Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , AgNbO
, AgNbO , and KNbO
, and KNbO
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kobayashi, Toru; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Yuji; Noguchi, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(9), p.09SP12_1 - 09SP12_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Physics, Applied)NaNbO , AgNbO
, AgNbO , and KNbO
, and KNbO with ABO
with ABO -type perovskite system is known to possess good ferroelectric properties. We directly determined the rattling space of each atom through local structure analysis. This analysis revealed the bonding sites with large fluctuations varied with varying ion size. Experimental evidence including soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy, indicates that the A-site ions are hybridized with oxygen.
-type perovskite system is known to possess good ferroelectric properties. We directly determined the rattling space of each atom through local structure analysis. This analysis revealed the bonding sites with large fluctuations varied with varying ion size. Experimental evidence including soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy, indicates that the A-site ions are hybridized with oxygen.
 /Eu
/Eu selectivity with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid and its bisamide chelates.
selectivity with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid and its bisamide chelates.Kaneko, Masashi; Sasaki, Yuji; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(5), p.515 - 526, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Density-functional theory calculations were applied to molecular structure and complex formation reaction modelings of metal ion complexes with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) and its bisamide (DTPABA) chelates to understand the metal ions selectivity between Am and Eu
and Eu . The calculated complexes with DTPA and DTPABA chelates reproduced the coordination geometries of experimental crystal structures. Calculated Gibbs free energies of the complex formation reactions indicated that Am
. The calculated complexes with DTPA and DTPABA chelates reproduced the coordination geometries of experimental crystal structures. Calculated Gibbs free energies of the complex formation reactions indicated that Am ion forms higher stable complexes with both chelates than Eu
ion forms higher stable complexes with both chelates than Eu ion, being consistent with the experimental results. The higher Am
ion, being consistent with the experimental results. The higher Am selectivity over Eu
selectivity over Eu was suggested to originate in the larger bond overlap between Am
was suggested to originate in the larger bond overlap between Am 5f-orbital and N 2s, 2p-orbital. This mean that the covalent contribution between metal ion and donor atoms differentiates the complex formation stabilities, leading to the Am
5f-orbital and N 2s, 2p-orbital. This mean that the covalent contribution between metal ion and donor atoms differentiates the complex formation stabilities, leading to the Am /Eu
/Eu selectivity. We expect that this study contributes to systematize the origin of metal ions selectivity and to accelerate novel ligands exploration.
selectivity. We expect that this study contributes to systematize the origin of metal ions selectivity and to accelerate novel ligands exploration.
Kaneko, Masashi; Suzuki, Hideya; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Inorganic Chemistry, 57(23), p.14513 - 14523, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:79.50(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We elucidated the separation mechanism between Am(III) and Cm(III) ions by using two different types of diamide ligands, diglycolamide (DGA) and alkylated diamide amine (ADAAM), by means of the density functional theory technique and electron density analysis. The molecular geometries and formation reactions of the metal-ligand complexes were modeled by using [M(DGA) ]
] and [M(ADAAM)(NO
and [M(ADAAM)(NO )
) (H
(H O)]. We successfully reproduced Cm(III) selectivity over Am(III) with DGA and Am(III) selectivity over Cm(III) with ADAAM. Furthermore, we analyzed the bonding properties between the metal ion and the diamide-type ligands by using model complexes, [M(DGA)
O)]. We successfully reproduced Cm(III) selectivity over Am(III) with DGA and Am(III) selectivity over Cm(III) with ADAAM. Furthermore, we analyzed the bonding properties between the metal ion and the diamide-type ligands by using model complexes, [M(DGA) ]
] and [M(ADAAM)(NO
and [M(ADAAM)(NO )
) (H
(H O)], and revealed the differences in terms of the bond dissociation energy and the metal 5f-orbital participation in the covalency between the Am(III) and the Cm(III) complexes. It was suggested that the differences were key factors to understand the Am(III)/Cm(III) selectivity.
O)], and revealed the differences in terms of the bond dissociation energy and the metal 5f-orbital participation in the covalency between the Am(III) and the Cm(III) complexes. It was suggested that the differences were key factors to understand the Am(III)/Cm(III) selectivity.
