Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
町田 昌彦; 山田 進; Kim, M.; 奥村 雅彦; 宮村 浩子; 志風 義明; 佐藤 朋樹*; 沼田 良明*; 飛田 康弘*; 山口 隆司; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)建屋内には、原子炉内から漏洩した放射性物質の汚染により高い放射線量を示す地点が多数存在し、廃炉作業を円滑に進める上での大きな障害の一つとなっている。この課題解決に資するため、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)は、経済産業省の廃炉・汚染水対策事業費補助金「原子炉建屋内の環境改善のための技術の開発(被ばく低減のための環境・線源分布のデジタル化技術の開発)」を受託し、令和3年度より2年間に渡り、放射線源の逆推定と推定線源に対する対策を仮想空間で実施可能とするためのデジタル技術の研究開発を実施してきた。本記事では、上記プロジェクトの成果(以下、前期プロジェクトと呼び、その2年間の研究開発の成果)を紹介する他、令和5年度4月より、新たに開始した継続プロジェクト(以下、後期プロジェクトと呼ぶ)の計画についても報告する。前期プロジェクトにて当初予定していた機械学習技術(LASSO)については、建屋内の複雑な構造情報と汚染源の性質を反映した一つの派生版手法へと結実させた成果を報告する他、実際の原子炉施設での検証結果を示す。更に、開発技術を集約したプラットフォームとしての機能を持つソフトウエア:3D-ADRES-Indoorを紹介し、継続して実施する予定の後期プロジェクトの研究開発計画も紹介する。
町田 昌彦; Shi, W.*; 山田 進; 宮村 浩子; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司; 青木 勇斗; 伊藤 倫太郎; 山口 隆司; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
In order to find radioactive hot spots inside reactor building rooms from structural data together with air dose rate measurement data, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) has been recently suggested as a promising scheme. The scheme has been examined in simplified room models and its high estimation feasibility has been confirmed by employing Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) as a radiation simulation code. In this paper, we apply the scheme to complex room models inside real reactor buildings. The target rooms are pool canal circulation system room and main circulation system room in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) at Oarai area, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In these real rooms, we create STL format structural data based on Computer Aided Design (CAD) models made directly from their point group data measured by laser scanning devices, and we notice that the total number of their surface meshes in these real rooms reaches to the order of 1 million. Then, this order of the mesh number clearly indicates that one needs a simplified radiation simulation code considering only direct transmission of gamma ray as a radiation calculation instead of PHITS demanding high computational costs. By developing such a simplified code and customizing it to perform LASSO scheme, we consequently confirm that LASSO scheme driven by the simplified simulation can also successfully predict unknown radioactive hot spots on real structural models.
寺西 美佳*; 山口 弘子*; 坂本 綾子; 日出間 純*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 115, 2015/03
Ion beams induce DNA damage, such as strand breaks, possibly resulting in an increased mutation frequency. To elucidate the mechanism of mutation induction in plants, it is important to know about which DNA damage converted into a mutation. In this study, we examined the method for determining the number of DNA strand breaks induced by carbon ion beams in Arabidopsis seedlings. Seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana (wild-type Colombia) were aseptically sown on Murashige and Skoog agar plates. The seedlings were irradiated with carbon ion beams from an AVF cyclotron. After irradiation, whole plants were harvested immediately in order to detect the induced DNA strand breaks. The number of DNA strand breaks increased with increasing dose of carbon ion beams. Irradiation of seedlings with 960 Gy of carbon ion beams resulted in up to 2.3 strand breaks per megabase (Mb). In this study, only DNA double strand breaks can be detected using the non-denatured agarose gel electrophoresis. To elucidate the mechanism of mutation induction in plants, measurement of the extent of DNA damage other than DNA strand breaks should be needed. Further analysis is in progress.
