Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Shamoto, Shinichi; Yasui, Yukio*; Matsuura, Masato*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(3), p.033235_1 - 033235_6, 2020/08
Ultralow energy magnon in yttrium iron garnet crystal has been studied by inelastic neutron scattering in an energy range from 10 to 45  eV. When a magnetic field of about 0.1 T is applied along [111], ultralow energy magnon anomaly is found at 10 K.
eV. When a magnetic field of about 0.1 T is applied along [111], ultralow energy magnon anomaly is found at 10 K.
 RhSi
RhSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Watanabe, Isao*; Yasui, Yukio*; Chang, L.-J.*; Kondo, Keietsu; Ito, Takashi; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Hagihara, Masato*; Frontzek, M. D.*; et al.
Communications Materials (Internet), 1, p.43_1 - 43_6, 2020/07
High-temperature short-range order is discovered up to 720 K in Mn RhSi by complementary use of neutron scattering and muon spin relaxation measurements.
RhSi by complementary use of neutron scattering and muon spin relaxation measurements.
 ladder
ladderUeda, Hiroshi*; Onoda, Shigeki*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Yoshizawa, Daichi*; Morioka, Toshiaki*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Hagihara, Masato*; Soda, Minoru*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(14), p.140408_1 - 140408_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) ZrCuO
ZrCuO with incommensurate magnetic structure
with incommensurate magnetic structureYasui, Yukio*; Igawa, Naoki; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034012_1 - 034012_6, 2015/09
Magnetic structure has been studied by using neutron diffraction for quasi one-dimensional quantum spin system Li ZrCuO
ZrCuO with CuO
with CuO ribbon chains. The CuO
ribbon chains. The CuO ribbon system Li
ribbon system Li ZrCuO
ZrCuO exhibits the antiferromagnetic transition at T
exhibits the antiferromagnetic transition at T
 7 K, however, the magnetic transition is not accompanied with ferroelectricity. At 3K, we observed magnetic superlattice reflections at Q = (0, k, l
7 K, however, the magnetic transition is not accompanied with ferroelectricity. At 3K, we observed magnetic superlattice reflections at Q = (0, k, l
 ) and (h, 0, l
) and (h, 0, l
 ) (h, k and l = even) with
) (h, k and l = even) with 
 0.488 by the powder neutron diffraction. By the combined studies of neutron diffraction and magnetization data, the magnetic structure of Li
0.488 by the powder neutron diffraction. By the combined studies of neutron diffraction and magnetization data, the magnetic structure of Li ZrCuO
ZrCuO is proposed. On the bases of the obtained data, reasons for absence of ferroelectricity in Li
is proposed. On the bases of the obtained data, reasons for absence of ferroelectricity in Li ZrCuO
ZrCuO are discussed.
are discussed.
 ions for LaCo
ions for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O
Asai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igawa, Naoki; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.014034_1 - 014034_6, 2014/06
We have carried out the neutron scattering measurements for a single crystal of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O in order to investigate the ferromagnetic ordering induced by Rh
in order to investigate the ferromagnetic ordering induced by Rh substitution for Co
substitution for Co of LaCoO
of LaCoO . The ordered moment is evaluated to be 0.4
. The ordered moment is evaluated to be 0.4 0.2
0.2
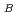 , which is consistent with the saturation magnetization of LaCo
, which is consistent with the saturation magnetization of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O . It indicates that the ferromagnetic ordering of LaCo
. It indicates that the ferromagnetic ordering of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O originates from the short-range ferromagnetic ordering disordered by Rh
originates from the short-range ferromagnetic ordering disordered by Rh ions.
ions.
 in LaCo
in LaCo Rh
Rh O
O investigated by structural phenomena
investigated by structural phenomenaAsai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kobayashi, Wataru*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Kumai, Reiji*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(11), p.114606_1 - 114606_6, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co
have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O
ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O octahedron of LaCo
octahedron of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh
are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO
substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co
from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co
ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh
ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh ions.
ions.
 Ti
Ti O
O
Chang, L.-J.*; Onoda, Shigeki*; Su, Y.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; Tsuei, K.-D.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Lees, M. R.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 3, p.992_1 - 992_7, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:174 Percentile:96.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences) planes of Na
planes of Na CoO
CoO
 yH
yH O
OMoyoshi, Taketo*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Solid State Sciences, 12(5), p.656 - 659, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) CoO
CoO

 D
D O; Neutron scattering
O; Neutron scatteringMoyoshi, Taketo*; Yasui, Yukio*; Soda, Minoru*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(7), p.074705_1 - 074705_6, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron scattering investigations on single crystal Na CoO
CoO y(D
y(D O) have been carried out. Strong 2-D diffuse scattering due to the short-range ordered state of D
O) have been carried out. Strong 2-D diffuse scattering due to the short-range ordered state of D O molecules are observed. Significant scattering has been also observed for phonons originating from the vibrations of the short-range ordered D
O molecules are observed. Significant scattering has been also observed for phonons originating from the vibrations of the short-range ordered D O molecules. No firm evidence for the magnetic fluctuations has been found for the hydrated superconducting component Na
O molecules. No firm evidence for the magnetic fluctuations has been found for the hydrated superconducting component Na CoO
CoO y(D
y(D O), while the very weak intensity modulation observed in the scans along (1/2,1/2,l) suggests the existence of the antiferromagnetic fluctuations in the non-hydrated parts of the sample.
