Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
豊森 佑夏*; 辻 悟*; 光田 紫乃布*; 岡山 陽一*; 芦田 汐未*; 森 敦紀*; 小林 徹; 宮崎 有史; 矢板 毅; 荒江 祥永*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 89(12), p.1480 - 1486, 2016/09
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:29.47(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Preparation of 2,2'-bithiophene derivatives bearing  -alkenyl groups at the 3,3'-positions and ring-closing metathesis reactions of the obtained compound were performed. The reaction of bithiophene bearing 3-butenyl substituents with 5mol% Grubbs 1st generation catalyst underwent ring-closing metathesis (RCM) to afford the cyclized product 7 showing winding vine-shaped molecular asymmetry in up to 88% yield. Enantioselective RCM was also achieved by the use of chiral Schrock Hoveyda molybdenum-alkylidene catalyst in up to 87% ee.
-alkenyl groups at the 3,3'-positions and ring-closing metathesis reactions of the obtained compound were performed. The reaction of bithiophene bearing 3-butenyl substituents with 5mol% Grubbs 1st generation catalyst underwent ring-closing metathesis (RCM) to afford the cyclized product 7 showing winding vine-shaped molecular asymmetry in up to 88% yield. Enantioselective RCM was also achieved by the use of chiral Schrock Hoveyda molybdenum-alkylidene catalyst in up to 87% ee.
高橋 慎也*; 井上 隆信*; 対馬 孝治*; 崎岡 聖導*; 松永 武
環境工学研究論文集, 46, p.565 - 572, 2009/00
岐阜県伊自良川上流の渓流を対象として、降雨時の水質変化とその要因を、主要イオン濃度・pH・電気伝導度・流量観測・水の水素安定同位体比分析を用いた流量の成分分離により解析した。対象河川では、降雨による流量増加時に、ほとんどの主要イオン濃度,pH,電気伝導度が低下し、pH及び電気伝導度の変化量は降雨量と負の相関関係にあった。水の水素安定同位体比測定を用いた流量の成分分離の結果、降水流出成分比率は降雨量によって全く異なり、降雨量が多い場合は降水流出成分の寄与が大きくなることが示された。成分分離結果をもとにして、平水時河川水と降雨の主要イオン濃度から算出した降雨時のイオン濃度の変化から、対象河川における水質変化の主な要因は降水流出成分の寄与であることが示された。
高橋 正俊*; 永井 晴康; 茅野 政道
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-028, 105 Pages, 2000/09
チェルノブイル事故を契機として、原研では世界の原子力事故に対して、最大で半地球規模までの放射能の拡散をリアルタイムで予測できるシステムWSPEEDIの開発を行ってきたが、今般、国際的なシステム評価研究などを通して、システムが実用的に用いることのできる段階にあると判断した。そのため国際的な情報交換ネットワーク(地球環境安全ネットワーク)を米国、欧州やアジアの原子力研究機関に展開し、事故情報や予測情報の迅速な交換手段の確立を図ることとした。本手引きでは、事故時の環境データや予測計算結果の専用ホームページへの登録、検索、管理と、電子会議システムの使用方法について述べる。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 板橋 志保*; 藤崎 健太*; 伏見 英彦*; 長谷川 直*; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; et al.
