Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
早川 頌*; 山本 耀二郎*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 218, p.111987_1 - 111987_10, 2023/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:14.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)On-the-fly kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC), a computational technique for atomistic simulations, has attracted attention because it increases the simulation timescale beyond that of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations while maintaining atomistic fidelity. However, for most kMC methods, when events with high and low activation energies coexist in the event list, trivial events with extremely low activation energies that do not essentially affect the phenomena of interest, so-called flicker events, are frequently selected, making it challenging to observe the key dynamics. In this study, we use Self-Evolving Atomistic kMC (SEAKMC), one of the on-the-fly kMC methods, to model the unstable-to-stable transformations of irregular three-dimensional self-interstitial-atom (SIA) clusters in Cu generated through collision cascade. By setting an activation energy threshold once every five steps, transformations into stable configurations are enhanced. The algorithm renders the simulation timescales one or two orders of magnitude longer than those possible with MD simulations. Further, the probability of transformations into stable configurations is increased by 40 times compared to that of the original SEAKMC method. In addition, we find that the stable configurations obtained by the transformation of the SIA clusters are mostly Frank loops. In summary, this new algorithm for the SEAKMC method helps to resolve the inefficiency of kMC methods resulting from the selection of flicker events and will aid the study of meso-timescale atomistic dynamics.
津川 聖人*; 早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 愛知 正温*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 215, p.111806_1 - 111806_8, 2022/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:29.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Molecular dynamics simulations were conducted to evaluate the interactions between an edge dislocation and a rigid, impenetrable precipitate in Cu by changing the distance between the glide plane of the dislocation and the center of the precipitate ( ). In these calculations, the precipitate was introduced as a super particle that moved according to the total force exerted by the matrix atoms on the precipitate atoms. When the center of the precipitate was close to the glide plane, an Orowan loop was formed around the precipitate after the dislocation detached, and the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) was similar to the value evaluated by the results at
). In these calculations, the precipitate was introduced as a super particle that moved according to the total force exerted by the matrix atoms on the precipitate atoms. When the center of the precipitate was close to the glide plane, an Orowan loop was formed around the precipitate after the dislocation detached, and the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) was similar to the value evaluated by the results at 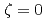 . However, when the glide plane was far from the center of the precipitate, either a vacancy loop or loops generated through the Hirsch mechanism were formed, depending on whether the center of the precipitate was below or above the glide plane. The magnitude of the CRSS was not symmetric about
. However, when the glide plane was far from the center of the precipitate, either a vacancy loop or loops generated through the Hirsch mechanism were formed, depending on whether the center of the precipitate was below or above the glide plane. The magnitude of the CRSS was not symmetric about 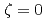 . This study confirmed that it is necessary to analyze the CRSS by changing
. This study confirmed that it is necessary to analyze the CRSS by changing  to construct a predictive model for the hardening caused by the formation of lattice defects, and that precipitate hardening appears to be smaller than the value estimated using the results at
to construct a predictive model for the hardening caused by the formation of lattice defects, and that precipitate hardening appears to be smaller than the value estimated using the results at 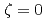 .
.
津川 聖人*; 早川 頌*; 岩瀬 祐樹*; 沖田 泰良*; 鈴木 克幸*; 板倉 充洋; 愛知 正温*
Computational Materials Science, 210, p.111450_1 - 111450_9, 2022/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:75.5(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Precipitation strengthening has been utilized to improve the properties of metallic materials so far. Since interactions between precipitates and dislocations are micro-mechanisms responsible for this phenomenon, a molecular dynamics (MD) simulation is a powerful tool for quantifying this phenomenon. In this study, we introduced a method to simulate a rigid and impenetrable precipitate against a direct contact with a dislocation using a single interatomic potential representing the bulk material. The total force exerted on all atoms in the precipitate region was divided by the number of atoms in the region. This average force was then applied to each atom in the region to simulate one super particle that moved depending on the total force exerted by the matrix atoms on the precipitate atoms. We used MD simulations to quantify the interaction of a precipitate with an edge dislocation. After the dislocation overcame the precipitate, an Orowan loop was formed along the outer circumference of the precipitate. The energy of the loop was 2.1  0.1 eV/b, which was higher than that obtained using the elasticity. The hardening caused by the precipitate was larger than that caused by voids of the same size. The proposed method can be applied to simulate interactions of precipitates with dislocations in any type of metallic material, especially when a dislocation bypasses a precipitate without changing its structure, except when a strong repulsive force acts between them.
