Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Sekine, Manabu; Endo, Toshiaki; Yamagata, Ichiro; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Tanno, Takashi; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-030, 57 Pages, 2013/11
It is necessary to develop the fast reactor core materials, which can achieve high-burnup operation improving safety and economical performance. Ferritic steels are expected to be good candidate core materials to achieve this objective because of their excellent void swelling resistance. Therefore, oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel and 11Cr-ferritic/martensitic steel (PNC-FMS) have been respectively developed for cladding and wrapper tube materials in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In this study, the effects of fast neutron irradiation on mechanical properties and microstructure of 9Cr-and 12Cr-ODS steel claddings for fast reactor were investigated. Specimens were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo using the CMIR-6 at temperatures between 420 and 835 C to fast neutron doses ranging from 16 to 33 dpa. The post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at irradiation temperatures.
C to fast neutron doses ranging from 16 to 33 dpa. The post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at irradiation temperatures.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Yano, Yasuhide; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Koyama, Shinichi; Tanaka, Kenya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(5), p.470 - 480, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)Four experimental fuel assemblies (EFAs) containing 9Cr-ODS steel cladding fuel pins were previously irradiated in the BOR-60. One of the EFAs achieved the best data, a peak burn-up of 11.9at% and a neutron dose of 51 dpa, without any microstructure instability or any fuel pin rupture. On the other hand, in another EFA (peak burn-up, 10.5at%; peak neutron dose, 44 dpa), peculiar irradiation behaviors such as microstructure instability and fuel pin rupture occurred. The combined effects of matrix Cr heterogeneity (presence of metallic Cr inclusions) and high-temperature irradiation were concluded to be the main cause of the peculiar microstructure change of 9Cr-ODS steel cladding tubes in the BOR-60 irradiation tests. They contributed to the fuel pin rupture.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Yano, Yasuhide; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Koyama, Shinichi; Tanaka, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/12
This paper describes evaluation results of in-reactor integrity of 9Cr and 12Cr-ODS steel cladding tubes and the plan for reliability improvement in homogeneous tube production. A fuel assembly in the BOR-60 irradiation test including 9Cr and 12Cr-ODS fuel pins has achieved the highest burn-up, i.e. peak burn-up of 11.9at% and peak neutron dose of 51dpa, without any fuel pin rupture and microstructure instability. In another fuel assembly containing 9Cr and 12Cr-ODS steel fuel pins whose peak burn-up was 10.5at%, one 9Cr-ODS steel fuel pin failed near the upper end of the fuel column. A peculiar microstructure change occurred in the vicinity of the ruptured area. The primary cause of this fuel pin rupture and microstructure change was shown to be the presence of metallic Cr inclusions in the 9Cr-ODS steel tube, which had passed an ultrasonic inspection test for defects. In the next stage from 2011 to 2013, the fabrication technology of full pre-alloy 9Cr-ODS steel cladding tube will be developed.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*
JAEA-Research 2009-050, 57 Pages, 2010/01
It is important to understand EDZ in assessing performance of repository and designing of plug. It is known that it remains possible that the large-scale EDZ is generated due to strain localization from boring investigations and tunnel excavation analyses and rock properties changes with increase of depth. Excavation analysis of vertical shaft in sedimentary rock taken into account strain softening, depth variation of rock properties and the actual construction procedure had been done in order to understand EDZ of Horonobe URL. The large-scale EDZ due to strain localization was generated around the border between Koetoi formation and Wakkanai formation. From result obtained from excavation analysis, scale of EDZ obtained from excavation analysis is from 60 cm to 120 cm. And it was estimated that seismic velocity changed by 20 percent, elastic modulus changed by 30 percent and hydraulic conductivity changed by 0.1 m/s order.
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya
Dai-12-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.933 - 940, 2008/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is planning to conduct researches into geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes in the Horonobe site located in Hokkaido, Japan. As part of the underground research facilities, two 500m-long vertical shafts have been constructed in tertiary sedimentary rocks since 2005. The surrounding rocks are known to exhibit strain-softening characteristics, necessitating appropriate modelling in the stability analysis. In addition the rocks physical properties often vary with depth. This study shows the results of three-dimensional numerical analysis of the ventilation shaft, taking the construction sequence and the variation of rock properties with depth into consideration.
