Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Muraoka, Ami*; Chiyonobu, Shun*; Arato, Hiroyuki*; Martizzi, P.*; Ishii, Eiichi
Sekiyu Gijutsu Kyokai-shi (CD-ROM), 87(1), p.86 - 88, 2022/00
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kenji*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Tokuzawa, Tokihiko*; Akiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Shoji, Mamoru*; Michael, C. A.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 58(1), p.70 - 90, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle confinement processes were studied in detail on LHD. Diffusion coefficients (D) and convection velocities (V) were estimated from density modulation experiments. The magnetic configuration and collisionality were widely scanned in order to investigate parameter dependences of D and V. In order to study the effect of the magnetic configuration, magnetic axis positions (R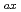 ) were scanned from 3.5 m to 3.9 m. This scan changed the magnetic ripples quite significantly, enabling the effects of neoclassical properties on measured values to be widely elucidated. Dependences of electron temperature (T
) were scanned from 3.5 m to 3.9 m. This scan changed the magnetic ripples quite significantly, enabling the effects of neoclassical properties on measured values to be widely elucidated. Dependences of electron temperature (T ) and helically trapped normalized collsionality (
) and helically trapped normalized collsionality (
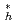 ), where
), where 
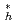 =1 indicates a rough boundary between the 1/
=1 indicates a rough boundary between the 1/ and plateau regimes, were examined using the heating power scan of neutral beam injection (NBI). It was found out that generally larger (or smaller) contributions of neoclassical transport resulted in more hollow (or peaked) density profiles. The larger neoclassical contribution was found to be situated at a more outwardly shifted R
and plateau regimes, were examined using the heating power scan of neutral beam injection (NBI). It was found out that generally larger (or smaller) contributions of neoclassical transport resulted in more hollow (or peaked) density profiles. The larger neoclassical contribution was found to be situated at a more outwardly shifted R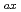 for the same T
for the same T , and higher T
, and higher T or lower
or lower 
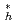 at each R
at each R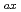 . However, it is to be noted that R
. However, it is to be noted that R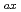 =3.5 m showed different characteristics from these trends in that this case showed a more peaked density profile at higher T
=3.5 m showed different characteristics from these trends in that this case showed a more peaked density profile at higher T .
.
Tanaka, Kenji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Comparative studies were carried out in LHD heliotron and JT-60U tokamak plasmas to elucidate the most essential parameter(s) for control of density profiles in toroidal systems. A difference in the collisionality dependence was found between the two devices. In LHD, the density peaking factor decreased with decrease of the collisionality at the magnetic axis position (R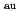 ) 3.6 m, while the density peaking factor gradually increased with a decreased of collisionality at R
) 3.6 m, while the density peaking factor gradually increased with a decreased of collisionality at R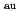 = 3.5 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. The difference in the collisionality dependence between R
= 3.5 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. The difference in the collisionality dependence between R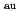 = 3.5 and R
= 3.5 and R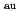 = 3.6 m is likely due to the contribution of the anomalous transport. At R
= 3.6 m is likely due to the contribution of the anomalous transport. At R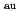 = 3.5 m, larger anomalous transport caused a similar collisionality dependence. Change of the fluctuation property was observed with different density profiles in the plasma core region on both devices. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. For a magnetic axis positions (R
= 3.5 m, larger anomalous transport caused a similar collisionality dependence. Change of the fluctuation property was observed with different density profiles in the plasma core region on both devices. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. For a magnetic axis positions (R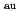 ) at 3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P
) at 3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P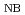 was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. Change of density profiles from peaked to hollow indicates change in the convection direction. This is due to increase in neoclassical processes. The reduction of the density peaking factor with increase of P
was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. Change of density profiles from peaked to hollow indicates change in the convection direction. This is due to increase in neoclassical processes. The reduction of the density peaking factor with increase of P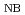 in LHD is partly due to the neoclassical effect and partly due to the anomalous effect.
in LHD is partly due to the neoclassical effect and partly due to the anomalous effect.
Tanaka, Kenji*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Tokuzawa, Tokihiko*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 3, p.S1069_1 - S1069_7, 2008/08
Density profiles in LHD were measured and particle transport coefficients were estimated from density modulation experiments in LHD. The dataset of different magnetic axis, toroidal magnetic filed and heating power provided data set of widely scanned neoclassical transport. At minimized neoclassical transport configuration (
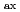 = 3.5 m,
= 3.5 m, 
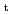 = 2.8 T) showed peaked density profile. Its peaking factor increased gradually with decrease of collisional frequency. This is a similar result observed in JT-60U. At other configuration, peaking factor reduced with decrease of collsional frequency. Data set showed that larger contribution of neoclassical transport produced hollowed density profile. Comparison between neoclassical and estimated particle diffusivity showed different minimum condition. Clear difference of spatial profile of turbulence was observed between hollowed and peaked density profiles. Major part of fluctuation existed in the unstable region of ion temperature gradient mode.
