Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 岡部 博孝*; Li, B.*; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 175, p.111199_1 - 111199_8, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:15.7(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Muon spin rotation ( SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe
SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe . The detailed investigation of the
. The detailed investigation of the  SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Applied Physics, 130(19), p.195701_1 - 195701_7, 2021/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:7.86(Physics, Applied)Hydrogen defects sometimes form shallow impurity levels in semiconductors, and it is an important topic for semiconductor research to investigate their details. One of the experimental methods to determine the state of hydrogen is the muon spin rotation ( SR) experiment. By observing formation of a pseudo-hydrogen atom, called muonium, it is possible to investigate the hydrogen defect levels. In a previous theoretical study, the pinning levels were calculated for various materials as a reference for hydrogen defect levels, and these levels were universally distributed near the hydrogen electrode potential. Based on the prediction,
SR) experiment. By observing formation of a pseudo-hydrogen atom, called muonium, it is possible to investigate the hydrogen defect levels. In a previous theoretical study, the pinning levels were calculated for various materials as a reference for hydrogen defect levels, and these levels were universally distributed near the hydrogen electrode potential. Based on the prediction,  SR experiments were performed for germanium sulfide (GeS) and germanium telluride (GeTe), where the hydrogen electrode potential is located in the bandgap for GeS, but not for GeTe. As a result, the
SR experiments were performed for germanium sulfide (GeS) and germanium telluride (GeTe), where the hydrogen electrode potential is located in the bandgap for GeS, but not for GeTe. As a result, the  SR spectra showed that the muonium forms in GeS, while it does not in GeTe. In GeS, 58
SR spectra showed that the muonium forms in GeS, while it does not in GeTe. In GeS, 58 of the muons formed muoniums. The activation energy was obtained as
of the muons formed muoniums. The activation energy was obtained as 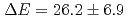 meV. The hyperfine coupling frequency was
meV. The hyperfine coupling frequency was 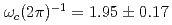 GHz, and the Bohr radius of muonium was 1.3 times larger than that in vacuum. These properties indicated that the identified muonium does not form a typical impurity level that affects the electrical properties.
GHz, and the Bohr radius of muonium was 1.3 times larger than that in vacuum. These properties indicated that the identified muonium does not form a typical impurity level that affects the electrical properties.
 Mn
Mn N films with ferrimagnetic compensation
N films with ferrimagnetic compensation伊藤 啓太*; 安富 陽子*; Zhu, S.*; Nurmamat, M.*; 田原 昌樹*; 都甲 薫*; 秋山 了太*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; 小口 多美夫*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(10), p.104401_1 - 104401_8, 2020/03
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:73.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spintronics devices utilizing a magnetic domain wall motion have attracted increasing attention, and ferrimagentic materials with almost compensated magnetic moments are highly required to realize the fast magnetic domain wall motion. Here, we report a key function for this purpose in anti-perovskite Co Mn
Mn N films. Perpendicular magnetization emerges for
N films. Perpendicular magnetization emerges for 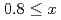 , and the saturation magnetization reaches a minimum value at
, and the saturation magnetization reaches a minimum value at 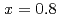 .
.
 atoms in Ni
atoms in Ni Fe
Fe N (
N (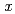 = 1 and 3) films revealed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and magnetic circular dichroism
= 1 and 3) films revealed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and magnetic circular dichroism高田 郁弥*; 伊藤 啓太*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; 高梨 弘毅*; 木村 昭夫*; 末益 崇*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 2(2), p.024407_1 - 024407_5, 2018/02
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:48.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism measurements were performed at the Ni and Fe 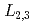 absorption edges for Ni
absorption edges for Ni Fe
Fe N (
N (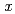 = 1 and 3) epitaxial films. Shoulders at approximately 2 eV above the Ni
= 1 and 3) epitaxial films. Shoulders at approximately 2 eV above the Ni 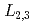 main peaks in the XAS spectrum of Ni
main peaks in the XAS spectrum of Ni FeN were interpreted to originate from hybridization of orbitals between Ni 3
FeN were interpreted to originate from hybridization of orbitals between Ni 3 at face-centered (II) sites and N 2
at face-centered (II) sites and N 2 at body-centered sites, while such features were missing in NiFe
at body-centered sites, while such features were missing in NiFe N film. Similar shoulders were observed at Fe
N film. Similar shoulders were observed at Fe 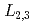 edges in both films. Hence, Ni atoms preferentially occupied corner (I) sites, where the hybridization was weak because of the relatively long distance between Ni at I sites and N atoms. The relatively large magnetic moment deduced from sum-rule analysis of NiFe
edges in both films. Hence, Ni atoms preferentially occupied corner (I) sites, where the hybridization was weak because of the relatively long distance between Ni at I sites and N atoms. The relatively large magnetic moment deduced from sum-rule analysis of NiFe N also showed a good agreement with the presence of Ni atoms at I sites.
