Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakurai, Junya*; Torigata, Keisuke*; Matsunaga, Manabu*; Takanashi, Naoto*; Hibino, Shinya*; Kizu, Kenichi*; Morita, Akira*; Inomoto, Masahiro*; Shimohata, Nobuaki*; Toyota, Kodai; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 111(5), p.246 - 262, 2025/04
 Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg
O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain
chainFujihara, Masayoshi; Jeschke, H. O.*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114408_1 - 114408_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)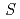 = 1/2 Heisenberg
= 1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd
chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and
O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and  SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the
SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the 
 -
-
 antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions
antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions 
 and
and 
 are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of
are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of 
 is two to three times larger than that of
is two to three times larger than that of 
 , thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of
, thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of 
 . The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K (
. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K ( 0.036
0.036 
 ), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:92.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) = 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph
= 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrographIto, Yuta*; Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Arai, Fumiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 120(15), p.152501_1 - 152501_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:92.72(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Masses of 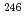 Es,
Es, 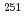 Fm and the transfermium nuclei
Fm and the transfermium nuclei 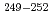 Md, and
Md, and  No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed
No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed 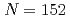 neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of
neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of 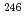 Es and
Es and  Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of
Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of  Md as anchor points for
Md as anchor points for  decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to
decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to  Bh and
Bh and  Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter
Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter 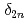 derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed
derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed 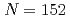 neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cho, S.*; Hyodo, Tetsuo*; Jido, Daisuke*; Ko, C. M.*; Lee, S. H.*; Maeda, Saori*; Miyahara, Kenta*; Morita, Kenji*; Nielsen, M.*; Onishi, Akira*; et al.
Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, 95, p.279 - 322, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:113 Percentile:89.92(Physics, Nuclear)With upgraded detectors at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), it has become possible to measure hadrons beyond their ground states in high energy heavy ion collisions. Therefore, heavy ion collisions provide a new method for studying exotic hadrons that are either molecular states made of various hadrons or compact system consisting of muliquarks. Because their structures are related to the fundamental properties of Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD), studying exotic hadrons is currently one of the most active areas of research in hadron physics. The present review is a summary of the current understanding of a selected set of exotic candidate particles that can be potentially measured in heavy ion collisions.
Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; MacCormick, M.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 407, p.160 - 165, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:79.30(Instruments & Instrumentation)Various isotopes of Ac, Ra, Fr, and Rn were produced by fusion-evaporation reactions using a  Ca beam. The energetic ions were stopped in and extracted from a helium gas cell. The extracted ions were identified using a multi-reflection time-of-fight mass spectrograph. In all cases, it was observed that the predominant charge state for the extracted ions, including the alkali Fr, was 2+.
Ca beam. The energetic ions were stopped in and extracted from a helium gas cell. The extracted ions were identified using a multi-reflection time-of-fight mass spectrograph. In all cases, it was observed that the predominant charge state for the extracted ions, including the alkali Fr, was 2+.
Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Kaji, Daiya*; Arai, Fumiya*; MacCormick, M.*; Murray, I.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Jeong, S.*; Kimura, Sota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(1), p.011305_1 - 011305_6, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:94.99(Physics, Nuclear)Using a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph located after a gas cell coupled with the gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS-II, the masses of several  -decaying heavy nuclei were directly and precisely measured. The nuclei were produced via fusion-evaporation reactions and separated from projectilelike and targetlike particles using GARIS-II before being stopped in a helium-filled gas cell. Time-of-flight spectra for three isobar chains,
-decaying heavy nuclei were directly and precisely measured. The nuclei were produced via fusion-evaporation reactions and separated from projectilelike and targetlike particles using GARIS-II before being stopped in a helium-filled gas cell. Time-of-flight spectra for three isobar chains,  Fr-
Fr- Rn-
Rn- At-
At- Po,
Po,  Fr-
Fr-  Rn-
Rn- At-
At- Po-
Po- Bi, and
Bi, and  Fr-
Fr- Rn-
Rn- At, were observed. Precision atomic mass values were determined for
At, were observed. Precision atomic mass values were determined for 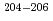 Fr,
Fr, 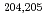 Rn, and
Rn, and 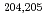 At. Identifications of
At. Identifications of  Bi,
Bi, 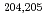 Po,
Po,  Rn, and
Rn, and  At were made with N
At were made with N 10 detected ions, representing the next step toward use of mass spectrometry to identify exceedingly low-yield species such as superheavy element ions.
