Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
 Co
CoLokotko, T.*; Leblond, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Poves, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Authelet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:72.43(Physics, Nuclear)The structures of the neutron-rich  Co isotopes were investigated via (
Co isotopes were investigated via ( ) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the
) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the 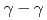 coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the
coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the  Co isotopes.
Co isotopes.
 Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,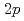 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
, 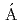 *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.24(Physics, Nuclear)The nuclear structure of the  Ni nucleus was investigated by (
Ni nucleus was investigated by ( ,
,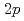 ) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt
) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt  rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by
rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by 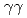 and
and 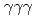 coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
 Ne by proton knockout reactions
Ne by proton knockout reactionsMurray, I.*; MacCormick, M.*; Bazin, D.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Crawford, H. L.*; Fallon, P.*; Li, K.*; Lee, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.011302_1 - 011302_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.84(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Sakurai, Hiroshi*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Morimoto, Koji*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Enyo, Hideto*
Isotope News, (特別号2), p.2 - 14, 2018/01
no abstracts in English
 Sc and development of the
Sc and development of the 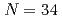 subshell closure
subshell closureSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Go, Shintaro*; Holt, J. D.*; Lee, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(6), p.064310_1 - 064310_10, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:79.83(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 =28 and
=28 and  =50; Spectroscopy of
=50; Spectroscopy of 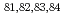 Zn
ZnShand, C. M.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; G
k, Zs.*; G rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 773, p.492 - 497, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:87.26(Astronomy & Astrophysics) -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of  Mg via knockout reactions at intermediate energies
Mg via knockout reactions at intermediate energiesMomiyama, Satoru*; Doornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Niikura, Megumi*; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(3), p.034328_1 - 034328_8, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.95(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 shore of the "island of inversion" and the reduced neutron magicity toward
shore of the "island of inversion" and the reduced neutron magicity toward  O
ODoornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(4), p.041301_1 - 041301_5, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:91.42(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Ne
NeLiu, H. N.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K. A.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 767, p.58 - 62, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:85.94(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Ne at
Ne at  230 MeV/nucleon
230 MeV/nucleonLee, J.*; Liu, H.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Minomo, Kosho*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2016(8), p.083D01_1 - 083D01_7, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Ar and the
Ar and the  =32 subshell closure
=32 subshell closureSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Baba, Hidetada*; Go, Shintaro*; Lee, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 114(25), p.252501_1 - 252501_6, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:88.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The neutron-rich nucleus  Ar is produced by the fragmentation reactions of
Ar is produced by the fragmentation reactions of  Ca,
Ca,  Sc, and
Sc, and  Ti at the RIBF facility in RIKEN, and its deexcited
Ti at the RIBF facility in RIKEN, and its deexcited  rays are observed for the first time. The first
rays are observed for the first time. The first 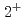 level in
level in  Ar is identified to lie at 1178(18)keV from the most intense
Ar is identified to lie at 1178(18)keV from the most intense  -ray spectra. This experimental data, together with the systematics of the
-ray spectra. This experimental data, together with the systematics of the 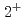 levels for surrounding nuclei, is analyzed with large-scale shell-model calculations. Consequently, the
levels for surrounding nuclei, is analyzed with large-scale shell-model calculations. Consequently, the 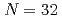 sub-shell gap in
sub-shell gap in  Ar is equivalent to that of
Ar is equivalent to that of  Ca, thus making the
Ca, thus making the 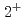 level in
level in  Ar higher than that of
Ar higher than that of  Ar. The shell-model calculation also predicts that the
Ar. The shell-model calculation also predicts that the 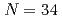 sub-shell gap enhances in going from Ca to Ar, which will be verified by forthcoming experiments for
sub-shell gap enhances in going from Ca to Ar, which will be verified by forthcoming experiments for  Ar.
Ar.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:110 Percentile:95.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Doornenbal, P.*; Scheit, H.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Li, K.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Steppenbeck, D.*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2014(5), p.053D01_1 - 053D01_9, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Ca
CaSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Go, Shintaro*; Homma, Michio*; et al.
Nature, 502(7470), p.207 - 210, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:333 Percentile:99.77(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Anayama, Yoshimasa*; Okuno, Koichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kaminaga, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.850 - 853, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:83.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A flexible heat resistant neutron shielding material has been developed, which consists of polymer resin with 1 weight % boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed resin, examined by the  Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H
Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H , H
, H O, CO and CO
O, CO and CO from the resin have been measured at 250
from the resin have been measured at 250  C environment. The resin will be applied around the port of the vacuum vessel as an additional shielding material and prevented the effects on the neutron streaming of the superconducting tokamak device such as JT-60SA.
