Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C control rods in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors during meltdown; B-Li isotopic signatures in cesium-rich microparticles
C control rods in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors during meltdown; B-Li isotopic signatures in cesium-rich microparticles笛田 和希*; 高見 龍*; 蓑毛 健太*; 諸岡 和也*; 堀江 憲路*; 竹原 真美*; 山崎 信哉*; 斉藤 拓巳*; 塩津 弘之; 大貫 敏彦*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, p.128214_1 - 128214_10, 2022/04
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:68.71(Engineering, Environmental)Boron carbide control rods remain in the fuel debris of the damaged reactors in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, potentially preventing re-criticality; however, the state and stability of the control rods remain unknown. Sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe analyses have revealed B-Li isotopic signatures in radioactive Cs-rich microparticles (CsMPs) that formed by volatilization and condensation of Si-oxides during the meltdowns. The CsMPs contain 1518-6733 mg kg of
of 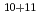 B and 11.99-1213 mg kg
B and 11.99-1213 mg kg of Li. The
of Li. The  B/
B/ B (4.15-4.21) and
B (4.15-4.21) and  Li/
Li/ Li (213-406) isotopic ratios are greater than natural abundances (
Li (213-406) isotopic ratios are greater than natural abundances ( 4.05 and
4.05 and  12.5, respectively), indicating that
12.5, respectively), indicating that  B(n,
B(n, )
) Li reactions occurred in B
Li reactions occurred in B C prior to the meltdowns. The total amount of B released with CsMPs was estimated to be 0.024-62 g, suggesting that essentially all B remains in reactor Units 2 and/or 3 and is enough to prevent re-criticality; however, the heterogeneous distribution of B needs to be considered during decommissioning.
C prior to the meltdowns. The total amount of B released with CsMPs was estimated to be 0.024-62 g, suggesting that essentially all B remains in reactor Units 2 and/or 3 and is enough to prevent re-criticality; however, the heterogeneous distribution of B needs to be considered during decommissioning.
諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
本研究は動的な引張-圧縮間その場中性子回折を用いて濃度変調と構造変調を伴ったシンクロ型LPSOマグネシウム合金の可逆繰り返し硬化挙動を調査することを目的とする。最大引張応力と最大圧縮応力は繰返し数の増加に伴い上昇し、繰返し数200回時の最大引張応力と最大圧縮応力はそれぞれ+97.4 and -176.7MPaである。これは、最大圧縮応力が圧縮変形時に生じる双晶(キンク帯)の影響により最大引張応力よりも大きくなったと示唆しており、このキンク帯は、動的な引張-圧縮間の(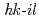 )結晶粒群の積分強度の変化から可逆的生成・消滅が生じている証拠が本実験手法により得られている。
)結晶粒群の積分強度の変化から可逆的生成・消滅が生じている証拠が本実験手法により得られている。
木谷 悠二*; 柴原 正和*; 生島 一樹*; 西川 聡*; 古川 敬*; 秋田 貢一; 鈴木 裕士; 諸岡 聡; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; et al.
no journal, ,
ショット粒衝突時の荷重分布をモデル化し、理想化陽解法FEMに対して導入することで、ショットピーニングによって発生する残留応力を予測可能な解析システムを構築した。次いで、ショットピーニングを施工した異材円筒多層溶接試験体に対して軸方向圧縮荷重を負荷し、荷重負荷状態および負荷後の弾性ひずみ分布を中性子回折により測定した。その結果、解析値と実測値の定性的傾向は互いに対応することが確認され、構築した解析システムの妥当性が示された。
鈴木 裕士; 諸岡 聡; 秋田 貢一; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
中性子応力測定の信頼性に影響する系統誤差について、見かけひずみと無応力状態の格子定数について、それらが中性子応力測定の正確度に及ぼす影響についてまとめた。以下に要点をまとめて示す。飛行時間中性子回折法においては、入射ビームの発散が見かけひずみの大きさに影響する。一方、角度分散中性子回折法における見かけひずみは、モノクロメータの曲率半径や入射スリットサイズによって決まる波長分布やビーム発散分布に影響される。また、測定体積内において粗大結晶粒が偏在する場合や、急激な集合組織変化を有する場合にも、見かけひずみを生じる場合がある。これら見かけひずみは、測定に用いる光学系の最適化とモデルによる補正により、実用上十分なレベルまで見かけひずみを低減することができるが、それでも不十分な場合やモデル化が困難な場合には、試料を180度フリップする前後で測定したひずみ分布を平均化することで、見かけひずみをキャンセルすることができる。一方、角度分散法では、中性子ビームパスに生じるブラッグエッジの影響により、材料深部で見かけひずみを生じる場合があるが、入射ビームの波長をブラッグエッジから外すことにより、その影響を取り除くことができる。無応力状態の格子定数測定においては、巨視応力の解放のため、Comb標準試験体の歯幅サイズを3mm以下とすることが望ましい。
諸岡 聡; Gong, W.*; 相澤 一也; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Recently, a series of magnesium alloys containing a 18R Long-Period Stacking Ordered (LPSO) structure, have attracted considerable attention because they exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and reasonable ductility. To determine the plastic deformation behaviour of LPSO structure and the origin of the deformation mechanism are important for further materials development. In this study, deformation-kinking behavior of a Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy was investigated by in-situ neutron diffraction during cyclic deformation. In-situ TOF neutron diffraction experiments during tension-compression and compression-tension cyclic loading at room temperature were performed by TAKUMI at MLF of J-PARC. The peak stress in the compression is larger than that of the tension, suggesting that quasi-twinning accompanying with hardening was occurred in compression deformation. On the other hand, results of individual (hkl) lattice strains in the loading direction show that, the (60.0) family grains in the loading direction accommodated a greater portion of elastic strain than that of the (00.18) family grains in the loading direction start accommodated less portion. This indicated that the latter started to yield prior to that of the former, causing the former to carry more applied load, i.e., intergranular stress. The large intergranular stresses generated with the progress of deformation, were speculated to accelerate the backward plastic flow that resulting in an increase of the Bauschinger stress and Bauschinger strain.
