Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Izumi, Yoshinobu*; Matsuo, Yoichiro*; Sakamoto, Ayako; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Kojima, Takao*; Shimizu, Kikuo*
no journal, ,
In cases of ion-beam irradiations, several features of deep interest can be observed, contrasting with the low-LET radiations such as  -rays. In order to elucidate the induction mechanisms of mutations peculiar to ion beams, carbon-ion beams with LETs of 13 keV/
-rays. In order to elucidate the induction mechanisms of mutations peculiar to ion beams, carbon-ion beams with LETs of 13 keV/ m - 107 keV/
m - 107 keV/ m and proton beam with LET of 0.45 keV/
m and proton beam with LET of 0.45 keV/ m were irradiated to budding yeast. Carbon-ion beams and proton beam irradiation were performed in TIARA or HIMAC, and WERC, respectively. After irradiations, survival ratios and mutation frequencies were analyzed as well as sequencing and gene expression analyses. In order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis caused by radiations, we used
m were irradiated to budding yeast. Carbon-ion beams and proton beam irradiation were performed in TIARA or HIMAC, and WERC, respectively. After irradiations, survival ratios and mutation frequencies were analyzed as well as sequencing and gene expression analyses. In order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis caused by radiations, we used 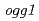 (BER-) which is deficient in the elimination of 8-oxodGTP and
(BER-) which is deficient in the elimination of 8-oxodGTP and 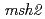 (MMR-) deficient in the mismatch-repair function. For comparison, we also used
(MMR-) deficient in the mismatch-repair function. For comparison, we also used 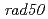 (NHEJ-) and
(NHEJ-) and 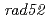 (HR-) that were deficient in the double-strand breaks (DSBs)-repair function.
(HR-) that were deficient in the double-strand breaks (DSBs)-repair function.
Hayakawa, Kosetsu; Masebo, Yumeno*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Kojima, Yoichiro*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
Soil clay minerals are expected to be a new thermoelectric material in the high temperature range, but the mechanism of their thermoelectricity has not been clarified yet. We have focused on weathered biotite (WB), a soil clay mineral composed of elements such as Si, Fe, Al, Mg, and K. We have found that the structure of WB changes under high temperature conditions, which can be observed by infrared absorption spectroscopy. In-situ observation by infrared absorption spectroscopy has shown that the structure of WB changes under high temperature conditions. However, the detailed structure has not yet been identified. In this study, we developed a method for synchrotron XAFS analysis of WB at high temperatures, where thermoelectric properties are observed, and succeeded in obtaining data from room temperature up to 873K.
Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Masebo, Yumeno*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Kojima, Yoichiro*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
We have been studying the development of functional materials derived from WB as an application of molten-salt treatment technology. We have experimentally demonstrated that Sr can be adsorbed on the interlayer of WB by molten-salt treatment. However, the correlation between Cs adsorption and Sr adsorption has not yet been clarified, although Sr adsorption was examined for Cs adsorbed WB in a previous study. Therefore, in this study, the amount and structure of Sr adsorption with and without Cs adsorption were investigated using XRF, XRD and XAFS. The results showed that the Sr adsorption dependence may differ depending on the presence or absence of Cs in WB.