= 2.8 T) showed peaked density profile. Its peaking factor increased gradually with decrease of collisional frequency. This is a similar result observed in JT-60U. At other configuration, peaking factor reduced with decrease of collsional frequency. Data set showed that larger contribution of neoclassical transport produced hollowed density profile. Comparison between neoclassical and estimated particle diffusivity showed different minimum condition. Clear difference of spatial profile of turbulence was observed between hollowed and peaked density profiles. Major part of fluctuation existed in the unstable region of ion temperature gradient mode.
 O
O ; Understanding of the details of the Ising spin and the competitive interactions which made the devil's flower bloom
; Understanding of the details of the Ising spin and the competitive interactions which made the devil's flower bloomOwada, Kenji; Fujii, Yasuhiko; Muraoka, Jiro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Noda, Yukio*; Osumi, Hiroyuki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Isobe, Masahiko*; et al.
Hoshako, 21(2), p.87 - 96, 2008/03
Devil's flower has been found in a temperature-pressure phase diagram of NaV O
O , which shows a charge disproportionation (CD) at ambient pressure. By a complementary use of an X-ray structural analysis and a resonant X-ray diffraction, which is sensitive to CD, we have investigated the structural relationship between two ground states appeared in lower and higher pressure regions including the charge arrangements. It has been clarified that two equivalent types of charge arrangement in CD correspond to the Ising variable in NaV
, which shows a charge disproportionation (CD) at ambient pressure. By a complementary use of an X-ray structural analysis and a resonant X-ray diffraction, which is sensitive to CD, we have investigated the structural relationship between two ground states appeared in lower and higher pressure regions including the charge arrangements. It has been clarified that two equivalent types of charge arrangement in CD correspond to the Ising variable in NaV O
O . The atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. The results lead us to the conclusion that it is the first time that the devil's flower blooms in a charge-disproportionation system. The results also lead us to a hypothesis that the competitive interactions between a Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
. The atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. The results lead us to the conclusion that it is the first time that the devil's flower blooms in a charge-disproportionation system. The results also lead us to a hypothesis that the competitive interactions between a Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
 O
O under high pressure; A Synchrotron X-ray diffraction study
under high pressure; A Synchrotron X-ray diffraction studyOwada, Kenji; Fujii, Yasuhiko; Muraoka, Jiro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi; Noda, Yukio*; Osumi, Hiroyuki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Isobe, Masahiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 76(9), p.094113_1 - 094113_10, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:44.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Structural relations between two ground states of the ANNNI (Axial Next Nearest Neighbor Ising) compound NaV O
O , C
, C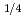 - and C
- and C -phases below and above the transition pressure
-phases below and above the transition pressure 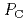 = 1 GPa, were investigated by X-ray diffraction and scattering techniques. The structure of the C
= 1 GPa, were investigated by X-ray diffraction and scattering techniques. The structure of the C -phase is well explained by the
-phase is well explained by the  (
(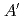 ) pattern which is one of four layers (
) pattern which is one of four layers (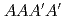 ) of the C
) of the C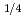 -phase, however, the amount of the atomic shifts under the conditions 1.6 GPa and 6 K is 27% that under ambient pressure. On the other hand, resonant X-ray scattering showed that the charges are disproportionated under high pressure. Based on these facts, it was concluded that charge disproportionation corresponds to the Ising variable in NaV
-phase, however, the amount of the atomic shifts under the conditions 1.6 GPa and 6 K is 27% that under ambient pressure. On the other hand, resonant X-ray scattering showed that the charges are disproportionated under high pressure. Based on these facts, it was concluded that charge disproportionation corresponds to the Ising variable in NaV O
O , where the atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. These results lead to the hypothesis that the competitive interactions between the Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
, where the atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. These results lead to the hypothesis that the competitive interactions between the Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
 O
O uniquely determined by resonant X-ray scattering
uniquely determined by resonant X-ray scatteringOwada, Kenji; Fujii, Yasuhiko; Katsuki, Yuya*; Muraoka, Jiro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi; Sawa, Hiroshi*; Ninomiya, Emi*; Isobe, Masahiko*; Ueda, Yutaka*
Physical Review Letters, 94(10), p.106401_1 - 106401_4, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:72.06(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The present resonant X-ray scattering has been performed on a monoclinically-split single domain of NaV O
O . The observation of a critically enhanced contrast between V
. The observation of a critically enhanced contrast between V and V
and V ions has led us to the unequivocal conclusion of the charge-order pattern of low-temperature phase of NaV
ions has led us to the unequivocal conclusion of the charge-order pattern of low-temperature phase of NaV O
O below
below  = 35 K. In spite of the possible four types of configuration of the zig-zag-type charge-order patterns in the
= 35 K. In spite of the possible four types of configuration of the zig-zag-type charge-order patterns in the 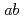 -plane (A, A', B and B'), the stacking sequence along the
-plane (A, A', B and B'), the stacking sequence along the  -axis is determined as the AAA'A' type by comparison with model calculations. By assigning the A and A' configurations to Ising spins, one can reasonably explain the previously discovered "devil's staircase"-type behavior with respect to the modulation of layer-stacking sequences at high pressures and low temperatures, which clearly resembles the global phase diagram theoretically predicted by the ANNNI model.