高野 成央*; 高橋 祐子*; 山本 充*; 寺西 美佳*; 山口 弘子*; 坂本 綾子; 長谷 純宏; 藤澤 弘子*; Wu, J.*; 松本 隆*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 54(4), p.637 - 648, 2013/07
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:50.15(Biology)UVB radiation suppresses photosynthesis and protein biosynthesis in plants, which in turn decreases growth and productivity. Here, an ultraviolet-B (UVB)-tolerant rice mutant, 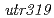 (
(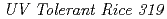 ), was isolated from a mutagenized population derived from 2,500 M1 seeds that were exposed to carbon ions. The
), was isolated from a mutagenized population derived from 2,500 M1 seeds that were exposed to carbon ions. The 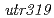 mutant was more tolerant to UVB than the wild type. Neither the levels of UVB-induced CPDs, nor the repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers or (6-4) pyrimidine-pyrimidone photodimers was altered in the
mutant was more tolerant to UVB than the wild type. Neither the levels of UVB-induced CPDs, nor the repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers or (6-4) pyrimidine-pyrimidone photodimers was altered in the 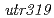 mutant. Thus, the
mutant. Thus, the 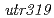 mutant may be impaired in the production of a previously unidentified factor that confers UVB tolerance. To identify the mutated region in the
mutant may be impaired in the production of a previously unidentified factor that confers UVB tolerance. To identify the mutated region in the 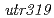 mutant, microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis was performed. Two adjacent genes on chromosome 7were predicted to represent the mutant allele. Sequence analysis of the chromosome region in
mutant, microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis was performed. Two adjacent genes on chromosome 7were predicted to represent the mutant allele. Sequence analysis of the chromosome region in 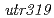 revealed a deletion of 45,419 bp. Database analysis indicated that the Os07g0265100 gene,
revealed a deletion of 45,419 bp. Database analysis indicated that the Os07g0265100 gene, 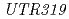 , encodes a putative protein with unknown characteristics or function. In addition, the homologs of UTR319 are conserved only among land plants. Therefore,
, encodes a putative protein with unknown characteristics or function. In addition, the homologs of UTR319 are conserved only among land plants. Therefore, 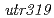 is a novel UVB-tolerant rice mutant and UTR319 may be crucial for the determination of UVB sensitivity in rice, although the function of UTR319 has not yet been determined.
is a novel UVB-tolerant rice mutant and UTR319 may be crucial for the determination of UVB sensitivity in rice, although the function of UTR319 has not yet been determined.
小田 啓二*; 今坂 雄一*; 山内 知也*; 中根 佳弘; 遠藤 章; 俵 裕子*; 山口 恭弘
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.570 - 574, 2005/11
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:44.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)原子核飛跡検出器は、中性子に対する積算型個人線量計として広く利用されているが、10数MeV以上の高エネルギー中性子に対しては感度が急激に低下する問題がある。そこで、高エネルギー中性子との核反応によって重荷電粒子を放出し、飛跡検出器と組合せることにより、検出効率及びエネルギー特性を改良できるラジエータを提案した。中性子との相互作用に基づく解析により、重水素化物質とポリエチレンから成る二層構造が検出効率の特性改善に有望であることを見いだした。この二重構造において、重水素化物質層は、ポリエチレン層で中性子との核反応により発生した陽子の減速材としての役割に加え、自らの層内で発生する重水素の供給源の役割も担っている。そしてTIARAの準単色中性子場を用いた照射実験により、軽水及び重水ラジエータの二重構造による増感効果を実験的に確認した。また二層の厚さを変えることにより、相対感度の中性子エネルギー依存性をある程度制御できることを見いだした。
遠藤 章; 佐藤 達彦; 佐藤 大樹; 志風 義明; 谷村 嘉彦; 三枝 純; 堤 正博; 山口 恭弘; 金子 広久; 小田 啓二*; et al.