Kinomura, Koji*; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Matsui, Hiroya; Sanada, Hiroyuki
Dai-37-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.307 - 312, 2008/01
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Matsui, Hiroya; Sanada, Hiroyuki
Dai-37-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.301 - 306, 2008/01
no abstracts in English
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Jo, Mayumi*; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Heisei-19-Nendo Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Hokkaido Shibu Sokai Oyobi Shunki Koenkai Koen Yoshishu, p.9 - 10, 2007/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting the Horonobe Underground Reseach Laboratory Project as a part of geological isolation research and development at Horonobe-town in Hokkaido, Japan. The rocks around URL have high porosity and low permeability. Therefore, the excess pore pressure caused by URL excavation is possible to affect to the stability of surrounding rock. In this point of view, the authors carried out a stress-seepage coupled analysis to understand the process of the pore pressure change due to excavation and the influence to the stability of surrounding rock and support system. As a result, the large excess pore pressure causes a part in surrounding rock on excavation in an anisotropic initial stress condition and it dissipates with time. The pore pressure change causes the complex deformation in the surrounding rock as well. However, the phenomena are not significant influence to the stability of the surrounding rock and support system.
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Jo, Mayumi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Horii, Hideyuki*
Dai-36-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.39 - 44, 2007/01
In case rock exhibits time-dependent deformation, it is important to evaluate this effect on the tunnel stability, since the rock deforms elastically as well as inelatically even at the time of excavation. This paper introduces an engineering approach method to explain the effect of time-dependent deformation of rock at tunnel excavation stages on the stability. The mechanical parameters to describe a Burgers type rheological model are determined, based upon the drained triaxial creep test results performed on mudstone samples. With the parameters determined, plane-strain 2 dimensional numerical analyses are subsequently performed. In the analysis a couple of indices to describe the degree and timing of time-dependent deformation are introduced with reference to the instantaneous elastic deformation, and their effects on the amount of deformation and support pressure subsequent to the support erection are investigated.
Homma, Toshimitsu; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Togawa, Orihiko
Hoken Butsuri, 36(4), p.308 - 313, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
Aramaki, Takafumi; Mizushima, Toshihiko; Kuji, Tomoyuki*; Povinec, P. P.*; Togawa, Orihiko
Radiocarbon, 43(2B), p.857 - 867, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
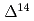 C in the north pacific and the pursuit of the anthropogenic carbon
C in the north pacific and the pursuit of the anthropogenic carbonAramaki, Takafumi; Watanabe, Shuichi*; Tsunogai, Shizuo*; Kuji, Tomoyuki*; Mizushima, Toshihiko; Togawa, Orihiko
JAERI-Conf 2000-019, p.73 - 75, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Aramaki, Takafumi; Mizushima, Toshihiko; Mizutani, Yoshihiko*; Yamamoto, Tadatoshi; Togawa, Orihiko; Kabuto, Shoji*; Kuji, Tomoyuki*; Gottdang, A.*; Klein, M.*; Mous, D. J. W.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 172(1-4), p.18 - 23, 2000/10
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:81.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Homma, Toshimitsu; Togawa, Orihiko; Takahashi, Tomoyuki
BIOMOVS: Proc. of Symp. on the Validity of Environmental Transfer Models, p.447 - 455, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Kinomura, Koji*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kwon, E.*; Komatsu, Kenichiro*; Yamada, Yoichi*; Hasegawa, Yuri*; Sato, Sho*; Sakai, Seiji; Kawachi, Kazuhiko*; Yokoo, Kuniyoshi*; Ono, Shoichi*; Kasama, Yasuhiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Kinomura, Koji*; Matsui, Hiroya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiroi, Kosuke; Ogawa, Tomoyuki*
no journal, ,
Izawa, Kazuhiko; Maekawa, Tomoyuki; Aoyama, Yasuo; Sono, Hiroki; Ogawa, Kazuhiko; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English