Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Kadowaki, Masanao; Yamashita, Yosuke*; Nagatomo, Toshiharu*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.320_1 - 320_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:70.08(Multidisciplinary Sciences)State-of-the-art chemistry climate models (CCMs) have indicated that a future decrease in ozone-depleting substances (ODSs) combined with an increase in greenhouse gases (GHGs) would increase the column ozone amount in most regions except the tropics and Antarctic. However, large Arctic ozone losses have occurred at a frequency of approximately once per decade since the 1990s, despite the ODS concentration peaking in the mid-1990s. To understand this, CCMs were used to conduct 24 experiments with ODS and GHG concentrations set based on predicted values for future years; each experiment consisted of 500-member ensembles. The 50 ensemble members with the lowest column ozone in the mid- and high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere showed a clear ODS dependence associated with low temperatures and a strong westerly zonal mean zonal wind. Even with high GHG concentrations, several ensemble members showed extremely low spring column ozone in the Arctic when ODS concentration remained above the 1980-1985 level. Hence, ODS concentrations should be reduced to avoid large ozone losses in the presence of a stable Arctic polar vortex. The average of the lowest 50 members indicates that GHG increase towards the end of the twenty-first century will not cause worse Arctic ozone depletion.
Hata, Kuniki; Lin, M.*; Yokoya, Akinari*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (103), p.29 - 34, 2017/04
Reactivity of edaravone (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one), which is known to show high antioxidative properties, with oxidative species, such as hydroxyl radical (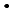 OH) and azide radical (N
OH) and azide radical (N
 ), was investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment, and generation behavior of edaravone radicals produced through these reactions were observed. It was shown that OH-adducts are produced by the reaction with
), was investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment, and generation behavior of edaravone radicals produced through these reactions were observed. It was shown that OH-adducts are produced by the reaction with 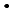 OH in contrast to the other oxidative radicals, which react with edaravone by an electron transfer reaction. Chemical repair properties of edaravone against DNA lesions produced by reactions of DNA with oxidative species were also investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment with deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) and a
OH in contrast to the other oxidative radicals, which react with edaravone by an electron transfer reaction. Chemical repair properties of edaravone against DNA lesions produced by reactions of DNA with oxidative species were also investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment with deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) and a  -radiolysis experiment with plasmid DNA solutions. It was observed that edaravone reduced dGMP radicals just after produced in a dilute aqueous solution and inhibited some base lesions on plasmid DNA more effectively than single strand breaks. These results show that edaravone may protect living system from oxidative stress, such as radiation, by not only scavenging oxidative species but also reducing precursors of DNA leisons.
-radiolysis experiment with plasmid DNA solutions. It was observed that edaravone reduced dGMP radicals just after produced in a dilute aqueous solution and inhibited some base lesions on plasmid DNA more effectively than single strand breaks. These results show that edaravone may protect living system from oxidative stress, such as radiation, by not only scavenging oxidative species but also reducing precursors of DNA leisons.
Yang, S.*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Matsuura, Chihiro*; Hiroishi, Daisuke*; Lertnaisat, P.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 123, p.14 - 19, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.46(Chemistry, Physical) -radiolysis of boiling water has been investigated. The G-value of H
-radiolysis of boiling water has been investigated. The G-value of H evolution was found to be very sensitive to the purity of water. In high-purity water, both H
evolution was found to be very sensitive to the purity of water. In high-purity water, both H and O
and O gases were formed in the stoichiometric ratio of 2:1; a negligible amount of H
gases were formed in the stoichiometric ratio of 2:1; a negligible amount of H O
O remained in the liquid phase. The G-values of H
remained in the liquid phase. The G-values of H and O
and O gas evolution depend on the dose rate: lower dose rates produce larger yields. To clarify the importance of the interface between liquid and gas phase for gas evolution, the gas evolution under Ar gas bubbling was measured. A large amount of H
gas evolution depend on the dose rate: lower dose rates produce larger yields. To clarify the importance of the interface between liquid and gas phase for gas evolution, the gas evolution under Ar gas bubbling was measured. A large amount of H was detected, similar to the radiolysis of boiling water. The evolution of gas was enhanced in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous solution. Deterministic chemical kinetics simulations elucidated the mechanism of radiolysis in boiling water.
was detected, similar to the radiolysis of boiling water. The evolution of gas was enhanced in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous solution. Deterministic chemical kinetics simulations elucidated the mechanism of radiolysis in boiling water.
Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Muroya, Yusa*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 119, p.213 - 217, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.51(Chemistry, Physical)A quick measurement system of a continuous absorption spectrum covering a wide range from 200 to 950 nm was constructed by employing an optical multi-channel detector. Ion beam pulse radiolysis with 12.5 MeV/u He, 18.3 MeV/u C and 17.5 MeV/u Ne ions were performed with the measurement system. Transient absorption spectrum of (SCN)
 was clearly observed in KSCN aqueous solutions within a few minutes in spite of their very small absorbance, demonstrating high sensitivity of 0.001-0.003 in absorbance in the range from 260 to 660 nm as well as short measurement time of a few minutes. Two different absorption peaks attributed to Br
was clearly observed in KSCN aqueous solutions within a few minutes in spite of their very small absorbance, demonstrating high sensitivity of 0.001-0.003 in absorbance in the range from 260 to 660 nm as well as short measurement time of a few minutes. Two different absorption peaks attributed to Br
 and Br
and Br
 were observed simultaneously in NaBr aqueous solutions, showing powerfulness of the measurement system in overviewing chemical kinetics under ion beam irradiation especially in not well investigated chemical systems.
were observed simultaneously in NaBr aqueous solutions, showing powerfulness of the measurement system in overviewing chemical kinetics under ion beam irradiation especially in not well investigated chemical systems.
Yamashita, Shinichi*; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Maehashi, Yuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hata, Kuniki; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
RSC Advances (Internet), 5(33), p.25877 - 25886, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:37.68(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pulse radiolysis experiments were carried out to observe transient absorptions of reaction intermediates produced in N O
O and Ar-saturated aqueous solutions containing 0.9-900 mM NaBr. The most important species among the reaction intermediates are BrOH
and Ar-saturated aqueous solutions containing 0.9-900 mM NaBr. The most important species among the reaction intermediates are BrOH 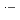 and Br
and Br
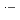 , which commonly have absorption peaks around 360 nm. The experimental results were compared with the results of simulation based on a spur diffusion model. Each of several complicated sequential radiation-induced chemical reactions was carefully considered, optimizing its rate constant within a range of reported values. All the experimental results were able to be universally reproduced by the simulation, assuming a reaction not yet reported, 2BrOH
, which commonly have absorption peaks around 360 nm. The experimental results were compared with the results of simulation based on a spur diffusion model. Each of several complicated sequential radiation-induced chemical reactions was carefully considered, optimizing its rate constant within a range of reported values. All the experimental results were able to be universally reproduced by the simulation, assuming a reaction not yet reported, 2BrOH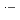
 Br
Br + 2OH
+ 2OH , with a rate constant of 3.8
, with a rate constant of 3.8  10
10 M
M s
s , which is significant only within 10 micro-s for rather high bromide concentrations (
, which is significant only within 10 micro-s for rather high bromide concentrations ( 10 mM). Primary
10 mM). Primary 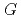 values, which are yields after sufficient diffusion from the spur to the perimeter region during 100 ns, of major water decomposition products, as well as of the reaction intermediates, were calculated for N
values, which are yields after sufficient diffusion from the spur to the perimeter region during 100 ns, of major water decomposition products, as well as of the reaction intermediates, were calculated for N O
O and Ar-saturated conditions as a function of NaBr concentration.
and Ar-saturated conditions as a function of NaBr concentration.
Hata, Kuniki; Urushibara, Ayumi*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Lin, M.*; Muroya, Yusa*; Shikazono, Naoya; Yokoya, Akinari; Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Journal of Radiation Research, 56(1), p.59 - 66, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.40(Biology)Yamashita, Yuji; Tanabe, Yosuke*; Adachi, Yasuhisa*
Nogyo Noson Kogakkai Rombunshu, 81(6), p.33 - 37, 2013/12
We obtained breakthrough curves of humic acids with different molecular weight through the column packed with glass beads with various NaCl concentrations. Each breakthrough curve of each humic acid reached almost a stable plateau at which the relative concentration was less than unity. The relative concentrations at each plateau decreased with an increase in the NaCl concentration. Dimensionless deposition rate constants and collision efficiencies of humic acids were calculated. Collision efficiencies were plotted as a function of NaCl concentration to draw a colloidal stability curve. In both humic acids, the obvious boundary points, which were known as the critical deposition concentration (CDC), were obtained from the colloidal stability curve. The value of CDC of smaller molecular weight fraction was higher than that of larger one. In the slow deposition condition, the slope of the stability curve of larger molecular weight fraction was steeper than that of smaller one.