no journal, ,
平成15 17年度にわたり、連携重点研究「陽子加速器施設における線量評価に関する研究」において、高崎研TIARAを利用して行った高エネルギー中性子用モニタ,線量計の開発の成果を報告する。J-PARC等の高エネルギー加速器施設においては、遮蔽体を透過し線量寄与が大きい高エネルギー中性子に対する放射線防護が重要である。そこで、高エネルギー中性子に対して適切な線量応答特性を有する中性子モニタ,個人線量計の開発を進めるとともに、測定値の保証に不可欠な校正技術に関する研究を行った。モニタの開発では、液体シンチレータとデジタルオシロスコープを用いた信号解析技術により、1GeVまでの中性子に適用できるモニタを開発した。個人線量計の開発では、固体飛跡検出器に重水素化物質とポリエチレンから成る二層構造ラジエータを付加することで高エネルギー中性子に対する感度,エネルギー特性を改善する方法を見いだした。これを高速顕微鏡による高速読み取り技術と組合せ、積算型個人線量計として利用できる見通しを得た。校正技術の開発では、TIARA準単色中性子場の特性評価を行い、照射野内外の中性子スペクトル,散乱線の寄与割合等を評価し、今後の校正場構築のための基礎データを取得した。
17年度にわたり、連携重点研究「陽子加速器施設における線量評価に関する研究」において、高崎研TIARAを利用して行った高エネルギー中性子用モニタ,線量計の開発の成果を報告する。J-PARC等の高エネルギー加速器施設においては、遮蔽体を透過し線量寄与が大きい高エネルギー中性子に対する放射線防護が重要である。そこで、高エネルギー中性子に対して適切な線量応答特性を有する中性子モニタ,個人線量計の開発を進めるとともに、測定値の保証に不可欠な校正技術に関する研究を行った。モニタの開発では、液体シンチレータとデジタルオシロスコープを用いた信号解析技術により、1GeVまでの中性子に適用できるモニタを開発した。個人線量計の開発では、固体飛跡検出器に重水素化物質とポリエチレンから成る二層構造ラジエータを付加することで高エネルギー中性子に対する感度,エネルギー特性を改善する方法を見いだした。これを高速顕微鏡による高速読み取り技術と組合せ、積算型個人線量計として利用できる見通しを得た。校正技術の開発では、TIARA準単色中性子場の特性評価を行い、照射野内外の中性子スペクトル,散乱線の寄与割合等を評価し、今後の校正場構築のための基礎データを取得した。
徳永 廣子*; 石橋 松二郎*; 有坂 文雄*; 新井 栄揮; 黒木 良太; 山口 類*; 荒川 力*; 徳永 正雄*
no journal, ,
ヌクレオシド二リン酸化キナーゼ(NDK)は、ほとんどの生物種に広く保存された酵素である。グラム陰性中度好塩菌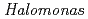 sp. 593由来のNDK(HaNDK)とグラム陰性非好塩菌
sp. 593由来のNDK(HaNDK)とグラム陰性非好塩菌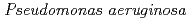 由来NDK(PaNDK)は高い相同性(78% identity, 89% similarity)を示すにもかかわらず、前者は2量体構造、後者は4量体構造を形成する。両者のアミノ酸配列の比較や立体構造予測から、134番目のアミノ酸残基が複合体構造の違いに大きく関与していると予測された。また、HaNDKはGlu134をAlaに置換すると4量体を形成するようになり、逆にPaNDKはAla134をGluに置換すると2量体を形成することが判明した。これらの結果から、野生型HaNDK及び変異型PaNDKは、Glu134のマイナス電荷による反発的相互作用により、4量体形成が阻害されていることが示唆された。
由来NDK(PaNDK)は高い相同性(78% identity, 89% similarity)を示すにもかかわらず、前者は2量体構造、後者は4量体構造を形成する。両者のアミノ酸配列の比較や立体構造予測から、134番目のアミノ酸残基が複合体構造の違いに大きく関与していると予測された。また、HaNDKはGlu134をAlaに置換すると4量体を形成するようになり、逆にPaNDKはAla134をGluに置換すると2量体を形成することが判明した。これらの結果から、野生型HaNDK及び変異型PaNDKは、Glu134のマイナス電荷による反発的相互作用により、4量体形成が阻害されていることが示唆された。
寺西 美佳*; 山口 弘子*; 坂本 綾子; 日出間 純*
no journal, ,
放射線は生物のDNAに作用し、様々なDNA損傷(DNA鎖切断、酸化損傷など)を引き起こす。このDNA損傷の種類に応じて、機能する損傷修復機構が異なっており、修復機構の種類によって修復の正確さは異なっている。この正確さの違いが修復エラーにつながり、エラーの結果として生じる突然変異の違いにつながる。そのため、放射線照射によって誘発されるDNA損傷の種類と、その誘発頻度を定量的に解析することは、イオンビーム誘発突然変異のメカニズムを理解する上で重要である。そこで本研究では、イオンビームと 線によってシロイヌナズナに誘発されるDNA損傷を、二本鎖切断、一本鎖切断、酸化ピリミジン損傷に分け、定量した。その結果、野生型シロイヌナズナにおいて最も誘発されやすいDNA損傷は、カーボンイオンビームでは二本鎖切断、ヘリウムイオンビームと
線によってシロイヌナズナに誘発されるDNA損傷を、二本鎖切断、一本鎖切断、酸化ピリミジン損傷に分け、定量した。その結果、野生型シロイヌナズナにおいて最も誘発されやすいDNA損傷は、カーボンイオンビームでは二本鎖切断、ヘリウムイオンビームと 線では一本鎖切断であった。発芽後7日齢のシロイヌナズナに照射した場合に第5葉の面積を50%減少させる線量(カーボンイオンビームは20Gy、
線では一本鎖切断であった。発芽後7日齢のシロイヌナズナに照射した場合に第5葉の面積を50%減少させる線量(カーボンイオンビームは20Gy、 線は64Gy)で誘発されるゲノムあたりのDNA損傷数は、二本鎖切断がそれぞれ5.2個と8.3個、酸化ピリミジン損傷が2.6個と12.5個であった。酸化ピリミジン損傷は、