0.1 eV/b, which was higher than that obtained using the elasticity. The hardening caused by the precipitate was larger than that caused by voids of the same size. The proposed method can be applied to simulate interactions of precipitates with dislocations in any type of metallic material, especially when a dislocation bypasses a precipitate without changing its structure, except when a strong repulsive force acts between them.
森 承宇*; 松田 那由多*; 沖田 泰良*; 愛知 正温*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Materialia, 21, p.101371_1 - 101371_6, 2022/03
The nonlinear ultrasonic (NLU) technique is a nondestructive method for detecting nanostructure in crystalline materials. In this study, a method was developed to quantify the changes in NLU signals associated with nanostructure using molecular dynamics (MD). A nonreflective boundary, which reduces the computational cost to the first power of the wavelength, was used to achieve this. This method is distinct from previous studies using a conventional MD, for which the computational cost is proportional to the square of the wavelength. The nonreflective boundary eliminates the influence of reflected waves at the detection position by setting a buffer region at the end of the simulation cell opposite from the wave source, and periodically resetting the displacements and velocities of all atoms in this region. This method allows the introduction of elastic waves with wavelengths longer than the cell size, and only an extension of time is required, according to the extension of the wavelength, without increasing the cell size. Hence, it is possible to extend the NLU wavelength by approximately four orders of magnitude, which approaches the wavelengths used for inspections and, thus, to use MD to simulate the changes in the NLU signals induced by nanostructure. The NLU signal values obtained by the two methods were in good agreement for a perfect Fe crystal and a Fe crystal containing 1% monovacancies. No significant frequency dependence of the acoustic nonlinearity parameter was found at 0 K. This method will contribute to the development of an inspection technique based on scientific principles.
沖田 泰良*; 寺山 怜志*; 津川 聖人*; 小林 恵太; 奥村 雅彦; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 202, p.110865_1 - 110865_9, 2022/02
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:48.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, a Neural Network Potential (NNP) using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) was developed for Zr, which is used as fuel cladding material in light water reactors. The reference data were obtained through first-principles calculations of various quantities, such as strained hexagonal-closed-packed (hcp) cells, strained face-centered cubic cells, cells containing a vacancy, several vacancies, and surfaces and  -surface energy on all five slip planes in the hcp structures. These data were converted to training data for the ANN, which were invariant to the rotation and translation of the atoms and independent of the number of atoms in the cells. The ANN was defined as a three-layer structure and the number of the nodes was set to 26-12-18-1. The NNP reproduced the first-principles calculations, particularly for the shear deformation, vacancy formation energy, surface energy, and
-surface energy on all five slip planes in the hcp structures. These data were converted to training data for the ANN, which were invariant to the rotation and translation of the atoms and independent of the number of atoms in the cells. The ANN was defined as a three-layer structure and the number of the nodes was set to 26-12-18-1. The NNP reproduced the first-principles calculations, particularly for the shear deformation, vacancy formation energy, surface energy, and  -surface energy, with much higher accuracy than any of the existing potentials that have been developed for classical molecular dynamics simulations. The NNP was applied to identify the formation process of c-type dislocation loops in Zr, which is a key microstructure responsible for abrupt increases in hydrogen absorption. The formation process was determined by the balance of the vacancy formation energy, surface energy and the
-surface energy, with much higher accuracy than any of the existing potentials that have been developed for classical molecular dynamics simulations. The NNP was applied to identify the formation process of c-type dislocation loops in Zr, which is a key microstructure responsible for abrupt increases in hydrogen absorption. The formation process was determined by the balance of the vacancy formation energy, surface energy and the  -surface energy on the basal plane, both of which were precisely reproduced only by the NNP developed in this study. The formation process was identified based on the atomistic behavior of the NNP.