no journal, ,
We isolated two novel species of the genus  , one from top of troposphere (
, one from top of troposphere (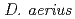 ) and the other from bottom of stratosphere (
) and the other from bottom of stratosphere (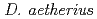 ). Can these newly isolated bacterial species and strains survive harsher environment such as space environment and/or other astronomical objects such as Mars? To address these questions, we have analyzed the survival of these microbial species and strains under the extreme conditions. Environment at high altitude is extreme for microorganisms not only because of high UV radiation, but also other stresses such as extreme dryness. To clarify how dryness affects to the survivability of microorganisms, we examined the effects of desiccation and high humidity on survival and DNA double strand breaks (DSB) of
). Can these newly isolated bacterial species and strains survive harsher environment such as space environment and/or other astronomical objects such as Mars? To address these questions, we have analyzed the survival of these microbial species and strains under the extreme conditions. Environment at high altitude is extreme for microorganisms not only because of high UV radiation, but also other stresses such as extreme dryness. To clarify how dryness affects to the survivability of microorganisms, we examined the effects of desiccation and high humidity on survival and DNA double strand breaks (DSB) of  ,
,  and spores of
and spores of 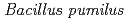 . They exhibited different survival rates and DSB patterns under desiccation and high humidity. Higher survival and less DSB occurred at lower temperatures. Spores of
. They exhibited different survival rates and DSB patterns under desiccation and high humidity. Higher survival and less DSB occurred at lower temperatures. Spores of 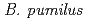 showed the highest survivability at each condition. Survivability of
showed the highest survivability at each condition. Survivability of  at desiccation condition is higher than that at the humid condition, although survivability of
at desiccation condition is higher than that at the humid condition, although survivability of  at desiccation condition is lower than that at the humid condition. We also tested the effects of various factors on survivability of
at desiccation condition is lower than that at the humid condition. We also tested the effects of various factors on survivability of  spp. Together with tests under desiccation condition, these test results suggested that
spp. Together with tests under desiccation condition, these test results suggested that  spp. which we tested can survive in space for years.
spp. which we tested can survive in space for years.
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 伏見 英彦*; 鳴海 一成; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; 河合 秀幸*; 小林 憲正*; et al.
no journal, ,
To explain how organisms on the Earth were originated at the quite early stage of the history of Earth, Panspermia hypothesis was proposed. Recent findings of the Martian meteorite suggested possible existence of extraterrestrial life, and interplanetary migration of life as well. On the other hand, microbes have been collected from high altitude using balloons, aircraft and meteorological rockets since 1936, though it is not clear how could those microbes be ejected up to such high altitude. Spore forming fungi and Bacilli, and Deinococci have been isolated in these experiments. If microbes could be found present even at the higher altitude of low earth orbit (400 km), the fact would endorse the possible interplanetary migration of terrestrial life. We proposed the "Tanpopo" mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes on Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS). In our proposal, microorganisms will be exposed to the space environment with/without model-clay materials that might protect microorganisms from vacuum UV and cosmic rays. Spore of 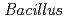 sp., and vegetative cells of
sp., and vegetative cells of  and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In preliminary experiments, clay-materials tend to increase survivability of microorganisms under irradiation of heavy ion beam and other radiation. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission.
and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In preliminary experiments, clay-materials tend to increase survivability of microorganisms under irradiation of heavy ion beam and other radiation. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission.
河口 優子*; 杉野 朋弘*; Yang, Y.*; 高橋 勇太*; 吉村 義隆*; 辻 尭*; 小林 憲正*; 田端 誠*; 橋本 博文*; 鳴海 一成; et al.
no journal, ,
われわれは、地球低軌道を周回する国際宇宙ステーション日本棟曝露部を利用する「微生物・有機物の宇宙曝露と微生物・宇宙塵の捕集実験」(たんぽぽ計画)を提案している。この計画では、微生物と生命の材料となり得る有機化合物が天体間を移動する可能性の検討と微小隕石の検出及び解析実験を行う予定である。超低密度シリカエアロゲルを一定期間軌道上に曝露し、衝突する微粒子内に含まれる微生物の捕集を行うとともに、地球低軌道上での微生物の生存可能性を検証するために、微生物曝露実験を行う。本発表では、捕集する微生物を解析するうえで障害となり得る点について検討した結果について報告する。また、微生物の曝露実験については、さまざまな 属細菌について、宇宙環境を模擬した条件下(紫外線,放射線等)での生存を検討した結果を報告する。
属細菌について、宇宙環境を模擬した条件下(紫外線,放射線等)での生存を検討した結果を報告する。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 河口 優子*; 杉野 朋弘*; 高橋 勇太*; 鳴海 一成; 高橋 裕一*; 林 宣宏*; 吉村 義隆*; 田端 誠*; et al.