10 detected ions, representing the next step toward use of mass spectrometry to identify exceedingly low-yield species such as superheavy element ions.
 Nb and
Nb and  Ta for chemical studies of element 105, Db, using the GARIS gas-jet system
Ta for chemical studies of element 105, Db, using the GARIS gas-jet systemHuang, M.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Murakami, Masashi*; Asai, Masato; Kaji, Daiya*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Kikutani, Yuki*; Komori, Yukiko*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 304(2), p.845 - 849, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.43(Chemistry, Analytical)A technique to utilize radioisotopes of Nb and Ta was developed for chemical studies of element 105, Db, by coupling a gas-jet transport system to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS). The short-lived  Nb and
Nb and  Ta were produced with nuclear reactions using a
Ta were produced with nuclear reactions using a  F beam whose energy was the same as that to produce
F beam whose energy was the same as that to produce  Db. Then, they were separated with GARIS and extracted to a chemistry laboratory with the gas-jet transport system. By changing only magnetic field of GARIS and inserting an energy degrader and a shutter for recoil ions, we could deliver the
Db. Then, they were separated with GARIS and extracted to a chemistry laboratory with the gas-jet transport system. By changing only magnetic field of GARIS and inserting an energy degrader and a shutter for recoil ions, we could deliver the  Nb and
Nb and  Ta to a chemistry device for
Ta to a chemistry device for  Db without changing other experimental conditions.
Db without changing other experimental conditions.
 Db in the
Db in the  Cm(
Cm( F,5
F,5 )
) Db reaction and decay properties of
Db reaction and decay properties of  Db and
Db and  Lr
LrHaba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Murakami, Masashi*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sakai, Ryutaro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 89(2), p.024618_1 - 024618_11, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:81.83(Physics, Nuclear)Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; Morita, Toshimasa; Sasaki, Akira; Terakawa, Kota*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2012; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.147, p.117 - 120, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We have developed the femto-second laser pump and soft X-ray laser probe system in order to observe the dynamical processes of the femto-second laser ablation. By using this system, we succeed to obtain the temporal evolution of the soft X-ray reflectivity from the laser induced Pt surface. The results lead that the rate of decrease in the reflectivity of the probe beam has a non-linear relation with the pump laser fluence.
Schury, P. H.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Naimi, S.*; Sonoda, Tetsu*; Mita, Koki*; Takamine, Aiko*; Okada, Kunihiro*; Wollnik, H.*; Chon, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 317(Part B), p.537 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:88.70(Instruments & Instrumentation)A multi-reflection time-of-flight (MRTOF) mass spectrograph has been implemented at RIKEN to provide high-precision mass measurements of very short-lived nuclei. Of particular interest are mass measurements of r-process nuclei and trans-uranium nuclei. In such nuclei, the MRTOF can perform on par with or better than traditional Penning trap systems. We demonstrate that the MRTOF-MS is capable of accurately attaining relative mass precision of  m/m
m/m  10
10 and describe it's utility with heavy, short-lived nuclei.
and describe it's utility with heavy, short-lived nuclei.
