity concentration was continuously measured in Dazaifu, western Japan, from 1999 to 2020, and its variation was analyzed. Daily
Be activity concentration was continuously measured in Dazaifu, western Japan, from 1999 to 2020, and its variation was analyzed. Daily  Be data analysis, encompassing an analysis for 22 years, revealed a concentration range of not detected - 18 mBq/m
Be data analysis, encompassing an analysis for 22 years, revealed a concentration range of not detected - 18 mBq/m , characterized by substantial monthly variation and smoothed annual variation. An average daily
, characterized by substantial monthly variation and smoothed annual variation. An average daily  Be activity concentration of 5.0
Be activity concentration of 5.0  2.6 mBq/m
2.6 mBq/m was considered to be representative at the ground-surface-level in 30-40
was considered to be representative at the ground-surface-level in 30-40 N. Results from a two-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated statistical significance in monthly and annual
N. Results from a two-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated statistical significance in monthly and annual  Be variabilities. The monthly variability of
Be variabilities. The monthly variability of  Be activity concentration was approximately four times greater than the annual variability. Frequency analysis revealed that the monthly variability comprised major 12-month and minor 6-month periodicities. The substantial decrease in
Be activity concentration was approximately four times greater than the annual variability. Frequency analysis revealed that the monthly variability comprised major 12-month and minor 6-month periodicities. The substantial decrease in  Be activity concentration during summer, a primary driver of monthly variation, was also observed at other locations in Japan, attributed to a stable high-pressure system in the Pacific Ocean that stalled over Japan's southern seas, followed by the inflow of air masses containing low
Be activity concentration during summer, a primary driver of monthly variation, was also observed at other locations in Japan, attributed to a stable high-pressure system in the Pacific Ocean that stalled over Japan's southern seas, followed by the inflow of air masses containing low  Be activity concentrations. The annual variation was primarily influenced by the 11-year solar activity cycle, which affects the intensity of cosmic rays that produce
Be activity concentrations. The annual variation was primarily influenced by the 11-year solar activity cycle, which affects the intensity of cosmic rays that produce  Be.
Be.
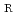 for negative stress ratios R based on trend in experimental data for fatigue crack growth rates of austenitic stainless steels for ASME code Section XI
for negative stress ratios R based on trend in experimental data for fatigue crack growth rates of austenitic stainless steels for ASME code Section XI Negyesi, M.*; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Hasegawa, Kunio; Lacroix, V.*; Morley, A.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 147(2), p.021201_1 - 021201_7, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)
Yamauchi, Hiroki; Metoki, Naoto; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Hong, T.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Hagihara, Masato; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(5), p.054705_1 - 054705_8, 2025/04
 SR
SRIto, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Kotai Butsuri, 60(4), p.197 - 206, 2025/04
We extended the dynamical Kubo-Toyabe model to resolve inconsistencies in a conventional protocol for  SR-based analysis of ion dynamics in solids. Our new model not only provides a means for quantitative analysis based on the immobile-muon assumption, but also offers a method to evaluate the validity of this assumption.
SR-based analysis of ion dynamics in solids. Our new model not only provides a means for quantitative analysis based on the immobile-muon assumption, but also offers a method to evaluate the validity of this assumption.
Chudo, Hiroyuki; Yokoi, Naoto*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Suzuki, Jun*; Imai, Masaki; Sato, Masahiro*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji*
Physical Review Letters, 134(13), p.130603_1 - 130603_5, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Tanizaki, Shiho*; Kubo, Tomohiro*; Bito, Yosuke*; Mori, Shigeki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Sato, Kotaro*
RSC Sustainability (Internet), 3(4), p.1714 - 1720, 2025/04
Namie, Masanari; Saito, Junichi; Oka, Ryotaro*; Kim, J.-H.*
Vacuum, 234, p.114038_1 - 114038_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Sugihara, Kenta*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Saito, Shigeru; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2024-026, 123 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the design of the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) at the J-PARC Transmutation Experimental Facility, a conceptual study was conducted on the J-PARC proton beam irradiation facility. This research was carried out based on the recommendations of the Nuclear Transmutation Technology Evaluation Task Force of the MEXT. The recommendations state that it is desirable to consider facility specifications that can make the most of the benefits of using the existing J-PARC proton accelerator while also solving the engineering issues of the ADS. We considered facilities that could respond to a variety of needs while reducing the facilities that were not needed in the TEF-T design. In order to clarify these diverse needs, we investigated the usage status of representative accelerator facilities around the world. As a result, it became clear that the main purposes of these facilities were (1) Material irradiation, (2) Soft error testing of semiconductor devices using spallation neutrons, (3) Production of RI for medical use, and (4) Proton beam use, and we investigated the facilities necessary for these purposes. In considering the facility concept, we assumed a user community in 2022 and reflected user opinions in the facility design. This report summarizes the results of the conceptual study of the proton irradiation facility, various needs and responses to them, the roadmap for facility construction, and future issues.