-surface energy on the basal plane, both of which were precisely reproduced only by the NNP developed in this study. The formation process was identified based on the atomistic behavior of the NNP.
G tz, M.*; Yakushev, A.*; G
tz, M.*; Yakushev, A.*; G tz, S.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D
tz, S.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; 浅井 雅人; Kindler, B.*; Krier, J.*; Lommel, B.*; 永目 諭一郎*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; 浅井 雅人; Kindler, B.*; Krier, J.*; Lommel, B.*; 永目 諭一郎*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 110(2), p.75 - 86, 2022/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:31.78(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)揮発性超重元素カルボニル錯体の研究には、原子番号の増加とともに超アクチノイド元素の生成率が低下するためにより効率的な方法が必要となる。新規に開発したダブルチャンバーシステムを用いて、反跳槽と反応槽を分離することにより、カルボニル錯体合成の障害となる入射イオンビームによる反応分子の分解を回避することにより、これを実現する。軽い超アクチノイド元素Sg, Bh, Hs、およびMtの同族元素同位体として5d金属短寿命同位体を原子力機構タンデム加速器で合成し、モデル実験を行うことで、本手法の実現可能性を検証した。

Chiera, N. M.*; 佐藤 哲也; Eichler, R.*; 富塚 知博; 浅井 雅人; 安達 サディア*; Dressler, R.*; 廣瀬 健太郎; 井上 浩樹*; 伊藤 由太; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 60(33), p.17871 - 17874, 2021/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:14.88(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)等温ガスクロマトグラフ法を用いて、105番元素ドブニウム(Db)の単一原子を対象として、揮発性オキシ塩化物を合成し、化学的性質を調べた。同一条件下で同族元素ニオブおよびタンタルの揮発性と比較したところ、NbOCl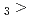 TaOCl
TaOCl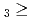 DbOCl
DbOCl の関係が得られた。これはDb分子中の共有結合性が周期表からの予想よりも強くなっているためと考えられる。本成果により、超アクチノイド元素の化学的性質に関する理論計算に対する信頼できる実験データを与えることができた。
の関係が得られた。これはDb分子中の共有結合性が周期表からの予想よりも強くなっているためと考えられる。本成果により、超アクチノイド元素の化学的性質に関する理論計算に対する信頼できる実験データを与えることができた。
寺山 怜志*; 岩瀬 祐樹*; 早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Computational Materials Science, 195, p.110479_1 - 110479_12, 2021/07
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:57.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Austenitic stainless steels, which are used as incore structural materials in light water reactors, are characterized by an extremely low stacking fault energy (SFE) among face-centered cubic (FCC) metals. To evaluate the effects of SFE on defect formation under high-energy particle irradiation, molecular dynamics simulations were performed using the interatomic potential sets for FCC metals with different SFEs and a primary knock-on atom energy (E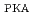 ) of 100 keV at 600 K. The results show that the number of residual defects is independent of the SFE. However, the characteristics of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters do depend on the SFE. For clusters smaller than a certain size, the ratio of glissile SIA clusters decreases as the SFE increases, which is similar to the trend observed at the low E
) of 100 keV at 600 K. The results show that the number of residual defects is independent of the SFE. However, the characteristics of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters do depend on the SFE. For clusters smaller than a certain size, the ratio of glissile SIA clusters decreases as the SFE increases, which is similar to the trend observed at the low E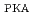 . However, for larger clusters, which can be detected only at a high E
. However, for larger clusters, which can be detected only at a high E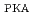 , the ratio of glissile clusters increases. These results correspond to static energy calculations, in which the difference in the formation energy between a Frank loop and perfect loop (
, the ratio of glissile clusters increases. These results correspond to static energy calculations, in which the difference in the formation energy between a Frank loop and perfect loop ( E
E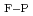 ) for the small clusters decreases as the SFE increases. In contrast, for the larger clusters, the SFE dependence of
) for the small clusters decreases as the SFE increases. In contrast, for the larger clusters, the SFE dependence of  E
E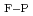 changes due to the shape restrictions of stable perfect loops. At a high temperature of 600 K, large vacancy clusters with stacking faults can be detected at E
