Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Okayama University*
JAEA-Review 2023-038, 48 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Embedded system using a radiation-hardened processor" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to be developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic processor with a 10 MGy total-ionizing-dose (TID) tolerance, a radiation-hardened processor without any optical component with a 4 MGy TID tolerance, a radiation-hardened memory with a 4 MGy TID tolerance, and a radiation-hardened power supply unit with a 1 MGy TID tolerance. Moreover, Japanese research group will support radiation- hardened field programmable gate arrays, power supply units, and radiation-hardened optical systems for radiation-hardened robot systems and radiation sensor systems developed by UK team.
 -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray fieldKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Terasaka, Yuta; Tomita, Hideki*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Uritani, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:92.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)We focus on the thickness and property controls of inorganic scintillators used for thermal neutron detection in intense  -ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20
-ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20 (a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF
(a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF :Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a
:Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron detection for GS20
-ray field, the neutron detection for GS20 with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a
with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron/
-ray field, the neutron/ -ray discrimination of GS20
-ray discrimination of GS20 was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Okayama University*
JAEA-Review 2022-017, 56 Pages, 2022/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Radiation tolerant rapid criticality monitoring with radiation-hardened FPGAs" conducted in FY2020. This research is developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic FPGA with a 1 Grad total-ionizing-dose tolerance on which optical technologies are introduced onto a semiconductor technology and a radiation hardened FPGA with a 200 Mrad total-ionizing-dose tolerance not using any optical component. Moreover, Japanese research group will support hardware acceleration on FPGAs used for neutron-detection system developed by UK team.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-026, 47 Pages, 2021/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of radiation hardened diamond image sensing devices" conducted in FY2020. The research objective of this project is to develop image sensing devices which work under the high radiation condition. The devices will be realized using radiation hardened diamond semiconductor devices as charge transfer devices and photodetectors. The research project has mainly two targets such as to confirm charge coupled devices operation on diamond unipolar devices and to characterize photo conductivity of diamond detectors.
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 342, p.117580_1 - 117580_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.84(Chemistry, Physical)Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) and pulsed-field-gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFGNMR) analyses of a nanofluid composed of silicon dioxide (SiO ) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO
) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO
particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO nanofluids.
nanofluids.
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 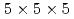
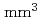 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0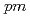 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:87.80(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Shizuoka University*
JAEA-Review 2020-059, 42 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Radiation tolerant rapid criticality monitoring with radiation-hardened FPGAs". This research is developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic FPGA with a 1 Grad total-ionizing-dose tolerance on which optical technologies are introduced onto a semiconductor technology and a radiation hardened FPGA with a 200 Mrad total-ionizing-dose tolerance not using any optical component. Moreover, Japanese research group will support hardware acceleration on FPGAs used for neutron-detection system developed by UK team. Finally, we will provide our radiation-hardened FPGA for the UK neutron-detection system.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-027, 27 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of radiation hard diamond image sensing devices". The research objective of this project is to develop image sensing devices which work under the high radiation condition. The devices will be realized using radiation hard diamond semiconductor devices as charge transfer devices and photodetectors. The research project has mainly two targets such as to confirm charge coupled devices operation on diamond unipolar devices and to characterize photo conductivity of diamond detectors.
Atz, M.*; Salazar, A.*; Hirano, Fumio; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 124, p.28 - 38, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)The likelihood for criticality in the far field of a repository was evaluated for direct disposal of commercial light water reactor used nuclear fuel. Two models were used in combination for this evaluation: (1) a neutronics model to estimate the minimum critical masses of spherical, water-saturated depositions of fuel material; (2) a transport model to simulate the dissolution of fuel material from multiple canisters and the subsequent transport of the solutes through host rock to a single accumulation location. The results suggest that accumulation of a critical mass is possible under conservative conditions but that these conditions are unlikely to occur, especially in the vicinity of a carefully-arranged repository.
 Cs concentration in particles discharged from rice paddies to freshwater bodies after the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident
Cs concentration in particles discharged from rice paddies to freshwater bodies after the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accidentYoshimura, Kazuya; Onda, Yuichi*; Wakahara, Taeko*
Environmental Science & Technology, 50(8), p.4186 - 4193, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:57.39(Engineering, Environmental)Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2005-025, 351 Pages, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2005-002, 97 Pages, 2005/03
In the FNCA Coordinator Meeting held on March 2002, "Survey of the Basic Data on HRD in the Nuclear Field" was proposed as the first step for developing the HRD strategy by producing the quantitative data on HRD in nuclear field. The first results were reported during the 2002 FNCA Workshop on HRD held on October 2002. The survey results were analyzed in 2003, and summarized as "Summary of the Survey Data". It was reported during Workshop in 2003. The report consists of the updated data until early 2004 of the summary data.
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2004-014, 319 Pages, 2004/07
no abstracts in English
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2002-016, 104 Pages, 2002/07
The Human Resources Development (HRD) Project was added in 1999 as a Cooperation Activity of "the Forum for Nuclear Cooperation in Asia (FNCA)" which is organized by AEC of Japan. The HRD Project supports to solidify the foundation of nuclear development utilization in Asia by promoting human resources development in Asian countries. The principal activity of the HRD Project is to hold the Workshop on Human Resources Development in the Nuclear Field in Asia once a year. The objective of the Workshop is to clarify problems and needs of the human resources development of each country and to support it mutually by exchanging information etc. The report consists of a summary of the 3rd Workshop on Human Resources Development in the Nuclear Field in Asia held on October 29 - November 1, 2001 at the Nuclear Training Center of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute in Daejeon, Korea.
Seki, Yasushi
Genshiryoku eye, 48(6), P. 22, 2002/06
The Human Resources Development (HRD) Project in the framework of the Forum of Nuclear Cooperation in Asia (FNCA) is a very effective mechanism under which the representatives from neighboring 8 countries gather in one place to discuss and exchange information on HRD in nuclear field. Following major tasks are being carried out, (1)Investigate the needs on human resources development in each country and the mutual support activities such as information exchange utilizing internet homepages and exchange of textbooks have been started. More efficient utilization of the existing personnel exchange programs is also being planned. (2)Assistance in the formulation of HRD strategy in each country. (3)Cooperative actions such as exchange of information on the recruitment of young generation to nuclear field, which is an issue common to all member countries.None of these tasks can yield visible results easily. HRD takes much time and effort to build mutual understanding, cooperative relationship and obtain the results together. There is no quick medicine for HRD.
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2001-033, 89 Pages, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2001-020, 326 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Nuclear Technology and Education Center
JAERI-Review 2001-017, 95 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Niita, Koji*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Yujiro
JAERI-Data/Code 2001-007, 128 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English