Kokubun, Yuji; Hosomi, Kenji; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Koike, Yuko; Hasegawa, Ryo; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Iizawa, Shogo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-053, 116 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution prevention act, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2023. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Hayashizaki, Kohei; Hirooka, Shun; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Saito, Kosuke
Ceramics (Internet), 8(1), p.24_1 - 24_12, 2025/03
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Ito, Yuma*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 8, p.60_1 - 60_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Radiation DNA damage is formed from direct and indirect effects. The direct effect is the interaction between DNA and a radiation, while the indirect effect is the chemical reaction between DNA and radiolytic chemical species. We believed that when the direct effect is induced, multiple lesions are formed within 10 base pairs (about 3.4 nm) of DNA. The damage reduces repair efficiency and induces biological effects. In this study, DNA damage induced by only indirect effects was quantitatively evaluated. Our results indicated that the multiple damage is formed when only 10s of eV energy is deposited to water in the vicinity of DNA, although its formation probability is less than 1%. In other words, the possibility of late biological effects cannot be excluded simply by imparting energy to water in the extreme vicinity of DNA without direct interaction between radiation and DNA. Our results are one of the most important findings for understanding low-dose radiation risk.
 martensitic transformation in Ti-12Mo alloy
martensitic transformation in Ti-12Mo alloyChong, Y.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Inoue, Koji*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.50_1 - 50_11, 2025/03
Strain-induced  martensitic phase transformation (SIMT) critically affects the mechanical properties of metastable
martensitic phase transformation (SIMT) critically affects the mechanical properties of metastable  titanium alloys. In this study, the effects of
titanium alloys. In this study, the effects of  grain size and oxygen content on SIMT in a Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy were systematically investigated. It is found that SIMT is promoted by a decrease in grain size and in oxygen content. The mechanistic origins of the anomalous grain size dependency and the acute oxygen content dependency of SIMT are discussed based on multi-scale microstructural characterization and state-of-the-art simulations. Grain refinement does not raise the energy barrier for SIMT but rather provides more nucleation sites for strain-induced
grain size and oxygen content on SIMT in a Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy were systematically investigated. It is found that SIMT is promoted by a decrease in grain size and in oxygen content. The mechanistic origins of the anomalous grain size dependency and the acute oxygen content dependency of SIMT are discussed based on multi-scale microstructural characterization and state-of-the-art simulations. Grain refinement does not raise the energy barrier for SIMT but rather provides more nucleation sites for strain-induced  martensite, thereby promoting SIMT in fine-grained Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy. In contrast, for the Ti-12wt.%Mo-0.3 wt.%O alloy, oxygen atoms substantially increase the energy barrier for SIMT, due to a change in the local configuration of oxygen atoms during the phase transformation. In addition, atomprobe tomography reveals for the first time that oxygen atoms segregate at
martensite, thereby promoting SIMT in fine-grained Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy. In contrast, for the Ti-12wt.%Mo-0.3 wt.%O alloy, oxygen atoms substantially increase the energy barrier for SIMT, due to a change in the local configuration of oxygen atoms during the phase transformation. In addition, atomprobe tomography reveals for the first time that oxygen atoms segregate at 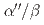 phase boundaries, thereby further restricting the growth of
phase boundaries, thereby further restricting the growth of  martensite.
martensite.
Nakasawa, Hayato*; Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Fujii, Masashi*; Matsumoto, Hironari*; Matsuda, Michiko*; Shimada, Takeshi*; Trivedi, V.*; Tachibana, Makoto*; Tsujii, Naohito*; et al.
Funtai Oyobi Fummatsu Yakin, 72(Suppl.), p.S997 - S1001, 2025/03
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 109, p.1421 - 1436, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Our preceding investigation revealed that multiple hydrogen traps at coherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn
precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn
through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn
interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn
interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
Egashira, Naoya*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Seto, Yusuke*; Ito, Yusuke*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Sano, Tomokazu*; 4 of others*
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(10), p.105903_1 - 105903_8, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Masuki, Yuma*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Umemura, Ayako*; Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Minami, Masayo*; Niwa, Masakazu; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 485, p.136843_1 - 136843_10, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Lacustrine deposits have 30-fold higher As abundance than the average crustal deposit. Arsenic is mostly concentrated as discrete horizons deposited in spring and autumn. As-rich layers contain FeAsS, AsS, and As S
S but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
Osawa, Takahito
Materia, 64(3), p.153 - 156, 2025/03
In order to obtain accurate information on the elemental composition in a sample, it is very important to select an appropriate analytical method, and it is necessary to have a correct understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of each analytical method. This paper introduces prompt gamma-ray analysis as an unusual method that is different from elemental analysis methods that readers may be familiar with, and explains what makes it different from well-known analysis methods. The research on cultural properties conducted with the prompt gamma-ray analysis system (PGA) and future developments will also be described.