Kimura, Taiki*; Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 47(42), p.14924 - 14931, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We demonstrated density functional calculations of Eu(III) and Am(III) complexes with pnictogen-donor (X) ligands, CH )
) X-CH
X-CH -CH
-CH -X(CH
-X(CH )
) (X = N, P, As and Sb). We investigated the optimized structures of the cmoplexes and the Gibbs energy differences in the complex formation reactions. Those results indicated that the N- and P-donor ligands have Am(III) ion selectivity over Eu(III) ion, especially, the P-donor ligand showed the highest selectivity. The tendency of the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity by the pnictogen-dono ligands was found to be comparable to that of soft acid classification in hard and soft acids and bases rule. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the bonding property between the metal ion and the pnictogen atoms correlated with the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity. In particular, the participation of f-orbital electrons of the metal ion in the covalency was indicated to have an important role for the selectivity.
(X = N, P, As and Sb). We investigated the optimized structures of the cmoplexes and the Gibbs energy differences in the complex formation reactions. Those results indicated that the N- and P-donor ligands have Am(III) ion selectivity over Eu(III) ion, especially, the P-donor ligand showed the highest selectivity. The tendency of the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity by the pnictogen-dono ligands was found to be comparable to that of soft acid classification in hard and soft acids and bases rule. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the bonding property between the metal ion and the pnictogen atoms correlated with the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity. In particular, the participation of f-orbital electrons of the metal ion in the covalency was indicated to have an important role for the selectivity.
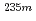 U oxide and fluoride
U oxide and fluorideShigekawa, Yudai*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Yasuda, Yuki*; Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Shinohara, Atsushi*
Physical Review C, 98(1), p.014306_1 - 014306_5, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.05(Physics, Nuclear)The nuclear half-life of 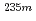 U has been reported to vary depending on the chemical environment. In this study, both the half-life and the internal-conversion (IC) electron energy spectrum were measured for
U has been reported to vary depending on the chemical environment. In this study, both the half-life and the internal-conversion (IC) electron energy spectrum were measured for 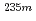 U with identical chemical environments for the first time.
U with identical chemical environments for the first time. 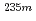 U oxide and fluoride samples were subjected to these measurements, and clear differences in the half-life and the energy spectrum between these samples were observed. The peaks in the energy spectra were identified with the relativistic density functional theory calculation, and the molecular orbital states of the
U oxide and fluoride samples were subjected to these measurements, and clear differences in the half-life and the energy spectrum between these samples were observed. The peaks in the energy spectra were identified with the relativistic density functional theory calculation, and the molecular orbital states of the 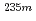 U oxide and fluoride estimated from the energy spectra and the calculation qualitatively explained the difference in the half-lives between the samples.
U oxide and fluoride estimated from the energy spectra and the calculation qualitatively explained the difference in the half-lives between the samples.
 ssbauer spectroscopic parameters
ssbauer spectroscopic parametersKaneko, Masashi
Hosha Kagaku, (35), p.36 - 39, 2017/03
This paper is an article for research introduction by winner of the Japan Society of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences Encouragement Price 2016. It was mentioned about the achievements which revealed the spin transition behavior of iron complex and the separation mechanism of actinides from lanthanides.
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Ueno, Yuko*; Ishiwata, Yoichi*; Eguchi, Ritsuko*; Watanabe, Masamitsu*; Shin, S.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Carbon, 39(9), p.1359 - 1402, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Hirono, Shigeru*; Umemura, Shigeru*; Ueno, Yuko*; Hayashi, Takayoshi*; Grush, M. M.*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Carbon, 39(9), p.1403 - 1407, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:58.98(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Hirata, Masaru; Bastug, T.*; Tachimori, Shoichi; Sekine, Rika*; Onoe, Jun*; Nakamatsu, Hirohide*
Advances in Quantum Chemistry, Volume 37, p.325 - 333, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Hirata, Masaru; Tachimori, Shoichi; Sekine, Rika*; Onoe, Jun*; Nakamatsu, Hirohide*
Advances in Quantum Chemistry, Volume 37, p.335 - 351, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Takenaka, Hisataka*; Ueno, Yuko*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Applied Physics Letters, 77(17), p.2653 - 2655, 2000/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.91(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Takeshima, Naoki*; Terazawa, Norihisa*; Aoki, Yasushi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nashiyama, Isamu; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.188 - 190, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Hiroshi
Kagaku To Kogyo, 45(5), p.941 - 944, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Hiroshi
Kagaku, 46(11), p.748 - 752, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
Phys.Status Solidi A, 66, p.175 - 181, 1981/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kawatsura, Kiyoshi; Ozawa, K.; ;
Phys.Lett.,A, 60(4), p.327 - 329, 1977/04
no abstracts in English
KURRI-TR-55, p.31 - 33, 1969/00
no abstracts in English
Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Suzuki, Hideya; Matsumura, Tatsuro
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed separation reagents between Am and Cm ions, which are minor actinides, to achieve partitioning and transmutation strategy. We aim to elucidate the Am/Cm separation mechanism by various reagents at a molecular level to design a novel extraction reagent. This study focused on the Am/Cm separation with diglycolamide (DGA) and alkyl-diacetoamidamine (ADAAM) reagents by using density functional theory. We modeled the complex formation reactions by referring to reported single crystal structures and solvent extraction experiments. As the result, we succeeded in reproducing the Am/Cm separation behaviors with DGA and ADAAM reagents. Moreover, the electronic state analyses of the extracted complexes indicated that a difference in chemical bonding property of 5f-electrons between Am and Cm differentiates the Am/Cm selectivity.