線は64Gy)で誘発されるゲノムあたりのDNA損傷数は、二本鎖切断がそれぞれ5.2個と8.3個、酸化ピリミジン損傷が2.6個と12.5個であった。酸化ピリミジン損傷は、 線でより多く誘発されており、吉原らにより報告されたG:CからA:TへのDNA変異頻度の上昇に関与する可能性が考えられた。
線でより多く誘発されており、吉原らにより報告されたG:CからA:TへのDNA変異頻度の上昇に関与する可能性が考えられた。
 ray and UVB radiation in Arabidopsis
ray and UVB radiation in Arabidopsis寺西 美佳*; 山口 弘子*; 坂本 綾子; 日出間 純*
no journal, ,
Radiation induce DNA damages, such as strand breaks, oxidative damage, and cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) possibly resulting in an increased mutation frequency. Although it is important to know which DNA damage converted into a mutation, little is known about the types and extent of DNA damage induced by radiation in plant cells. We measured the number of DNA damages induced by ionizing radiation (carbon and helium ion beams,  rays) and non-ionizing radiation (UVB) in Arabidopsis seedlings. The irradiated seedlings were harvested immediately and used for preparing an agarose plug, which were subjected to denature and non-denature agarose gel electrophoresis using static field electrophoresis and biased sinusoidal field gel electrophoresis. The number of DNA strand breaks were calculated using the molecular length standard curve and the quantity of DNA at each migration position as shown by the quantitative image data. As a result, irradiation of seedlings with 960 Gy of carbon ions resulted in up to 1.9 DNA double-strand breaks per megabase (Mb). Given that the total size of the Arabidopsis genome is 135 Mb, 960 Gy of carbon ions induce 257 DNA double-strand breaks per genome. Our results indicated that double-strand breaks were most inducible DNA damage by irradiation of carbon ions while single-strand breaks were most inducible by irradiation of helium ions and
rays) and non-ionizing radiation (UVB) in Arabidopsis seedlings. The irradiated seedlings were harvested immediately and used for preparing an agarose plug, which were subjected to denature and non-denature agarose gel electrophoresis using static field electrophoresis and biased sinusoidal field gel electrophoresis. The number of DNA strand breaks were calculated using the molecular length standard curve and the quantity of DNA at each migration position as shown by the quantitative image data. As a result, irradiation of seedlings with 960 Gy of carbon ions resulted in up to 1.9 DNA double-strand breaks per megabase (Mb). Given that the total size of the Arabidopsis genome is 135 Mb, 960 Gy of carbon ions induce 257 DNA double-strand breaks per genome. Our results indicated that double-strand breaks were most inducible DNA damage by irradiation of carbon ions while single-strand breaks were most inducible by irradiation of helium ions and  rays.