C environment. The resin will be applied around the port of the vacuum vessel as an additional shielding material and prevented the effects on the neutron streaming of the superconducting tokamak device such as JT-60SA.
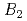 O
O (
( = Nb, Ta)
= Nb, Ta)Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Tsujimoto, Yoshihiro*; Kitada, Atsushi*; Takeiri, Fumitaka*; Kageyama, Hiroshi*; Ajiro, Yoshitami*; Nishi, Masakazu*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 320, p.012037_1 - 012037_5, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)The magnetic ground state of (CuCl)LaNb O
O has been suggested to be a spin-singlet state with an excitation gap of
has been suggested to be a spin-singlet state with an excitation gap of 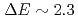 meV, while (CuCl)LaTa
meV, while (CuCl)LaTa O
O has an antiferromagnetic (AFM) ground state. The systems are suspected to be a frustrated quantum spin system due to the competition between the nearest and next-nearest exchange interactions. We have studied magnetic excitation in these systems by ToF inelastic neutron scattering technique. The measurements were performed on powder samples of (CuCl)LaNb
has an antiferromagnetic (AFM) ground state. The systems are suspected to be a frustrated quantum spin system due to the competition between the nearest and next-nearest exchange interactions. We have studied magnetic excitation in these systems by ToF inelastic neutron scattering technique. The measurements were performed on powder samples of (CuCl)LaNb O
O and (CuCl)LaTa
and (CuCl)LaTa O
O at a disk-chopper-type spectrometer AMATERAS in J-PARC. In both systems, a band-like excitation was observed at
at a disk-chopper-type spectrometer AMATERAS in J-PARC. In both systems, a band-like excitation was observed at 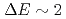 meV. The
meV. The  dependence of the intensity of magnetic excitation around 2 meV for (CuCl)LaNb
dependence of the intensity of magnetic excitation around 2 meV for (CuCl)LaNb O
O well reproduces that observed at a triple-axis spectrometer, exhibiting characteristics of spin-singlet dimers. On the other hand, (CuCl)LaTa
well reproduces that observed at a triple-axis spectrometer, exhibiting characteristics of spin-singlet dimers. On the other hand, (CuCl)LaTa O
O in the AFM state exhibits a different
in the AFM state exhibits a different  dependence.
dependence.
Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Anayama, Yoshimasa*; Onishi, Seiki; Sakurai, Shinji; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Okuno, Koichi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(4), p.585 - 590, 2011/04
Soft-type neutron shielding resin has been developed by improving an existing hard-type neutron shielding material by the epoxy-based resin as the additional shielding material. A flexible heat resistant neutron shielding material has been developed, which consists of newly polymer-based resin with boron. The neutron shielding performance of the developed flexible heat resistant resin by the  Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H, H
Cf neutron source is almost the same as that of the polyethylene. The outgas of H, H , NH
, NH , H
, H O, CO, O
O, CO, O , C
, C H
H and CO
and CO from the developed resin have been measured at high temperature environment (250
from the developed resin have been measured at high temperature environment (250 C) by thermal desorption spectroscopy methods. The soft-type resin and the newly developed heat resistant resin will be applied to prevent the effects of the neutron streaming and to control the movement of vibrated pipe as the seal material around the plumbing in the future fast reactor and the innovative fission reactor.
C) by thermal desorption spectroscopy methods. The soft-type resin and the newly developed heat resistant resin will be applied to prevent the effects of the neutron streaming and to control the movement of vibrated pipe as the seal material around the plumbing in the future fast reactor and the innovative fission reactor.
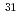 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Deguchi, Shigeki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; Inabe, Naoto*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_4, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:221 Percentile:97.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shibama, Yusuke; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Sakasai, Akira; Matsukawa, Makoto
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(10-12), p.1605 - 1609, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The conceptual design of JT-60SA cryostat is summarized. JT-60SA is designed to be a fully superconducting device and assumed deuterium operation, therefore a cryostat is introduced to secure three functions, which are thermal insulation for entire superconducting magnets, bio-shielding, and gravity support for the entire tokamak device. The cryostat is required to cover up the tokamak devices, which are 15 m of total height and 7 m of radius, and to support the total devices weight of 2550 tons. The cryostat consists of vessel body, gravity support and auxiliary facilities, such as 80 K thermal shield and exhaust system. Each of them is outlined with JT-60SA design conditions, and the operational condition of auxiliary system is clarified, especially, capacity of the exhaust system, which is related to the 80 K thermal shield design.