 Cm +
Cm +  O reaction
O reactionMurakami, Masashi*; Goto, Shinichi*; Murayama, Hirofumi*; Kojima, Takayuki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 88(2), p.024618_1 - 024618_8, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:71.33(Physics, Nuclear)Production cross sections of Rf isotopes in the  Cm +
Cm +  O reaction were measured at the beam energy range of 88.2 to 101.3 MeV by use of a gas-filled recoil ion separator. The excitation functions of
O reaction were measured at the beam energy range of 88.2 to 101.3 MeV by use of a gas-filled recoil ion separator. The excitation functions of 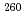 Rf,
Rf, 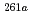 Rf, and
Rf, and  Rf were obtained together with those of spontaneously fissioning nuclides which have few-second half-lives and have been assigned to
Rf were obtained together with those of spontaneously fissioning nuclides which have few-second half-lives and have been assigned to 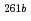 Rf and a longer-lived state of
Rf and a longer-lived state of  Rf. The excitation function of few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide exhibited the maximum cross section at the
Rf. The excitation function of few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide exhibited the maximum cross section at the  O beam energy of 94.8 MeV. The shape of the excitation function was almost the same as that of
O beam energy of 94.8 MeV. The shape of the excitation function was almost the same as that of 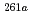 Rf, whereas it was quite different from those of
Rf, whereas it was quite different from those of 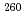 Rf and
Rf and  Rf. A few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide previously reported as
Rf. A few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide previously reported as 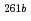 Rf and
Rf and  Rf observed in
Rf observed in Cm +
Cm +  O reaction was identified as
O reaction was identified as 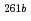 Rf.
Rf.
Koike, Fumihiro*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kato, Takako*; Morita, Shigeru*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Sudo, Shigeru*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.202 - 211, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.30(Physics, Applied)Atomic ionic states and transition properties of elements with atomic numbers Z ranging from 50 to 80 are discussed as these are important to the understanding of plasmas containing such heavy elements. As such, data productions and the current status of theoretical calculations in this field are discussed. Further, recent spectroscopic measurements and respective theoretical analyses for W, Gd, and Nd are provided.
Morita, Shigeru*; Dong, C. F.*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Hasuo, Masahiro*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Nakamura, Nobuyuki*; Oishi, Tetsutaro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.143 - 152, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:99.13(Physics, Applied)Tungsten spectra have been observed from Large Helical Device (LHD) and Compact electron Beam Ion Trap (CoBIT) in wavelength ranges of visible to EUV. The tungsten spectra from LHD are well analyzed based on the knowledge from CoBIT tungsten spectra. The C-R model code has been developed to explain the UTA spectra in details. Radial profiles of EUV spectra from highly ionized tungsten ions have been measured and analyzed by impurity transport simulation code with ADPAK atomic database code to examine the ionization balance determined by ionization and recombination rate coefficients. The ablation cloud of the impurity pellet is directly measured with visible spectroscopy.
 113 of the 113th element
113 of the 113th elementMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yoneda, Akira*; Tanaka, Kengo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(10), p.103201_1 - 103201_4, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:179 Percentile:97.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An isotope of the 113th element,  113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a
113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a  Zn beam on a
Zn beam on a  Bi target. We observed six consecutive
Bi target. We observed six consecutive  decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of
decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of  Db and
Db and  Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of
Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of  113,
113, 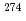 Rg (Z = 111),
Rg (Z = 111), 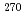 Mt (Z = 109),
Mt (Z = 109),  Bh (Z = 107),
Bh (Z = 107),  Db (Z = 105), and
Db (Z = 105), and  Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope
Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope  113, of the 113th element.
113, of the 113th element.
 Sg in the
Sg in the  Cm(
Cm( Ne,5
Ne,5 )
) Sg reaction and decay properties of two isomeric states in
Sg reaction and decay properties of two isomeric states in  Sg
SgHaba, Hiromitsu*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sakai, Ryutaro*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Physical Review C, 85(2), p.024611_1 - 024611_11, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:91.18(Physics, Nuclear)Two isomeric states in  Sg, i.e,
Sg, i.e,  Sg
Sg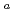 and
and  Sg
Sg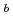 were produced in the
were produced in the  Cm(
Cm( Ne,5
Ne,5 ) reaction. Decay properties of
) reaction. Decay properties of  Sg
Sg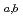 were investigated with a rotating-wheel apparatus for
were investigated with a rotating-wheel apparatus for  and spontaneous fission (SF) spectrometry under low background condition attained by a gas-jet transport system coupled to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator. Based on genetically correlated
and spontaneous fission (SF) spectrometry under low background condition attained by a gas-jet transport system coupled to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator. Based on genetically correlated  -
- (-
(- ) and
) and  -SF decay chains, 18 and 24 events were assigned to
-SF decay chains, 18 and 24 events were assigned to  Sg
Sg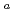 and
and  Sg
Sg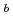 , respectively. The half-life and
, respectively. The half-life and  -particle energy of
-particle energy of  Sg
Sg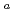 were measured to be
were measured to be 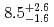 s and
s and 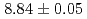 MeV, respectively, and those of
MeV, respectively, and those of  Sg
Sg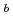 were
were 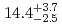 s and
s and 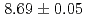 MeV.