rays.
鈴木 政浩; 町田 昌彦; 山口 隆司; 宮村 浩子; 山田 進; 岡本 孝司; 長谷川 幸弘*; 吉田 亨*; Wei, S.*
no journal, ,
In order to promote decommissioning in 1F, it is crucial to find out strong radioactive hot spots inside reactor building rooms based on environmental measurement data composed of structural surface model data and distribution data of air dose rates. Such hot spot prediction allows to reduce radiation risks of persons working inside 1F and consequently to safely construct access routes to remove fuel debris. We introduce a new scheme to inversely estimate radioactive source distributions using LASSO. The scheme is composed of multiple steps, e.g., one of the most essential steps is to select measurement points of air dose rates. In addition, we develop the other engines calculating 3D distributions of air dose rates from the estimated source distributions together with a tool simulating virtual countermeasures and visualizing various outputs of the above engines in 3D space. In the present paper, we overview R&D project to integrate the above three engines.
鈴木 政浩; 青木 勇斗; 山口 隆司; 町田 昌彦; 宮村 浩子; 岡本 孝司
no journal, ,
東京電力福島第一原子力発電所(以下、1Fという)における燃料デブリ取り出しの本格的実施に先立ち、線量率の高い原子炉建屋(以下、「R/B」という)内において、安全なアクセスルート構築を行うためには、高強度線源の除染や遮へい等の環境改善が必要である。原子力機構は、現場の線量率観測データ等を基に高強度線源の逆推定を行い、サイバー空間(VR)だけでなく、物理空間(MR、AR)も交えて、除染や遮へい等の効果を検討するシステム開発を進めている。本報告では、現在までの研究開発成果を示すとともに、1Fへの現場適用を図るために必要となる高機能化の取組みの概要を紹介する。
高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 持丸 貴則*; 山口 郁斗*; 吉見 優希*; 谷垣 実*; 後藤 淳*; 原田 博司*; 正木 弘子*; 伊藤 史哲*
no journal, ,
原子力機構では、大規模公共イベント等におけるテロ対策強化のため、会場周辺の広い範囲で核・放射性物質を迅速に検知するためのモニタリング技術開発を行っている。本プロジェクトでは、放射線検出器を測位センサと組み合わせ、様々な場面で使用可能な放射線マッピング装置の開発を進めている。高エネルギー加速器研究機構加速器施設におけるマッピング試験を実施し、放射線量の高いエリアを地図上に可視化できることを確認した。また、マッピング中のスペクトルデータを参照することにより核種同定を行い、設備の放射化状況を把握することができた。
小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 持丸 貴則*; 山口 郁斗*; 吉見 優希*; 山西 弘城*; 若林 源一郎*; 谷垣 実*; 原田 博司*; 正木 弘子*; et al.