changes due to the shape restrictions of stable perfect loops. At a high temperature of 600 K, large vacancy clusters with stacking faults can be detected at E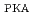 = 100 keV, resulting in the enhanced formation of these clusters at lower SFEs. Furthermore, several of these clusters were similar to perfect loops, with the edges split into two partial dislocations with stacking faults, although the largest clusters detected at low E
= 100 keV, resulting in the enhanced formation of these clusters at lower SFEs. Furthermore, several of these clusters were similar to perfect loops, with the edges split into two partial dislocations with stacking faults, although the largest clusters detected at low E s were similar to stacking fault tetrahedrons.
s were similar to stacking fault tetrahedrons.
早川 頌*; 土井原 康平*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 愛知 正温*; 鈴木 克幸*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(17), p.11509 - 11525, 2019/09
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:56.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed molecular dynamics simulations to evaluate the effects of stacking fault energy (SFE) on interactions between a screw dislocation and spherical voids in face-centered cubic (fcc) metals. It was observed that the frequency of the cross-slips is a critical factor affecting the interaction, with primarily three different interaction morphologies being observed: (1) the two partial dislocations detach from the void independently with a time lag, (2) the two partial dislocations detach from the void almost simultaneously on a single slip plane, and (3) the two partial dislocations detach from the void almost simultaneously while involving more than one cross-slip and a jog formation. The magnitude of the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) increases in the order mentioned above. The CRSS values for interaction morphology (2), which was observed most frequently in this study, were in good agreement with those predicted analytically by adjusting the parameters dependent on the SFE. Based on the obtained results, we discussed the applicability of the analytical model for void hardening in fcc metals. The results of this work contribute significantly to the modeling of mechanical property degradation in irradiated metals.
早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 川畑 友弥*; 鈴木 克幸*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(16), p.11096 - 11110, 2019/08
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:42.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed molecular dynamics simulations of displacement cascades in FCC metals under Poisson's deformation using interatomic potentials differing in stacking fault energy (SFE), in order to investigate the effect of tensile strain on the SFE dependence of defect formation processes. There was no clear SFE dependence of the number of residual defects and the size distribution of defect clusters under both no strain and the applied strain, while the strain enhanced the defect formation to a certain extent. We also observed that the strain affected the formations of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters depending on their size and the Burgers vector. These results were consistent with the analysis based on the defect formation energies. Meanwhile, the number of SIA perfect loops was higher at lower SFE under both no strain and the applied strain, leading to an increase in the ratio of glissile SIA clusters with a decrease in SFE. Further, the absolute number of SIA perfect loops was increased by the applied strain, while the SFE dependence of the number of SIA perfect loops was not affected. These findings were associated with the difference in formation energy between an SIA perfect loop and an SIA Frank loop. The insights extracted from this study significantly contribute to the modeling of microstructural evolution in nuclear materials under irradiation, especially for low SFE metals such as austenitic stainless steels.