N also showed a good agreement with the presence of Ni atoms at I sites.
 N films revealed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
N films revealed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism伊藤 啓太*; 都甲 薫*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; 小口 多美夫*; 末益 崇*; 木村 昭夫*
Journal of Applied Physics, 117(19), p.193906_1 - 193906_6, 2015/05
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:52.35(Physics, Applied)We performed XAS and XMCD measurements at Fe L and N K-edges for Fe
and N K-edges for Fe N epitaxial films grown by MBE. We compared experimental XAS and XMCD spectra with those simulated by a combination of a first-principles calculation and Fermi's golden rule. We revealed that the shoulders observed at Fe L
N epitaxial films grown by MBE. We compared experimental XAS and XMCD spectra with those simulated by a combination of a first-principles calculation and Fermi's golden rule. We revealed that the shoulders observed at Fe L -edges in the XAS and XMCD spectra were due to the electric dipole transition from the Fe 2p core-level to the hybridization state generated by
-edges in the XAS and XMCD spectra were due to the electric dipole transition from the Fe 2p core-level to the hybridization state generated by 
 anti-bonding between the orbitals of N 2p at the body-centered site and Fe 3d on the face-centered (II) sites. Thus, the observed shoulders were attributed to the local electronic structure of Fe atoms at II sites. As to the N K-edge, the line shape of the obtained spectra was explained by the dipole transition from the N 1s core-level to the hybridization state formed by
anti-bonding between the orbitals of N 2p at the body-centered site and Fe 3d on the face-centered (II) sites. Thus, the observed shoulders were attributed to the local electronic structure of Fe atoms at II sites. As to the N K-edge, the line shape of the obtained spectra was explained by the dipole transition from the N 1s core-level to the hybridization state formed by 
 and
and 
 anti-bondings between the Fe 3d and N 2p orbitals.
anti-bondings between the Fe 3d and N 2p orbitals.
 Fe
Fe N (x = 0, 3, 4) films grown by molecular beam epitaxy
N (x = 0, 3, 4) films grown by molecular beam epitaxy伊藤 啓太*; 佐内 辰徳*; 安富 陽子*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; 都甲 薫*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; 木村 昭夫*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Applied Physics, 115(17), p.17C712_1 - 17C712_3, 2014/05
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:60.33(Physics, Applied)We evaluated orbital (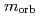 ) and spin magnetic moments (
) and spin magnetic moments (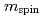 ) of Co
) of Co Fe
Fe N (x = 0, 3, 4) epitaxial thin films grown by molecular beam epitaxy using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism, and discussed the dependence of these values on x. Site-averaged
N (x = 0, 3, 4) epitaxial thin films grown by molecular beam epitaxy using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism, and discussed the dependence of these values on x. Site-averaged 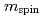 value of Fe atoms was deduced to be 1.91
value of Fe atoms was deduced to be 1.91 
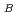 per atom, and that of Co atoms to be 1.47
per atom, and that of Co atoms to be 1.47 
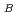 per atom in Co
per atom in Co FeN at 300 K. These values are close to 1.87
FeN at 300 K. These values are close to 1.87 
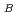 per Fe atom in Fe
per Fe atom in Fe N and 1.43
N and 1.43 
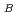 per Co atom in Co
per Co atom in Co N, respectively. This result implies that the Fe and Co atoms in the Co
N, respectively. This result implies that the Fe and Co atoms in the Co FeN films were located both at corner and face-centered sites in the anti-perovskite lattice. Spin magnetic moments per unit cell were decreased linearly with increasing x in Co
FeN films were located both at corner and face-centered sites in the anti-perovskite lattice. Spin magnetic moments per unit cell were decreased linearly with increasing x in Co Fe
Fe N. This tendency is in good agreement with theory predicted by the first-principle calculation.
N. This tendency is in good agreement with theory predicted by the first-principle calculation.