no journal, ,
原子力や放射線利用が広まる中、核物質や放射性物質を利用したテロリズムをいかに防ぐかが問われている。大規模イベント等においてのテロは、そのインパクトの高さから、核セキュリティ対策の導入が試みられている。ゲートモニターによる放射性物質検知は、エリア内への持ち込みを防ぎ、可搬型放射線検出器によるサーベイでは、エリア内には持ち込まれた核・放射性物質がないことを確認する。エリア内サーベイにおいては、多くの人員が必要となるため、システマティックで効率を高めるための技術が必要とされている。そこで我々は、文部科学省の核セキュリティ強化等推進事業費補助金の下で2020年度から技術開発を進めてきた。プロジェクトにおいては、放射線マッピング技術、中性子検出技術、可搬型ガンマ線検出器といった技術開発を進めてきた。本発シリーズ発表はプロジェクトの成果を報告するものであり、本発表はそのうちプロジェクトの概要について報告するものである。
高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 持丸 貴則*; 山口 郁斗*; 吉見 優希*; 山西 弘城*; 若林 源一郎*; 谷垣 実*; 原田 博司*; 正木 弘子*; et al.
no journal, ,
大規模イベント等において、核・放射性物質を使用したテロ等を未然に防止するために、位置と放射線量を測定可能な可搬型装置を用いたマッピング技術及びネットワークを通じた遠隔測定技術を用いたモニタリングシステムの開発を進めている。放射性物質を検知した際の核種同定精度向上のため、可搬型検出器として使用しているCsI(Tl)シンチレーション検出器をよりエネルギー分解能の高い検出器に置き換えるための開発を進めた。可搬型のLaBr シンチレーション検出器を導入するために、ワンボードPCでデータ収集を行い、GPSなどの位置情報等と合わせて定期的に記録できる装置を製作し、性能評価を行った。本発表では、可搬型ガンマ線検出器の試験結果及び比較について報告するとともに、本プロジェクトのまとめと今後の展望について発表する。
シンチレーション検出器を導入するために、ワンボードPCでデータ収集を行い、GPSなどの位置情報等と合わせて定期的に記録できる装置を製作し、性能評価を行った。本発表では、可搬型ガンマ線検出器の試験結果及び比較について報告するとともに、本プロジェクトのまとめと今後の展望について発表する。
山口 郁斗*; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 持丸 貴則*; 吉見 優希*; 山西 弘城*; 若林 源一郎*; 谷垣 実*; 原田 博司*; 正木 弘子*; et al.
no journal, ,
大規模イベント等における核セキュリティ強化のために、会場施設内等で使用できる放射線マッピング装置の開発を進めている。屋内で放射線の測定位置を取得するための技術として、LiDARを用いて周辺の構造物との位置関係を測定し、マップと自身の通過した軌跡を同時に取得するSLAMを導入し、放射線検出器の測定結果を合わせてマッピングする技術を開発した。4輪走行ロボットにLiDAR及び放射線検出器を搭載し、走行経路上の放射線量を測定する。本装置を用いて、高エネルギー加速器研究機構で放射線マッピング試験を実施した。本発表では、屋内マッピング技術の概要及び試験結果について報告する。
持丸 貴則*; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 山口 郁斗*; 吉見 優希*; 山西 弘城*; 若林 源一郎*; 谷垣 実*; 原田 博司*; 正木 弘子*; et al.
no journal, ,
核物質やそのほかの中性子源の検知には、高速中性子検出器が有効である場合がある。EJ-276は、高速中性子及びガンマ線に感度を有するプラスチックシンチレーション検出器で、波形弁別法を用いてガンマ線と中性子を弁別して計数することができる。高速中性子のみを検出するプラスチックシンチレーション検出器では、線源から直接飛来する中性子を支配的に検出し、周囲の構造物等で散乱した中性子は検出されないことから、中性子源の探索において有効である。この特徴を活かすため、角度によって検出効率が変化する検出器を組み合わせて線源方向を特定する技術を開発した。PuBe線源を用いて、高速中性子線源方向を特定するための性能評価試験を実施した。本発表では、開発した方向推定検出器の概要及び性能評価試験について報告する。