Hata, Kuniki; Urushibara, Ayumi; Yamashita, Shinichi; Shikazono, Naoya; Yokoya, Akinari; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 434(2), p.341 - 345, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:23.68(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Yamashita, Shinichi; Baldacchino, G.*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.*; Kimura, Atsushi; Murakami, Takeshi*; Katsumura, Yosuke
Free Radical Research, 46(7), p.861 - 871, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:53.35(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Radiation-induced reactions in aqueous solutions of a water-soluble coumarin derivative, coumarin-3-carboxyl acid (C3CA), have been investigated by pulse radiolysis with 35-MeV electron beam, final product analysis after  Co
Co 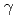 -irradiations, and deterministic model simulations. It was found that C3CA reacts with the hydroxyl radical (
-irradiations, and deterministic model simulations. It was found that C3CA reacts with the hydroxyl radical ( OH) as well as the hydrated electron at nearly diffusion-controlled rate constants: 6.8
OH) as well as the hydrated electron at nearly diffusion-controlled rate constants: 6.8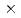 10
10 and 2.1
and 2.1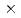 10
10 M
M s
s , respectively. Reactivity of C3CA toward O
, respectively. Reactivity of C3CA toward O

 was not confirmed. Production of a fluorescent molecule 7-hydroxy-coumarin-3-carboxylic acid (7OH-C3CA) was detected by a fluorescence spectrometer coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Production yields of 7OH-C3CA were in a range from 0.025 to 0.18 (100 eV)
was not confirmed. Production of a fluorescent molecule 7-hydroxy-coumarin-3-carboxylic acid (7OH-C3CA) was detected by a fluorescence spectrometer coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Production yields of 7OH-C3CA were in a range from 0.025 to 0.18 (100 eV) , depending on irradiation conditions. A variety of the yield with saturating gas, additive, and C3CA concentration implied that there are at least two pathways from scavenging reaction of C3CA toward
, depending on irradiation conditions. A variety of the yield with saturating gas, additive, and C3CA concentration implied that there are at least two pathways from scavenging reaction of C3CA toward  OH to 7OH-C3CA: peroxidation reaction followed by elimination of perhydroxyl radical and disproportionation reaction. A reaction mechanism involving the two pathways was proposed and incorporated into the simulations, showing good explanation of experimentally measured 7OH-C3CA yields with a constant conversion factor from
OH to 7OH-C3CA: peroxidation reaction followed by elimination of perhydroxyl radical and disproportionation reaction. A reaction mechanism involving the two pathways was proposed and incorporated into the simulations, showing good explanation of experimentally measured 7OH-C3CA yields with a constant conversion factor from  OH scavenging to 7OH-C3CA production, 4.7%, unless
OH scavenging to 7OH-C3CA production, 4.7%, unless 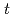 -BuOH is not added.
-BuOH is not added.
Maeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Baldacchino, G.*; Sihver, L.*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Katsumura, Yosuke
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 80(12), p.1352 - 1357, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.64(Chemistry, Physical)Coumari-3-carboxylic acid scavenges OH radical produced in water radiolysis, leading to production of a fluorescence probe at almost constant ratio relative to the amount of the scavenged OH radicals. This was applied in estimation of OH radical yield in water radiolysis especially with therapeutic heavy ions of GeV-class energies, i.e.  C
C beams of 135, 290 and 400 MeV/u. OH yields upstream of the Bragg peaks decreased with increasing penetration depth of the projectile ions while that downstream suddenly jumped up to near the value for low-LET radiations such as
beams of 135, 290 and 400 MeV/u. OH yields upstream of the Bragg peaks decreased with increasing penetration depth of the projectile ions while that downstream suddenly jumped up to near the value for low-LET radiations such as  -rays. This is due to low-LET secondary fragmentation ions produced during long trajectory of the primary projectile C ion. Quantitative explanation by nuclear fragmentation simulations with PHITS code was attempted and resulted in 15-45% underestimation in the region behind the Bragg peaks, which would be due to the difference in geometries between irradiations of the sample solutions and dosimetry with a small ionization chamber.
-rays. This is due to low-LET secondary fragmentation ions produced during long trajectory of the primary projectile C ion. Quantitative explanation by nuclear fragmentation simulations with PHITS code was attempted and resulted in 15-45% underestimation in the region behind the Bragg peaks, which would be due to the difference in geometries between irradiations of the sample solutions and dosimetry with a small ionization chamber.