O), while the very weak intensity modulation observed in the scans along (1/2,1/2,l) suggests the existence of the antiferromagnetic fluctuations in the non-hydrated parts of the sample.
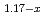 Pb
Pb VS
VS
Ino, Akihiro*; Okane, Tetsuo; Fujimori, Shinichi; Fujimori, Atsushi; Mizokawa, Takashi*; Yasui, Yukio*; Nishikawa, Takashi*; Sato, Masatoshi*
Physical Review B, 69(19), p.195116_1 - 195116_8, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Yasui, Yukio*; Ito, Masafumi*; Iikubo, Satoshi*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(2), p.464 - 468, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:80.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Yasui, Yukio*; Fujita, Toshiaki*; Miyashita, Takeshi*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72(7), p.1729 - 1734, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:89.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
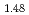 Nd
Nd Sr
Sr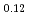 CuO
CuO
Ito, Masafumi*; Yasui, Yukio*; Iikubo, Satoshi*; Soda, Minoru*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kobayashi, Akito*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 72(7), p.1627 - 1630, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Zn
Zn Cr
Cr Se
Se
Iikubo, Satoshi*; Yasui, Yukio*; Oda, Keisuke*; Ono, Yohei*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 71(11), p.2792 - 2799, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.20(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -moments in Tb
-moments in Tb Ti
Ti O
O ; Neutron scattering study
; Neutron scattering studyYasui, Yukio*; Kanada, Masaki*; Ito, Masafumi*; Harashina, Hiroshi*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Okumura, H.*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Kadowaki, Hiroaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 71(2), p.599 - 606, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:89.63(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Ni
Ni SbO
SbO
Fukui, Akito*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The powder neutron crystal structure analysis and measurements of the magnetization and the specific heat have been carried out for the honeycomb lattice spin system Li Ni
Ni SbO
SbO . From the Rietveld analysis of the neutron diffraction data, we determined the crystal structure of Li
. From the Rietveld analysis of the neutron diffraction data, we determined the crystal structure of Li Ni
Ni SbO
SbO , where the space group is
, where the space group is 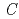 2/
2/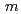 monoclinic and the distortion from ideal honeycomb lattice is
monoclinic and the distortion from ideal honeycomb lattice is  0.1 % only. The Weiss temperature
0.1 % only. The Weiss temperature 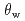 obtained from the temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility is 12.2 K, indicating that dominant interaction between the Ni
obtained from the temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility is 12.2 K, indicating that dominant interaction between the Ni spins is ferromagnetic one. However, from the behavior of the magnetic susceptibility and the specific heat, Li
spins is ferromagnetic one. However, from the behavior of the magnetic susceptibility and the specific heat, Li Ni
Ni SbO
SbO is found to exhibit an antiferromagnetic transition at
is found to exhibit an antiferromagnetic transition at 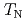 = 13.5 K.
= 13.5 K.
 Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O
Yasui, Yukio*; Fujimura, Akio*; Omori, Kiyoshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The magnetic structure of Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O with CuO
with CuO ribbon chains have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. The magnetic reflections were observed below
ribbon chains have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. The magnetic reflections were observed below 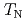 = 1.85 K and all of the magnetic reflections overlapped Bragg reflections. Considering that these are 16-Cu
= 1.85 K and all of the magnetic reflections overlapped Bragg reflections. Considering that these are 16-Cu ions in the unit cell, Cs
ions in the unit cell, Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O has the collinear-antiferromagnetic structure.
has the collinear-antiferromagnetic structure.
 revealed by the neutron diffraction study
revealed by the neutron diffraction studyKori, Shunsuke*; Igarashi, Taichi*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Taniguchi, Hiroki*; Tanisaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igawa, Naoki; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The neutron powder diffraction for the multiferroic material, NdCrTiO has been carried out to investigate the development of the magnetic order in the material. We found the intensities of magnetic peaks increased with decreasing temperature below the transition temperature T
has been carried out to investigate the development of the magnetic order in the material. We found the intensities of magnetic peaks increased with decreasing temperature below the transition temperature T . We discuss temperate dependence of magnetic moments and the development of magnetic order.
. We discuss temperate dependence of magnetic moments and the development of magnetic order.
 O
O ; Neutron scattering
; Neutron scatteringYasui, Yukio*; Sato, Kenji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Masatoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English