Chiera, N. M.; 佐藤 哲也; 富塚 知博; 浅井 雅人; 伊藤 由太; 白井 香里*; 鈴木 颯人; 床井 健運; 豊嶋 厚史; 塚田 和明; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 320(3), p.633 - 642, 2019/06
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.15(Chemistry, Analytical)等温ガスクロマトグラフ(IGC)装置を開発し、オンライン気相研究に向けた動作試験をおこなった。核反応によって合成した5族遷移金属ニオブおよびタンタルの短寿命同位体をガスジェット気流によってIGC装置へ直接搬送し、反応ガスとしてSOCl を用いてオキシ塩化物を生成する。このときのNbOCl
を用いてオキシ塩化物を生成する。このときのNbOCl およびTaOCl
およびTaOCl の生成条件並びに搬送条件を調べたところ、半減期(
の生成条件並びに搬送条件を調べたところ、半減期(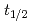 )が約30秒の核種について全体の効率が7%であると見込むことができた。したがって、本IGC装置は
)が約30秒の核種について全体の効率が7%であると見込むことができた。したがって、本IGC装置は Db(
Db(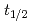 =34秒)適用可能であることがわかった。
=34秒)適用可能であることがわかった。
Chiera, N. M.; 佐藤 哲也; 富塚 知博; 浅井 雅人; 鈴木 颯人*; 床井 健運; 豊嶋 厚史; 塚田 和明; 永目 諭一郎
Inorganica Chimica Acta, 486, p.361 - 366, 2019/02
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:18.6(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)トレーサー量のNbOCl およびTaOCl
およびTaOCl の生成とその石英表面における吸着挙動を、等温ガスクロマトグラフ法を用いて調べた。吸着-脱離モデルをもとにしたモンテカルロ・シミュレーションにより、それぞれについて求められた吸着エンタルピー(
の生成とその石英表面における吸着挙動を、等温ガスクロマトグラフ法を用いて調べた。吸着-脱離モデルをもとにしたモンテカルロ・シミュレーションにより、それぞれについて求められた吸着エンタルピー(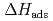 )は、-
)は、-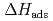 (NbOCl
(NbOCl ) = 102
) = 102  4 kJ/molおよび-
4 kJ/molおよび-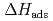 (TaOCl
(TaOCl ) = 128
) = 128  5 kJ/molだった。得られた値は、それぞれの化合物の昇華エンタルピーから経験的に予想される値と非常によく一致した。これにより、金属オキシ塩化物について
5 kJ/molだった。得られた値は、それぞれの化合物の昇華エンタルピーから経験的に予想される値と非常によく一致した。これにより、金属オキシ塩化物について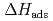 と
と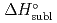 間に知られている経験式を更新することができた。さらに、NbおよびTaオキシ塩化物の
間に知られている経験式を更新することができた。さらに、NbおよびTaオキシ塩化物の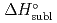 から外挿してDbOCl
から外挿してDbOCl について予想された
について予想された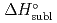 (DbOCl
(DbOCl )から、
)から、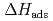 (DbOCl
(DbOCl )は135
)は135  2 kJ/molと予想された。本結果を元に、今後同一実験条件下でDbOCl
2 kJ/molと予想された。本結果を元に、今後同一実験条件下でDbOCl の吸着挙動研究をおこない、5族元素の揮発性について議論することができるとともに、その結果から、ドブニウムにおける相対論効果の影響について見積もることが可能となる。
の吸着挙動研究をおこない、5族元素の揮発性について議論することができるとともに、その結果から、ドブニウムにおける相対論効果の影響について見積もることが可能となる。
中西 大貴*; 川畑 友弥*; 土井原 康平*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 鈴木 克幸*
Philosophical Magazine, 98(33), p.3034 - 3047, 2018/09
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:47.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)原子炉内部で使用されるオーステナイト鋼は積層欠陥エネルギーが低いことで知られ、そのため積層欠陥を伴う照射欠陥クラスタが大きくなることが予想される。この傾向を定量評価するため、FCC金属のモデルポテンシャルにおいて積層欠陥エネルギーだけを変化させたものを用い照射欠陥生成の分子動力学シミュレーションを様々な温度において実行し、生成した照射欠陥クラスタの種類と数を調べた。その結果移動可能な格子間原子クラスタの生成数が積層欠陥エネルギーとともに大きく変化することが見出された。
早川 頌*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 愛知 正温*; 鈴木 克幸*
Philosophical Magazine, 98(25), p.2311 - 2325, 2018/06
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:40.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)BCC鉄における格子間原子クラスタは容易方向へのすべり運動とは別に垂直方向への保存的上昇運動を行い、これにより三次元的な運動を行う。この拡散の三次元性は転位への吸収確率に大きく影響し、材料のスエリングなどの照射劣化挙動を左右する。この保存的上昇運動を分子動力学計算とモンテカルロ計算を組み合わせた手法で解析し、移動障壁エネルギーを評価したところ、従来の弾性理論により予想されていた値よりはるかに大きい値が得られた。
土井原 康平*; 沖田 泰良*; 板倉 充洋; 愛知 正温*; 鈴木 克幸*
Philosophical Magazine, 98(22), p.2061 - 2076, 2018/05