Oka, Toshitaka; Yamashita, Shinichi; Midorikawa, Masamichi*; Saiki, Seiichi; Muroya, Yusa*; Kamibayashi, Masato*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Anzai, Kazunori*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Analytical Chemistry, 83(24), p.9600 - 9604, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:77.98(Chemistry, Analytical)Chemical reactions of a novel gauche-type spin trap, G-CYPMPO (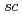 -5-(5,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-yl)-5-methy-1-pyrroline 1-oxide, torsion angle: O1-P1-C6-N1 of 52.8
-5-(5,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphosphinan-2-yl)-5-methy-1-pyrroline 1-oxide, torsion angle: O1-P1-C6-N1 of 52.8 ), with reactive oxygen species were examined by pulse radiolysis technique with 35 MeV electron beam and electron spin resonance spectroscopy after
), with reactive oxygen species were examined by pulse radiolysis technique with 35 MeV electron beam and electron spin resonance spectroscopy after  Co
Co  -ray irradiation. The spin trapping reaction rate constants of G-CYPMPO toward hydroxyl radical and hydrated electron were estimated to be (4.2
-ray irradiation. The spin trapping reaction rate constants of G-CYPMPO toward hydroxyl radical and hydrated electron were estimated to be (4.2 0.1)
0.1) 10
10 and (11.8
and (11.8 0.2)
0.2) 10
10 M
M s
s , respectively. Half-lives of spin adducts, hydroxyl radical and perhydroxyl radical adducted G-CYPMPO were estimated to be
, respectively. Half-lives of spin adducts, hydroxyl radical and perhydroxyl radical adducted G-CYPMPO were estimated to be  35 and
35 and  90 min, respectively. A comparison of the results with earlier reports using different radical sources suggests that the purity of the solution and/or the radical generation technique may influence the stability of spin adducts.
90 min, respectively. A comparison of the results with earlier reports using different radical sources suggests that the purity of the solution and/or the radical generation technique may influence the stability of spin adducts.
Maeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Baldacchino, G.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Murakami, Takeshi*; Katsumura, Yosuke
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 80(4), p.535 - 539, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:91.73(Chemistry, Physical)Aqueous coumarin-3-carboxylic Acid (3CCA) solutions were irradiated with eight different ion beams covering LET range from 0.5 to above 2000 eV/nm. 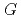 -values of 7OH-3CCA, one of hydroxylated products in radiolysis of the solutions, have been determined by fluorescence-HPLC technique in 3CCA concentration range from 0.1 to 26 mM. The formation yield of 7OH-3CCA increased with increasing concentration of 3CCA while it decreased with increasing LET value of ion beam. Compared with our previous reports on
-values of 7OH-3CCA, one of hydroxylated products in radiolysis of the solutions, have been determined by fluorescence-HPLC technique in 3CCA concentration range from 0.1 to 26 mM. The formation yield of 7OH-3CCA increased with increasing concentration of 3CCA while it decreased with increasing LET value of ion beam. Compared with our previous reports on 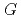 (
( OH) at a scavenging capacity of 10
OH) at a scavenging capacity of 10 s with absorption spectroscopy, it was found that
s with absorption spectroscopy, it was found that 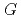 (7OH-3CCA) is about (4.7
(7OH-3CCA) is about (4.7 0.6)% of
0.6)% of 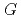 (
( OH), which is consistent for all of the ion beams used in the present study. However, 7OH-3CCA yields in high CCA concentration region, especially by using extremely high LET ions, were much higher than expected values based on the above conversion factor and
OH), which is consistent for all of the ion beams used in the present study. However, 7OH-3CCA yields in high CCA concentration region, especially by using extremely high LET ions, were much higher than expected values based on the above conversion factor and 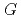 (
( OH) value predicted in theoretical work.
OH) value predicted in theoretical work.
Hata, Kuniki; Lin, M.; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Muroya, Yusa*; Fu, H. Y.*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Nakagawa, Hidehiko*
Journal of Radiation Research, 52(1), p.15 - 23, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:60.99(Biology)Yamashita, Shinichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Baldacchino, G.*; Katsumura, Yosuke
Charged Particle and Photon Interactions with Matter; Recent Advances, Applications, and Interfaces, p.325 - 354, 2010/12
Irradiation effects induced by heavy ions are much different from those by low-LET radiations. Such distinctiveness has been applied to cancer therapy, surface processing, analytical techniques, and so on. However, detailed mechanism through which such distinctiveness appears has not been clarified yet. In this chapter, what have experimentally been found recently, especially within these five years, in water radiolysis with positively-charged atomic heavy ions are shown. Steady-state radiolysis studies and pulse radiolysis studies are separately summarized because these two approaches inherently involve own advantages and limitations. Gathering reported products yields and kinetics, track structures and intra-track dynamics are discussed. One of the most characteristic features of recent studies is that track-segment or -differential yields were intensively measured compared to earlier studies.