MeV.
Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Egusa, Soichiro*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Kirishima, Akira*; Yamagishi, Isao; Morita, Yasuji; Yamana, Hajimu*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 290(2), p.475 - 478, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:86.52(Chemistry, Analytical)Palladium complexation in concentrated nitric acid solutions was studied by UV/Vis absorption spectrophotometry. The ionic strength of the solutions was fixed to  = 1, 3, or 5 M by mixing of HNO
= 1, 3, or 5 M by mixing of HNO and HClO
and HClO . The major palladium species were found to be Pd
. The major palladium species were found to be Pd , PdNO
, PdNO
 , and Pd(NO
, and Pd(NO )
) . The formation constant of PdNO
. The formation constant of PdNO
 was determined to be
was determined to be 
 = 1.32 (
= 1.32 ( = 1 M), 1.49 (
= 1 M), 1.49 ( = 3 M), or 1.47 (
= 3 M), or 1.47 ( = 5 M), while that of Pd(NO
= 5 M), while that of Pd(NO )
) to be
to be 
 = 0.45 (
= 0.45 ( = 3 M) or 0.14 (
= 3 M) or 0.14 ( = 5 M).
= 5 M).
 Hs and
Hs and  Hs
HsSato, Nozomi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(9), p.094201_1 - 094201_7, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.60(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of  Hs and
Hs and  Hs produced in the
Hs produced in the 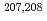 Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, 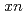 ) [
) [ =1, 2] reactions were studied using a gas-filled recoil ion separator at the linear accelerator facility of RIKEN. A total of 6 decay chains were assigned to
=1, 2] reactions were studied using a gas-filled recoil ion separator at the linear accelerator facility of RIKEN. A total of 6 decay chains were assigned to  Hs. Cross sections for the
Hs. Cross sections for the  Hs production in the
Hs production in the  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe,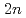 ) and
) and  Pb(
Pb( Fe,
Fe, ) reactions were measured to be
) reactions were measured to be 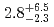 pb and
pb and 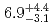 pb, respectively. The isotope
pb, respectively. The isotope  Hs decayed with a half-life of
Hs decayed with a half-life of 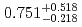 ms by
ms by  -particle emission and spontaneous fission. The
-particle emission and spontaneous fission. The  -particle energy of
-particle energy of  Hs was observed at 10.61
Hs was observed at 10.61 0.04 and 10.80
0.04 and 10.80 0.08 MeV. The spontaneous fission branch of
0.08 MeV. The spontaneous fission branch of  Hs was found to be
Hs was found to be 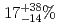 .
.
Tajikara, Masayoshi*; Yasue, Kenichi; Yanagida, Makoto*; Furusawa, Akira*; Tanaka, Norifumi*; Morita, Yoshimune*; Sugai, Toshihiko
Chirigaku Hyoron, 84(2), p.118 - 130, 2011/03
Many papers reported that Quaternary climate and sea-level fluctuations have controlled riverbed elevation in the river basins in the northeastern Japan. However, in the southwestern Japan, such climatic-controlled riverbed fluctuations have not been reported, except a few reports based on uncertain chronological data. In this research, we investigated fluvial terraces along the Tokigawa river that flows through the low relief mountainous areas, and examined whether riverbed fluctuations similar to these in rivers in the northeastern Japan occurred in the river basin. We mapped fluvial terraces based on air photo analysis, and inferred the age and climate at the time of formation of these terraces based on  C dating, tephra analysis, and pollen analysis. Based on results of these analyses, we concluded that the fluvial terraces in the river basin have been formed in consequence of the riverbed fluctuation linked to the climate change.
C dating, tephra analysis, and pollen analysis. Based on results of these analyses, we concluded that the fluvial terraces in the river basin have been formed in consequence of the riverbed fluctuation linked to the climate change.