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:71.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)原子炉材料、特に炉内構造材のオーステナイトの照射脆化を評価する際に、オーステナイトの特徴である低い積層欠陥エネルギーの影響を評価する必要がある。本研究では積層欠陥エネルギーだけを変化させたFCC金属のモデルポテンシャルを用いて転位とボイドの相互作用形態を評価し、ボイドの大きさと積層欠陥エネルギーの値によって様々な相互作用形態があることを見出した。
 ; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
村川 武志*; 林 秀行*; 角南 智子; 栗原 和男; 玉田 太郎; 黒木 良太; 鈴木 守*; 谷澤 克行*; 岡島 俊英*
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 69(12), p.2483 - 2494, 2013/12
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:68.77(Biochemical Research Methods)アルスロバクター-グロビフォルミス由来銅アミン酸化酵素の結晶構造を抗凍結剤として低分子ポリエチレングリコール(LMW PEG; 平均分子量 200)を用いて1.08
200)を用いて1.08 分解能で決定した。最終的な結晶構造学的
分解能で決定した。最終的な結晶構造学的 因子と
因子と
 値は、それぞれ13.0%と15.0
値は、それぞれ13.0%と15.0 であった。LMW PEGの幾つかの分子は、活性部位を含むタンパク質内部の空洞を占めており、それが分子全体の温度因子の著しい低下をもたらし、結果として、単量体分子量が約70,000と比較的大きなタンパク質にも拘わらず原子分解能の構造に至ったことがわかった。推定される全水素原子の約40%は、
であった。LMW PEGの幾つかの分子は、活性部位を含むタンパク質内部の空洞を占めており、それが分子全体の温度因子の著しい低下をもたらし、結果として、単量体分子量が約70,000と比較的大きなタンパク質にも拘わらず原子分解能の構造に至ったことがわかった。推定される全水素原子の約40%は、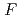
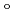 -
-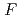
 差図中に明確な電子密度を持って観察され、複数のマイナーな配座異性体も多くの残基に対して同定された。また、翻訳後に誘導されたキノン補因子と銅原子を含む活性部位における異方的な変位の揺らぎを見積った。さらに、複数の二原子分子、恐らく分子性酸素がタンパク質と結合し、そのうちの一つは二量体界面の中央に位置する空洞から活性部位まで基質である二原子酸素のための進入経路として以前から提案されている領域に位置していた。
差図中に明確な電子密度を持って観察され、複数のマイナーな配座異性体も多くの残基に対して同定された。また、翻訳後に誘導されたキノン補因子と銅原子を含む活性部位における異方的な変位の揺らぎを見積った。さらに、複数の二原子分子、恐らく分子性酸素がタンパク質と結合し、そのうちの一つは二量体界面の中央に位置する空洞から活性部位まで基質である二原子酸素のための進入経路として以前から提案されている領域に位置していた。
吉田 由香里*; 鈴木 義行*; Al-Jahdari, W. S.*; 浜田 信行*; 舟山 知夫; 白井 克幸*; 加藤 弘之*; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(1), p.87 - 92, 2012/02
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:41.9(Biology)To clarify the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values of carbon ion (C) beams in normal brain tissues, a rat organotypic slice culture system was used. The cerebellum was dissected from 10-day-old Wistar rats, cut parasagittally into approximately 600- m-thick slices and cultivated using a membrane-based culture system with a liquid-air interface. Slices were irradiated with 140 kV X-rays and 18.3 MeV/amu C-beams (linear energy transfer = 108 keV/
m-thick slices and cultivated using a membrane-based culture system with a liquid-air interface. Slices were irradiated with 140 kV X-rays and 18.3 MeV/amu C-beams (linear energy transfer = 108 keV/ m). After irradiation, the slices were evaluated histopathologically using hematoxylin and eosin staining, and apoptosis was quantified using the TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Disorganization of the external granule cell layer (EGL) and apoptosis of the external granule cells (EGCs) were induced within 24 h after exposure to doses of more than 5 Gy from C-beams and X-rays. In the early postnatal cerebellum, morphological changes following exposure to C-beams were similar to those following exposure to X-rays. The RBEs values of C-beams using the EGL disorganization and the EGC TUNEL index endpoints ranged from 1.4 to 1.5. This system represents a useful model for assaying the biological effects of radiation on the brain, especially physiological and time-dependent phenomena.
