Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
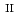 complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transition
complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transitionJi, T.*; Su, S.*; Wu, S.*; Hori, Yuta*; Shigeta, Yasuteru*; Huang, Y.*; Zheng, W.*; Xu, W.*; Zhang, X.*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 63(25), p.e202404843_1 - e202404843_6, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)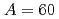
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:77.95(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Tsurumi, Miwa*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Ikkatai, Yuko*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; Shinoda, Taro*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Tsuji, Naoki*; Diniz, G.*; Kataoka, Jun*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 50(13), p.e2023GL103612_1 - e2023GL103612_9, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:63.69(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary) -edge X-ray absorption fine structure study of
-edge X-ray absorption fine structure study of  -type
-type 
 CuO
CuO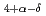 (
(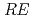 = Rare Earth); Toward unified understanding of electronic state of
= Rare Earth); Toward unified understanding of electronic state of 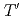 -type cuprate
-type cuprateChen, Y.*; Asano, Shun*; Wang, T.*; Xie, P.*; Kitayama, Shinnosuke*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Taniguchi, Takanori*; Fujita, Masaki*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 38, p.011050_1 - 011050_6, 2023/05
Wang, Y.*; Jia, G.*; Cui, X.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Q.*; Gu, L.*; Zheng, L.*; Li, L. H.*; Wu, Q.*; Singh, D. J.*; et al.
Chem, 7(2), p.436 - 449, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:277 Percentile:99.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Taiki*; Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Boll, R. A.*; Brewer, N. T.*; Van Cleve, S.*; Dean, D. J.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(5), p.052502_1 - 052502_6, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:85.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Martikainen, J.*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Schatz, T.*; Nakashima, Hitoshi*; Okihara, Mitsunobu*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sato, Toshinori
Proceedings of the Nordic Grouting Symposium 2019 (Internet), 13 Pages, 2019/09
This paper shows a result of the part of the study on characterisation of penetration of the colloidal silica grout (CSG) under saline groundwater, aiming to understand the impact of salinity on grout penetration by verifying the improved penetration theory with laboratory tests. This theory was proposed to add a time factor  to the existing penetration theory of Funehag, especially under the saline groundwater conditions. A series of grout injection tests by the fracture test system were performed. The CSG of one European and Japanese were injected in the system, filled with the five different groundwater simulants. All no-flow tests were successful, resulting in the formation of relatively homogeneous gelled zones. Based on the analysis of acquired
to the existing penetration theory of Funehag, especially under the saline groundwater conditions. A series of grout injection tests by the fracture test system were performed. The CSG of one European and Japanese were injected in the system, filled with the five different groundwater simulants. All no-flow tests were successful, resulting in the formation of relatively homogeneous gelled zones. Based on the analysis of acquired  , it was found that as an alternative method, designing a longer gel time by multiplying the inverse value of
, it was found that as an alternative method, designing a longer gel time by multiplying the inverse value of  can be proposed to attain the required penetration. Although the results were fruitful, further investigation is necessary to develop this penetration theory.
can be proposed to attain the required penetration. Although the results were fruitful, further investigation is necessary to develop this penetration theory.
Miradji, F.; Suzuki, Chikashi; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Suzuki, Eriko; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko; Barrachin, M.*; Do, T. M. D.*; Murakami, Kenta*; Suzuki, Masahide*
Proceedings of 9th Conference on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2019) (Internet), 21 Pages, 2019/03
Pokor, C.*; Herbelin, A.*; Couvant, T.*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
NEA/NSC/R(2016)5 (Internet), p.317 - 360, 2017/05
In aged BWR plants, certain locations in the mid-plane of the core shroud experience fluence levels at which the materials become susceptible to irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC). BWRVIP (Boiling Water Reactor Vessel Internals Program) has developed crack growth disposition methodologies for evaluating intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) in the internal components of BWRs and the Japan Nuclear Energy Safety organization (JNES) has been conducting a project related to IASCC crack growth rate data as a part of safety research and development study for the aging management and maintenance of the nuclear power plants. Although many investigators proposed prediction models for SCC and IASCC growth rates for austenitic stainless steels and Ni alloys, even more improvements of models are necessary as compared with the detailed experimental results, because these models are still preliminary models.