Yan, Y.*; Lin, M.; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Muroya, Yusa*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Hata, Kuniki; Meesungnoen, J.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*
Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 88(10), p.1026 - 1033, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.10(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The optical absorption spectra of the solvated electron (e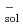 ) in sub- and super-critical methanol are measured by both electron pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis techniques, at temperatures in the range 220-270
) in sub- and super-critical methanol are measured by both electron pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis techniques, at temperatures in the range 220-270  C. Over the density range studied (
C. Over the density range studied ( 0.45-0.59 g/cm
0.45-0.59 g/cm ), the position of the absorption maximum (
), the position of the absorption maximum (
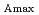 ) of e
) of e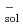 is found to shift only slightly to the red with decreasing density. In agreement with our previous work in water, at a fixed pressure,
is found to shift only slightly to the red with decreasing density. In agreement with our previous work in water, at a fixed pressure, 
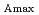 decreases monotonically with increasing temperature in passing through the phase transition at
decreases monotonically with increasing temperature in passing through the phase transition at 
 (239.5
(239.5  C). By contrast, at a fixed density,
C). By contrast, at a fixed density, 
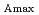 exhibits a minimum as the solvent passes above the critical point into the supercritical state. These behaviors are discussed in terms of microscopic arguments based on the changes that occur in the methanol properties and methanol structure in the sub- and supercritical regimes.
exhibits a minimum as the solvent passes above the critical point into the supercritical state. These behaviors are discussed in terms of microscopic arguments based on the changes that occur in the methanol properties and methanol structure in the sub- and supercritical regimes.
Lin, M.; Fu, H.*; Lampre, I.*; De Waele, V.*; Muroya, Yusa*; Yan, Y.*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Mostafavi, M.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 113(44), p.12193 - 12198, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.32(Chemistry, Physical)With a revisit of the absorption coefficient of the solvated electron in propane-1,2,3-triol, the temperature dependent behavior of the absorption spectrum of solvated electron was studied from room temperature to 573 K by pulse radiolysis techniques. The change in the absorption spectrum of solvated electron in propane-1,2,3-triol observed by cooling down from a high temperature to 333 K is compared with that occurring during the electron solvation process at 333 K. The effect of the specific molecular structure of propane-1,2,3-triol compared to other alcohols is discussed.
Lin, M.; Katsumura, Yosuke; Muroya, Yusa*; Yamashita, Shinichi
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2009 (CD-ROM), p.66 - 70, 2009/10
Supercritical water cooled reactor (SCWR) is expected to be one of the most promised next generation reactors (GenIV). Proper water chemistry control, in particular, the injection of H into the coolant to convert O
into the coolant to convert O and H
and H O
O into H
into H O by radiolytic processes, may represent the key to keep the integrity of the reactors. In recent years, studies on the radiolytic yields and rate constants up to supercritical conditions were performed. The experimental results show that the radiolytic yields at temperatures above 300
O by radiolytic processes, may represent the key to keep the integrity of the reactors. In recent years, studies on the radiolytic yields and rate constants up to supercritical conditions were performed. The experimental results show that the radiolytic yields at temperatures above 300 C do not follow linear relationship with temperature and there is a very significant density effects under supercritical conditions, especially around
C do not follow linear relationship with temperature and there is a very significant density effects under supercritical conditions, especially around 
 . The rate constants of many reactions do not follow linear Arrhenius relationship and there is also strong density dependence under supercritical conditions.
. The rate constants of many reactions do not follow linear Arrhenius relationship and there is also strong density dependence under supercritical conditions.