m). After irradiation, the slices were evaluated histopathologically using hematoxylin and eosin staining, and apoptosis was quantified using the TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Disorganization of the external granule cell layer (EGL) and apoptosis of the external granule cells (EGCs) were induced within 24 h after exposure to doses of more than 5 Gy from C-beams and X-rays. In the early postnatal cerebellum, morphological changes following exposure to C-beams were similar to those following exposure to X-rays. The RBEs values of C-beams using the EGL disorganization and the EGC TUNEL index endpoints ranged from 1.4 to 1.5. This system represents a useful model for assaying the biological effects of radiation on the brain, especially physiological and time-dependent phenomena.
神沼 拓也*; 鈴木 義行*; 白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 野田 真永*; 吉田 由香里*; 舟山 知夫; 高橋 健夫*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(6), p.627 - 631, 2010/11
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:33.86(Biology)The direct biological effects of radiation, particularly accelerated heavy particle ions, on neurons are not fully known. Hence, the direct effect of carbon-ion beams on immature neurons was investigated by comparing to the effect of X-rays  using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days
using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days 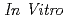 (DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/
(DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/ m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p
m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p  0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
立川 崇之; 中島 康平*; 手島 直哉; Kim, G.; 鈴木 喜雄; 武宮 博; 林 伸彦; 射場 克幸*
Proceedings of 3rd International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization (CSO 2010), p.322 - 326, 2010/05
We have developed the Simple Orchestration Application Framework (SOAF) on a grid infrastructure to control cooperative and multiple execution of simulation codes on remote computers from a client PC. SOAF enables researchers to generate a scenario of their executions by only describing a configuration file which includes the information of execution codes and file flows among them. SOAF does not need substantial modification of the simulation codes. We have applied SOAF to the "Burning Plasma Integrated Code" which consists of various plasma simulation codes which exist on distributed heterogeneous computers located in different sites. We succeeded in cooperative and concurrent execution of four plasma simulation codes without substantial modification.
戸塚 俊之; 鈴木 喜雄; 坂田 信也; 大島 貴幸; 射場 克幸*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(2-3), p.287 - 290, 2008/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)六ヶ所村からネットワーク経由でITERへ実験参加するシステムの構築が計画されており、ITERブローダーアプローチでは、JT-60SAを模擬ITERとして試験することが決められている。これを実現するために遠隔地からマン・マシンインターフェイス機能である放電条件の作成・参照や放電データの参照,運転状態の把握ができるシステムの開発を進めてきた。本報告では、新たに開発したパソコンのウェブブラウザ上で動作するJavaアプレットを利用した遠隔実験用JT-60マン・マシンインターフェイス機能の詳細について報告する。