alloy was investigated by in-situ neutron diffraction during cyclic deformation. In-situ TOF neutron diffraction experiments during tension-compression and compression-tension cyclic loading at room temperature were performed by TAKUMI at MLF of J-PARC. The peak stress in the compression is larger than that of the tension, suggesting that quasi-twinning accompanying with hardening was occurred in compression deformation. On the other hand, results of individual (hkl) lattice strains in the loading direction show that, the (60.0) family grains in the loading direction accommodated a greater portion of elastic strain than that of the (00.18) family grains in the loading direction start accommodated less portion. This indicated that the latter started to yield prior to that of the former, causing the former to carry more applied load, i.e., intergranular stress. The large intergranular stresses generated with the progress of deformation, were speculated to accelerate the backward plastic flow that resulting in an increase of the Bauschinger stress and Bauschinger strain.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.*; 山下 享介; 諸岡 聡; 原田 剛*; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
TAKUMI is a time-of-flight neutron diffractometer dedicated for engineering materials sciences. Experiments in TAKUMI vary from internal strain mapping in engineering components, microstructural evolutions during deformations of structural or functional materials at various temperatures, microstructural evolutions during manufacturing (thermo-mechanical) processes, as well as texture analyses of engineering materials. In the presentation, the current status of TAKUMI, its sample environmental devices, the scientific trends in TAKUMI and some research examples will be introduced.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.*; 山下 享介; 諸岡 聡; 鈴木 裕士; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
TAKUMI is a time-of-flight neutron diffractometer dedicated for engineering materials sciences, which was installed at beamline 19 in Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility of J-PARC. Careful analysis of the Bragg peaks in a neutron diffraction pattern can reveal important structural details of a sample material such as internal stresses, phase conditions, dislocations, texture etc. Experiments in TAKUMI vary from internal strain mapping in engineering components, microstructural evolutions during deformations of structural or functional materials at various temperatures, microstructural evolutions during manufacturing (thermo-mechanical) processes, as well as texture analyses of engineering materials. In the presentation, the current status of TAKUMI, its sample environmental devices, the scientific trends in TAKUMI and some research examples will be introduced.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 土田 紀之*; 諸岡 聡; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
Transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) phenomenon is paid attention because it gives a high work-hardening rate and a large uniform elongation as a result of deformation induced martensitic transformation during plastic loading. The deformation induced martensitic transformations in most metastable iron alloys occur after macro-yielding during deformation at room temperature (RT). There are arguments to explain whether the martensitic transformation during plastic loading is controlled by strain (the strain-induced transformation) or stress (the stress-assisted transformation). In this paper, we tried to observe the trigger of deformation induced martensitic transformation during tensile deformation by in situ tensile loading neutron diffraction (ND) of metastable iron alloys. In situ ND measurements during deformation have been confirmed as powerful tools to understand the strengthening mechanism during deformation of multiphase alloys.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; 相澤 一也
no journal, ,
TAKUMIは、材料工学や機械工学に関わる材料研究のための飛行時間型中性子回折装置である。機械部品内のひずみ・応力マッピング,構造材料または機能材料の低温から高温までの広い温度範囲の変形下での組織(結晶構造変化,欠陥,内部応力等)変化、製造(加工熱処理)過程での組織(結晶構造変化,欠陥等)変化、及び工学材料の集合組織測定である。最近流行の高エントロピー合金及び日本で開発された新概念のミルフィーユ構造材料に関する研究も行われている。これらの実験を行うために、TAKUMIは様々な試料環境装置を独自に、またはユーザーと一緒に開発した。