no journal, ,
生物にはさまざまな極限環境に存在するものがあり、生命の起原、Astrobiology研究の重要な研究対象として、それらの研究が進んでいる。高層大気圏も極限環境であり、そこでどのような生物が存在するのか研究が行われてきた。一方、生命の起源を考えるうえで、地球外に生命の起源を求める「パンスペルミア仮説」が古くから議論されてきた。これらのことを踏まえ、われわれのグループは、国際宇宙ステーション(ISS)上で、微生物や生命の材料になりうる有機化合物が天体間で移動可能かについての検証と、微小隕石の検出及び解析実験を行うことの提案と準備を行っている。そこでは、ISS外部に一定期間曝露した超低密度エアロゲルを用いて微小隕石やその他の微粒子を捕集し、エアロゲルの回収後にその表面と衝突トラックの顕微鏡観察等のさまざまな解析を行う。ISS軌道は強力な紫外線や放射線が降り注ぐ過酷な環境下であり、微生物は長期に生存するためには宇宙塵や粘土鉱物などの微粒子の内部に存在すると考えられる。そこで捕集した微粒子にDNA特異的な蛍光染色を行い、微生物の検出を行う。本発表では、上記のような微粒子を模した微生物と粘土鉱物の混合サンプルを用いた蛍光染色やPCRによる微生物の検出についての地上模擬実験の現状について報告する。また、宇宙曝露を予定している微生物の紫外線,放射線,真空,温度などに対する耐性について、地上対照実験を進めている。これについても併せて報告し、たんぽぽ計画の進行状況を報告する。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 高橋 勇太*; 鳴海 一成; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; 今井 栄一*; 河合 秀幸*; et al.
no journal, ,
We proposed the "Tanpopo" mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes, and organic compounds on Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS). Tanpopo consists of six subthemes. Two of them are on the possible interplanetary migration of microbes capture experiment of microbes at the ISS orbit and space exposure experiment of microbes. In this paper, we focus on the space exposure experiment of microbes. Microbes in space are assumed be exposed to the space environment with a kind of clay materials that might protect microbes from vacuum UV and cosmic rays, or exposed as the aggregates of which outer cells might protect inner cells from vacuum UV and cosmic rays. Dried vegetative cells of  and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In addition, we are planning to perform another space exposure experiments of microbes. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission and others.
and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In addition, we are planning to perform another space exposure experiments of microbes. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission and others.
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 河口 優子*; 杉野 朋弘*; 高橋 勇太*; 鳴海 一成; 中川 和道*; 田端 誠*; 小林 憲正*; 丸茂 克美*; et al.
no journal, ,
We propose a mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes, organic compounds and meteoroids on Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS) - Tanpopo mission. Ultra low-density aerogel (ca. 0.01 g/cm ) will be used to capture micrometeoroid and space debris. Particles captured by aerogel will be analyzed after the initial inspection of the gel and tracks. The particles will be characterized in terms of mineralogical, organic and microbiological properties. In addition to particle-capture experiment on ISS, we also proposed to perform direct exposure experiments of microorganisms and organic compounds. Several deinococcal species (and strains) including our high-altitude isolates, and some other microbes are candidates for exposure.
) will be used to capture micrometeoroid and space debris. Particles captured by aerogel will be analyzed after the initial inspection of the gel and tracks. The particles will be characterized in terms of mineralogical, organic and microbiological properties. In addition to particle-capture experiment on ISS, we also proposed to perform direct exposure experiments of microorganisms and organic compounds. Several deinococcal species (and strains) including our high-altitude isolates, and some other microbes are candidates for exposure.
横堀 伸一*; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; 今井 栄一*; 河合 秀幸*; 小林 憲正*; 三田 肇*; 中川 和道*; 鳴海 一成; 奥平 恭子*; et al.
no journal, ,
TANPOPO, Japanese name of dandelion, is a plant species, whose seeds with floss are spread by wind. We propose this mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes, and organic compounds at the Exposure Faculty of Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS). The Tanpopo mission consists of six subthemes - capture of microbes in space, exposure of microbes in space, capture of organic compounds in space, exposure of organic compounds in space, measurement of space debris at the ISS orbit, and evaluation of ultra low-density aerogel special for the TANPOPO mission. Our proposal was accepted as a candidate experiment on Exposed Facility of ISS-JEM. In this paper, we overview the TANPOPO mission and discuss the current status of experiments related to the microbe existence/survival set for this mission.
