Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Polevoi, A. R.*; Loarte, A.*; 林 伸彦; Kim, H. S.*; Kim, S. H.*; Koechl, F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Medvedev, S. Yu.*; 村上 匡且*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063019_1 - 063019_8, 2015/05
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:84.89(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The operational space (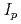 -
- ) for long pulse scenarios of ITER was assessed by 1.5D core transport modelling with pedestal parameters predicted by the EPED1 code. The analyses include the majority of transport models presently used for interpretation of experiments and ITER predictions. The EPED1 code was modified to take into account boundary conditions predicted by SOLPS for ITER. In contrast with standard EPED1 assumptions, EPED1 with the SOLPS boundary conditions predicts no degradation of the pedestal pressure as density is reduced. Lowering the plasma density to
) for long pulse scenarios of ITER was assessed by 1.5D core transport modelling with pedestal parameters predicted by the EPED1 code. The analyses include the majority of transport models presently used for interpretation of experiments and ITER predictions. The EPED1 code was modified to take into account boundary conditions predicted by SOLPS for ITER. In contrast with standard EPED1 assumptions, EPED1 with the SOLPS boundary conditions predicts no degradation of the pedestal pressure as density is reduced. Lowering the plasma density to 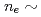 5-6
5-6  10
10 m
m leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure), which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to
leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure), which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to 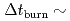 1000 s with Q
1000 s with Q 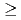 5 for
5 for 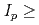 13 MA at moderate normalised pressure (
13 MA at moderate normalised pressure (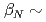 2). These ITER plasmas require the same level of additional heating power as the reference Q = 10 inductive scenario at 15 MA. However, unlike the "hybrid" scenarios considered previously, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios with
2). These ITER plasmas require the same level of additional heating power as the reference Q = 10 inductive scenario at 15 MA. However, unlike the "hybrid" scenarios considered previously, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios with 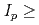 13 MA present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse Q
13 MA present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse Q 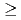 5 and deserve further analysis and experimental demonstration in present tokamaks.
5 and deserve further analysis and experimental demonstration in present tokamaks.
Polevoi, A. R.*; 林 伸彦; Kim, H. S.*; Kim, S. H.*; Koechl, F.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Loarte, A.*; Medvedev, S. Yu.*; 村上 匡且*; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 37D, p.P2.135_1 - P2.135_4, 2013/07
Long-pulse operation 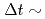 1000 s with
1000 s with 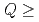 5 is foreseen in ITER to demonstrate high neutron fluence scenarios which can be of use for the nuclear technology and for the TBM. In this study we address the viability of achieving ITER's long-pulse scenario in plasma regimes with H-mode confinement level by characterizing the current-density operational space and the achievable Q with long pulse burning phases. The EPED1 model with boundary conditions from SOLPS predicts no degradation of pedestal pressure with decreasing density in ITER. Modelling of core transport with 1.5D transport models carried out with pedestal parameters predicted by EPED1+SOLPS indicate that there is a large operational space for long pulse plasma operation with high fusion gain
5 is foreseen in ITER to demonstrate high neutron fluence scenarios which can be of use for the nuclear technology and for the TBM. In this study we address the viability of achieving ITER's long-pulse scenario in plasma regimes with H-mode confinement level by characterizing the current-density operational space and the achievable Q with long pulse burning phases. The EPED1 model with boundary conditions from SOLPS predicts no degradation of pedestal pressure with decreasing density in ITER. Modelling of core transport with 1.5D transport models carried out with pedestal parameters predicted by EPED1+SOLPS indicate that there is a large operational space for long pulse plasma operation with high fusion gain 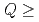 5. Reducing the plasma density to
5. Reducing the plasma density to 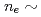 5-6 10
5-6 10 m
m leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure) which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to
leads to an increased plasma temperature (similar pedestal pressure) which reduces the loop voltage and increases the duration of the burn phase to 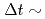 1000 s with
1000 s with 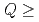 5 for
5 for 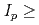 13 MA at moderate normalised pressure,
13 MA at moderate normalised pressure, 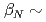 2. Unlike the "hybrid" scenarios, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the majority of the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse.
2. Unlike the "hybrid" scenarios, these H-mode plasmas do not require specially shaped q profiles nor improved confinement in the core for the majority of the transport models considered in this study. Thus, these medium density H-mode plasma scenarios present an attractive alternative to hybrid scenarios to achieve ITER's long pulse.
Snyder, P. B.*; 相羽 信行; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; 鎌田 裕; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085035_1 - 085035_8, 2009/08
被引用回数:170 パーセンタイル:98.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)中間波長のMHDモードの安定性解析は、トカマクペデスタル性能やELM機構の理解を進めるうえで重要である。近年のペデスタル領域における高精度計測及び高精度安定性解析コードの実現により、複数の大・中型トカマク装置において周辺MHD安定性解析が実現し、実験結果の理解や実験プランの策定及びプラズマ性能の向上に貢献している。本論文では、複数のトカマク装置における周辺MHD安定限界を、標準的な(Type-I)ELMのみならず小振幅ELM及びELM-freeな領域において評価し、それらを比較する。さらに、ペデスタル幅を予測するテストモデルとペデスタルの高さに対する安定性からの制約を合わせて考慮することで、ペデスタルの高さと幅を予測する新たなモデル(EPED1)を開発した。このモデルをこれまでの実験結果に適用したテスト結果、及びこのモデルを用いて行ったITERでのペデスタルの高さの予測についての初期結果を報告する。
Callen, J. D.*; Anderson, J. K.*; Arlen, T. C.*; Bateman, G.*; Budny, R. V.*; 藤田 隆明; Greenfield, C. M.*; Greenwald, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Hill, D. N.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1449 - 1457, 2007/11
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:25.84(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)最近開発されたパレオクラシカル輸送モデルが多数のトロイダルプラズマ装置のデータと比較された。DIII-D, Alcator C-MOD, NSTXのオーム加熱レベルのプラズマ,RTPの電子サイクロトロン波加熱プラズマ,JT-60Uの強い電子内部輸送障壁プラズマ,MST逆磁場ピンチ,SSPXスフェロマックの実験データを用いた。モデルから予想される径方向の電子熱輸送は、オーム加熱レベルの幅広い実験結果と一致し、2倍程度の誤差で電子熱輸送の下限を与えると思われる。
鎌田 裕; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
周辺ペデスタル研究の進展とITERへ向けた予測について、最近の世界の研究をレビューする。周辺ペデスタル構造を決めるパラメータリンケージを明らかにするとともに、プラズマ過程と原子分子過程の両方がペデスタル幅を決定すること,周辺圧力勾配がピーリングバルーニング理論で系統的に説明できること,計測機器の進展によってELMの発展が明らかとなり非線形理論で説明可能であること,小振幅ELMの系統的同定がすすんだことなど、大きな発展があった。これらに基づいて、ITERのプラズマ性能の予測,ELMの小規模化等の検討が大きく進んだ。