 high energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy
high energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopyCui, Y.-T.*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Hatanaka, Tatsuya*; Nakamura, Naoki*; Ando, Masaki*; Yoshida, Toshihiko*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Oji, Hiroshi*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.1482_1 - 1482_8, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:48.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ruan, Y.*; Gibson, B. C.*; Lau, D. W. M.*; Greentree, A. D.*; Ji, H.*; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.*; Johnson, B. C.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Monro, T. M.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 5, p.11486_1 - 11486_7, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Ni
NiChiara, C. J.*; Weisshaar, D.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Harker, J. L.*; Walters, W. B.*; Recchia, F.*; Albers, M.*; Alcorta, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(4), p.044309_1 - 044309_10, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:90.88(Physics, Nuclear)The neutron-rich isotope  Ni was produced by multi-nucleon transfer reactions of
Ni was produced by multi-nucleon transfer reactions of  Zn in the Argonne National Laboratory, and an in-beam
Zn in the Argonne National Laboratory, and an in-beam  -ray experiment were performed using the GRETINA array. The
-ray experiment were performed using the GRETINA array. The 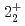 and
and 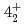 levels of
levels of  Ni were observed for the first time. Those levels are regarded as large deformed states associated with proton excitation from the
Ni were observed for the first time. Those levels are regarded as large deformed states associated with proton excitation from the 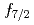 orbit because they cannot be reproduced by a shell-model calculation assuming a small valence space without
orbit because they cannot be reproduced by a shell-model calculation assuming a small valence space without 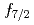 . A theoretical analysis based on the Monte Carlo shell model published in 2014 indicates that those levels corresponds to a prolate deformed band. The present result demonstrates the occurrence of shape coexistence in neutron-rich Ni isotopes other than a known case of
. A theoretical analysis based on the Monte Carlo shell model published in 2014 indicates that those levels corresponds to a prolate deformed band. The present result demonstrates the occurrence of shape coexistence in neutron-rich Ni isotopes other than a known case of  Ni, and confirms the predictive power of the Monte Carlo shell-model calculation.
Ni, and confirms the predictive power of the Monte Carlo shell-model calculation.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Imabayashi, Yoichi*; Itashiki, Yutaro*; Satoh, Daiki; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.81 - 87, 2015/02
Cancer therapy using heavy ion beam has been adopted as highly advanced medical treatment by reason of its clinical advantages. It has become more important to estimate the risk of secondary cancer from recent survey. During treatment, secondary particles such as neutrons and -rays are producedby heavy ion induced nuclear reactions in a patient body as well as beam delivery apparatuses. For the risk assessment of secondary cancer, it is essential to know contribution of secondary neutrons by extra dose to organs in the vicinity of the irradiated tumor because the secondary neutron has a long flight path length and gives undesired dose to normal tissues in a wide volume. The experimental data of neutron energy spectra are required for dose estimations with high accuracy. Especially, precise data around neutron energy of 1 MeV is required because neutron of the energy region has a large relative biological e ectiveness. Estimation of the secondary neutron yield data is important for estimation of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities.
Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Hashiguchi, Taro*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Satoh, Daiki; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Song, T. Y.*; Lee, C. W.*; Kim, J. W.*; Yang, S. C.*; Koba, Yusuke*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.127 - 132, 2015/02
Particle transport Monte Carlo codes such as PHITS, FLUKA and so on are used for radiation safety design of high energy accelerators. The validity of code is confirmed by comparison with many experimental data. In this study, we report proton, deuteron, and triton production double differential cross sections (DDXs) from a graphite target by 290 MeV/nucleon Ar ions. The measured spectra are compared with those calculated by PHITS and FLUKA codes.
Ruan, Y.*; Ji, H.*; Johnson, B. C.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Greentree, A. D.*; Gibson, B. C.*; Monro, T. M.*; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.*
Optical Materials Express (Internet), 5(1), p.73 - 87, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:80.93(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Buiron, L.*; Rimpault, G*; Fontaine, B.*; Kim, T. K.*; Stauff, N. E.*; Taiwo, T. A.*; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Gulliford, J.*; Fridmann, E.*; Pataki, I.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; The Role of Reactor Physics toward a Sustainable Future (PHYSOR 2014) (CD-ROM), 16 Pages, 2014/09
Within the activities of the Working Party on Scientific Issues of Reactor Systems (WPRS) of the OECD, an international collaboration is ongoing on the neutronic analyses of several Generation-IV Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) concepts. This paper summarizes the results obtained by participants from institutions of different countries (ANL, CEA, ENEA, HZDR, JAEA, CER, KIT, UIUC) for the large core numerical benchmarks. These results have been obtained using different calculation methods and analysis tools to estimate the core reactivity and isotopic composition evolution, neutronic feedbacks and power distribution. For the different core concepts analyzed, a satisfactory agreement was obtained between participants despite the different calculation schemes used. A good agreement was generally obtained when comparing compositions after burnup, the delayed neutron fraction, the Doppler coefficient, and the sodium void worth. However, some noticeable discrepancies between the k-effective values were observed and are explained in this paper. These are mostly due to the different neutronic libraries employed (JEFF3.1, ENDFB7.0 or JENDL-4.0) and to a lesser extent the calculations methods.
 113 of the 113th element
113 of the 113th elementMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yoneda, Akira*; Tanaka, Kengo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(10), p.103201_1 - 103201_4, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:178 Percentile:97.29(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An isotope of the 113th element,  113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a
113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a  Zn beam on a
Zn beam on a  Bi target. We observed six consecutive
Bi target. We observed six consecutive  decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of
decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of  Db and
Db and  Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of
Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of  113,
113, 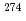 Rg (Z = 111),
Rg (Z = 111), 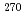 Mt (Z = 109),
Mt (Z = 109),  Bh (Z = 107),
Bh (Z = 107),  Db (Z = 105), and
Db (Z = 105), and  Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope
Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope  113, of the 113th element.
113, of the 113th element.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:74.58(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 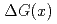 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:192 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.83(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.