平井 敬三*; 小松 雅史*; 赤間 亮夫*; 野口 享太郎*; 長倉 淳子*; 大橋 伸太*; 齋藤 哲*; 川崎 達郎*; 矢崎 健一*; 池田 重人*; et al.
no journal, ,
土壌から樹木への放射性セシウムの移行吸収とカリウム施肥による移行抑制効果の検討のため、福島県川内村のヒノキ新植地で長期モニタリング試験を開始した。福島第一原子力発電所事故当時はアカマツ・落葉広葉樹混交林で、第4次航空機モニタリング(2011年11月)による推定放射性物質沈着量は685k Bq m (
( Cs+
Cs+ Cs)である。2014年5月に8つの50
Cs)である。2014年5月に8つの50 50mプロットを設け、ヒノキ植栽後の8月にKとして100kg ha
50mプロットを設け、ヒノキ植栽後の8月にKとして100kg ha のKClを施肥し、11月に苗木を採取した。8月の平均空間線量率(
のKClを施肥し、11月に苗木を採取した。8月の平均空間線量率( Sv h
Sv h )は10cm高で1.18、1m高で0.94であった。土壌の平均
)は10cm高で1.18、1m高で0.94であった。土壌の平均 Cs濃度(kBq kg
Cs濃度(kBq kg )はリターで50.0、10-20cm深で0.1と下層へと低下した。またリターから20cm深までの存在量のうち58%がリター中に存在していた。11月に採取したヒノキ針葉の移行係数(土壌0-5cmに対する針葉の
)はリターで50.0、10-20cm深で0.1と下層へと低下した。またリターから20cm深までの存在量のうち58%がリター中に存在していた。11月に採取したヒノキ針葉の移行係数(土壌0-5cmに対する針葉の Cs濃度[Bq Bq
Cs濃度[Bq Bq ])は処理間に有意差はなかったが、土壌の
])は処理間に有意差はなかったが、土壌の Cs濃度が8kBq kg
Cs濃度が8kBq kg 以下では施肥区で小さい傾向にあった。
以下では施肥区で小さい傾向にあった。
福田 裕平; 比内 浩; 柴田 淳広; 野村 和則; 池田 昭*; 小畑 政道*; 市川 真史*; 高橋 陵太*; 平山 文夫*
no journal, ,
既設多核種除去設備及び増設多核種除去設備の前処理設備から発生した炭酸塩スラリー廃棄物を採取し、その性状比較を行うため、放射化学分析, pH測定, SEM-EDX分析を行った。放射化学分析の結果、H-3, Mn-54, Co-60, Sr-90, Sb-125, Cs-134, Cs-137が検出された。既設・増設のどちらのスラリーについてもSr-90が支配的であり、Sr-90濃度は、既設スラリー: 7 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm 、増設スラリー: 6
、増設スラリー: 6 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm であった。この既設・増設のスラリーの性状の違いは、既設・増設の処理工程の違いである鉄共沈工程の有無の差や処理を行った汚染水の組成の違いによるものと推定される。
であった。この既設・増設のスラリーの性状の違いは、既設・増設の処理工程の違いである鉄共沈工程の有無の差や処理を行った汚染水の組成の違いによるものと推定される。
福田 裕平; 荒井 陽一; 比内 浩; 野村 和則; 池田 昭*; 小畑 政道*; 市川 真史*; 高橋 陵太*; 平山 文夫*
no journal, ,
増設多核種除去設備の前処理設備にて発生し、約5か月間高性能容器(HIC)に保管されていた炭酸塩スラリーを、深さ位置を変えて3点(深さ60cm, 100cm, 150cm)採取し、ICP-AESによる元素濃度分析及び放射能分析等の各種分析を行い、炭酸塩スラリーの性状と採取深さ位置の関係を調べた。元素濃度分析の結果、Mg, Ca, Na等が検出されたが、各試料の金属元素組成比に違いは認められず、採取深さに関係なく試料中の固体成分の組成は同一であると推察する。しかし、固体成分の割合は、採取深さ60cmの試料に比べて、100cmと150cmの試料が大きい結果となった。また、Sr-90放射能濃度の結果も同様の傾向となった。スラリー中の粒子が沈降することにより、固体成分の割合が上昇し、その結果、放射能濃度が高くなったと推定される。これらの結果は、スラリー試料のインベントリ評価や、今後の評価の際のスラリー採取位置の検討に役立てられる。