-axis is determined as the AAA'A' type by comparison with model calculations. By assigning the A and A' configurations to Ising spins, one can reasonably explain the previously discovered "devil's staircase"-type behavior with respect to the modulation of layer-stacking sequences at high pressures and low temperatures, which clearly resembles the global phase diagram theoretically predicted by the ANNNI model.
Zushi, Hideki*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Mitarai, Osamu*; Nishitani, Takeo; Nagashima, Akira; Muraoka, Katsunori*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 76(2), p.145 - 162, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Muraoka, Ami*; Arato, Hiroyuki*; Chiyonobu, Shun*; Ishii, Eiichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kenji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Urano, Hajime; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Yamagishi, Osamu*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to understand particle transport systematically in toroidal plasmas, a density profile was compared in LHD helical and JT-60U tokamak plasmas. In large tokamak devices such as JT-60U, the density profile is always peaked and the peaked density profile can be explained based on outward diffusion flux and inward convection flux driven by microinstability. A peaking factor of the density profile was increased with decreasing collisionality. On the other hand, the density profile was changed from peaked one to hollow one depending on discharge conditions in LHD. The hollow density profile can be explained based on outward convection flux driven by neoclassical transport and inward diffusion flux driven by microinstability. In the configuration with a small helical ripple, where the neoclassical transport is reduced, the density profile tended to be peaked and dependence of the peaking factor on the collisionality was similar to that in tokamak plasmas. These results indicated that magnetic field ripple and microinstability are some of the main mechanisms determining the density profile.
Tanaka, Kenji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to understand mechanisms for determining density profiles in toroidal plasmas, density profiles were compared in JT-60U tokamak and LHD helical plasmas. Transport theory indicates that neoclassical transport is enhanced in helical plasmas with low collisionality due to helical ripple. In JT-60U plasmas, density peaking increased with decreasing the collisionality. In LHD plasmas for magnetic axis (Rax) of 3.5m with small effective helical ripple, density peaking slightly increased with decreasing the collisionality as similar to that in tokamak plasmas. On the other hand, in LHD plasmas for Rax 3.6m with relatively large effective helical ripple, density profile became hollow as the collisionality decreased. Different turbulence structures are observed for Rax=3.5m and Rax=3.6m in LHD plasmas. Turbulence propagated towards electron diamagnetic direction for Rax=3.5m and towards ion diamagnetic direction for Rax=3.6m. This difference could be related to the difference of density profiles, as well as difference of neoclassical transport. Furthermore, when density decreased in the core region due to increase of electron temperature, it was found that turbulence was first modified in the edge region and then in the core region.
3.6m with relatively large effective helical ripple, density profile became hollow as the collisionality decreased. Different turbulence structures are observed for Rax=3.5m and Rax=3.6m in LHD plasmas. Turbulence propagated towards electron diamagnetic direction for Rax=3.5m and towards ion diamagnetic direction for Rax=3.6m. This difference could be related to the difference of density profiles, as well as difference of neoclassical transport. Furthermore, when density decreased in the core region due to increase of electron temperature, it was found that turbulence was first modified in the edge region and then in the core region.
Muraoka, Ami*; Arato, Hiroyuki*; Chiyonobu, Shun*; Ishii, Eiichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kenji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Mishchenko, A.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; et al.
no journal, ,
Comparative studies were carried out in LHD heliotron and JT-60U tokamak plasmas to elucidate effects of turbulence transport on density profiles in toroidal systems. A difference in the collisionality dependence was found between the two devices. In LHD, the density peaking factor decreased with decrease of the collisionality at the magnetic axis position (R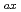 ) of 3.6 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. For R
) of 3.6 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. For R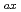 =3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P
=3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P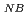 was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. The effects of curvature pinch on density profiles were also investigated in both devices. The curvature pinch produces a peaked density profile in JT-60U and a hollow density profile in LHD depending on their magnetic shear. However, these effects were too small to explain the density profiles observed in both devices.
was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. The effects of curvature pinch on density profiles were also investigated in both devices. The curvature pinch produces a peaked density profile in JT-60U and a hollow density profile in LHD depending on their magnetic shear. However, these effects were too small to explain the density profiles observed in both devices.