Baldacchino, G.*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Murakami, Takeshi*
Chemical Physics Letters, 468(4-6), p.275 - 279, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:78.90(Chemistry, Physical)This paper reports a sensitive method using HPLC-fluorescence detection of  OH in liquid water under high-energy heavy-ion irradiation. The coumarin-3-carboxylic-acid (3CCA) molecule was selected for probing
OH in liquid water under high-energy heavy-ion irradiation. The coumarin-3-carboxylic-acid (3CCA) molecule was selected for probing  OH and providing the fluorescent 7-hydroxy-coumarin-3-carboxylic-acid (7OH-3CCA). Since the concentration limit achievable is better than 1 nM, the radiolytic yields were determined with a sensitivity of 2
OH and providing the fluorescent 7-hydroxy-coumarin-3-carboxylic-acid (7OH-3CCA). Since the concentration limit achievable is better than 1 nM, the radiolytic yields were determined with a sensitivity of 2 10
10 mol/J for 4.8-GeV-
mol/J for 4.8-GeV- C
C of and 20-GeV-
of and 20-GeV- Ar
Ar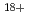 in the ns time-range. They decrease with the linear energy transfer from 2.8
in the ns time-range. They decrease with the linear energy transfer from 2.8 10
10 to 1.3
to 1.3 10
10 mol/J (
mol/J ( C
C of 11 eV/nm) and 1.5
of 11 eV/nm) and 1.5 10
10 to 0.9
to 0.9 10
10 mol/J (
mol/J ( Ar
Ar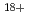 of 90 eV/nm) which is in agreement with the literature data.
of 90 eV/nm) which is in agreement with the literature data.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Murakami, Takeshi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1224 - 1229, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.86(Chemistry, Physical)Measurements of primary 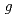 -values (at
-values (at  10
10 s after the initial ionizing event) of e
s after the initial ionizing event) of e
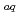 ,
,  OH and H
OH and H O
O were extended to the very high linear energy transfer (LET) region (
were extended to the very high linear energy transfer (LET) region ( 700 eV per nm) near the Bragg peak. Heavy ions (
700 eV per nm) near the Bragg peak. Heavy ions ( He
He ,
,  C
C ,
,  Ne
Ne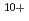 ,
,  Si
Si ,
,  Ar
Ar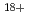 and
and  Fe
Fe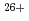 ) of energies up to 28 GeV were provided by the Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC) of the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) in Chiba, Japan. Energies of the ions were decreased down to about 10 MeV per u for
) of energies up to 28 GeV were provided by the Heavy Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC) of the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) in Chiba, Japan. Energies of the ions were decreased down to about 10 MeV per u for  He
He using an energy absorber made of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) plates in order to vary the LET values. Beam was visualized after passing through the energy absorber using agarose gel of aqueous solution containing methyl viologen and sodium formate in order to determine how long ions can penetrate into water. Based on the information of the penetration depth of ions in samples, much attention was paid to dose correction and LET evaluation. The obtained data were plotted as a function of (
using an energy absorber made of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) plates in order to vary the LET values. Beam was visualized after passing through the energy absorber using agarose gel of aqueous solution containing methyl viologen and sodium formate in order to determine how long ions can penetrate into water. Based on the information of the penetration depth of ions in samples, much attention was paid to dose correction and LET evaluation. The obtained data were plotted as a function of (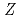
 /
/ )
) also instead of LET in order to discuss effects of physical track structures on product yields, resulted in better universality.
also instead of LET in order to discuss effects of physical track structures on product yields, resulted in better universality.
 (MV
(MV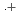 ) in deaerated methyl viologen solutions containing various concentrations of sodium formate and Monte Carlo simulation
) in deaerated methyl viologen solutions containing various concentrations of sodium formate and Monte Carlo simulationYamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Miyazaki, Toyoaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Meesungnoen, J.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*
Radiation Research, 170(4), p.521 - 533, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.99(Biology)Formation yields of methyl viologen cation radicals  (MV
(MV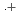 ) (100 eV)
) (100 eV) have been measured in deaerated aqueous solutions of methyl viologen, MV
have been measured in deaerated aqueous solutions of methyl viologen, MV , containing various concentrations of formate anion after irradiation with six different ion beams (from
, containing various concentrations of formate anion after irradiation with six different ion beams (from  He
He to
to  Fe
Fe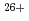 with incident energies varying from 0.6 to 28 GeV) provided by HIMAC at NIRS in Japan. In parallel to the above measurements, Monte Carlo simulations of the radiolysis of the MV
with incident energies varying from 0.6 to 28 GeV) provided by HIMAC at NIRS in Japan. In parallel to the above measurements, Monte Carlo simulations of the radiolysis of the MV -formate solutions have been performed to investigate complementarily mechanism from which distinctive irradiation effects of heavy ions are derived from the microscopic viewpoints experimentally non-feasible.
-formate solutions have been performed to investigate complementarily mechanism from which distinctive irradiation effects of heavy ions are derived from the microscopic viewpoints experimentally non-feasible.