 ssbauer isomer shift and the application to f-block metal coordination chemistry
ssbauer isomer shift and the application to f-block metal coordination chemistryKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki
no journal, ,
M ssbauer isomer shift obtained by measuring M
ssbauer isomer shift obtained by measuring M ssbauer spectroscopy has first-order linear responsibility to electron density at nucleus and varies based on the covalent interaction between an element and the surroundings. It assures the quantitative evaluation of the covalent interaction by comparing the linearity. This help us to validate the computational method for estimating the bonding property. We have presented the benchmarking of exchange-correlation functional of density functional theory using M
ssbauer spectroscopy has first-order linear responsibility to electron density at nucleus and varies based on the covalent interaction between an element and the surroundings. It assures the quantitative evaluation of the covalent interaction by comparing the linearity. This help us to validate the computational method for estimating the bonding property. We have presented the benchmarking of exchange-correlation functional of density functional theory using M ssbauer isomer shifts of Ru, Os, Eu and Np nuclides. We have indicated that the reproducibility of M
ssbauer isomer shifts of Ru, Os, Eu and Np nuclides. We have indicated that the reproducibility of M ssbauer isomer shift can be correlated to the mixing degree of exact Hartree-Fock exchange admixture in the functional. We will present the applications of the density functional theory to f-block coordination compounds to elucidate their structures and stabilities.
ssbauer isomer shift can be correlated to the mixing degree of exact Hartree-Fock exchange admixture in the functional. We will present the applications of the density functional theory to f-block coordination compounds to elucidate their structures and stabilities.
 Ru M
Ru M ssbauer isomer shift
ssbauer isomer shiftKaneko, Masashi; Kato, Akane*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
A linear relationship between M ssbauer isomer shift values and electron densities at nucleus position assures the quantitative evaluation of the covalent interaction between a M
ssbauer isomer shift values and electron densities at nucleus position assures the quantitative evaluation of the covalent interaction between a M ssbauer element and its surroundings. The use of this linear relationship makes us to predict a covalency in unknown compounds by electron density analysis based on quantum chemical calculations. As the first step to elucidate stability of ruthenium, which is known to be one of obstructive factors for separation process of high-level radioactive waste, in this study, we performed a fundamental investigation to predict the chemical bonding properties of nitrosylruthenium complexes. We modeled several nitrosylruthenium complexes with basic ligands, such chloride ion and ammonia, namely, [Ru(NO)L
ssbauer element and its surroundings. The use of this linear relationship makes us to predict a covalency in unknown compounds by electron density analysis based on quantum chemical calculations. As the first step to elucidate stability of ruthenium, which is known to be one of obstructive factors for separation process of high-level radioactive waste, in this study, we performed a fundamental investigation to predict the chemical bonding properties of nitrosylruthenium complexes. We modeled several nitrosylruthenium complexes with basic ligands, such chloride ion and ammonia, namely, [Ru(NO)L ] (L = Br
] (L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN ), by density functional calculation and estimated
), by density functional calculation and estimated  Ru M
Ru M ssbauer isomer shifts by electron density analysis. The calculated results reproduced the experimental metal-ligand bond lengths and M
ssbauer isomer shifts by electron density analysis. The calculated results reproduced the experimental metal-ligand bond lengths and M ssbauer isomer shifts within the error of 0.1 mm/s. We also calculated the orbital splitting values of Ru d-electron. The value increased in the order of L = Br
ssbauer isomer shifts within the error of 0.1 mm/s. We also calculated the orbital splitting values of Ru d-electron. The value increased in the order of L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN and correlated to that of M
and correlated to that of M ssbauer isomer shift values. This indicated that the covalent interation between metal and ligand originates in the d-electron contribution of ruthenium to the coordination bonds.
ssbauer isomer shift values. This indicated that the covalent interation between metal and ligand originates in the d-electron contribution of ruthenium to the coordination bonds.